A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
- A ball of mass m moving with velocity v, collide with the wall elastic...
Text Solution
|
- A particle of mass m moves along line PC with velocity v as shown. Wh...
Text Solution
|
- A ball of mass m moving with velocity v0 collides a wall as shown in f...
Text Solution
|
- A ball of mass m moving with velocity v(0) collides with a wall as sho...
Text Solution
|
- A ball of mass m moving with velocity v, collide with the wall elastic...
Text Solution
|
- A particle P collides elastically at M with a speed v . The change in ...
Text Solution
|
- A ball collides with a frictionless wall with velocity u as shown in t...
Text Solution
|
- A ball moving with a velocity v strikes a wall moving toward the wall ...
Text Solution
|
- 1 किग्रा द्रव्यमान की एक गेंद, जो 5 मीटर/सेकंड के वेग से गतिमान है , ए...
Text Solution
|
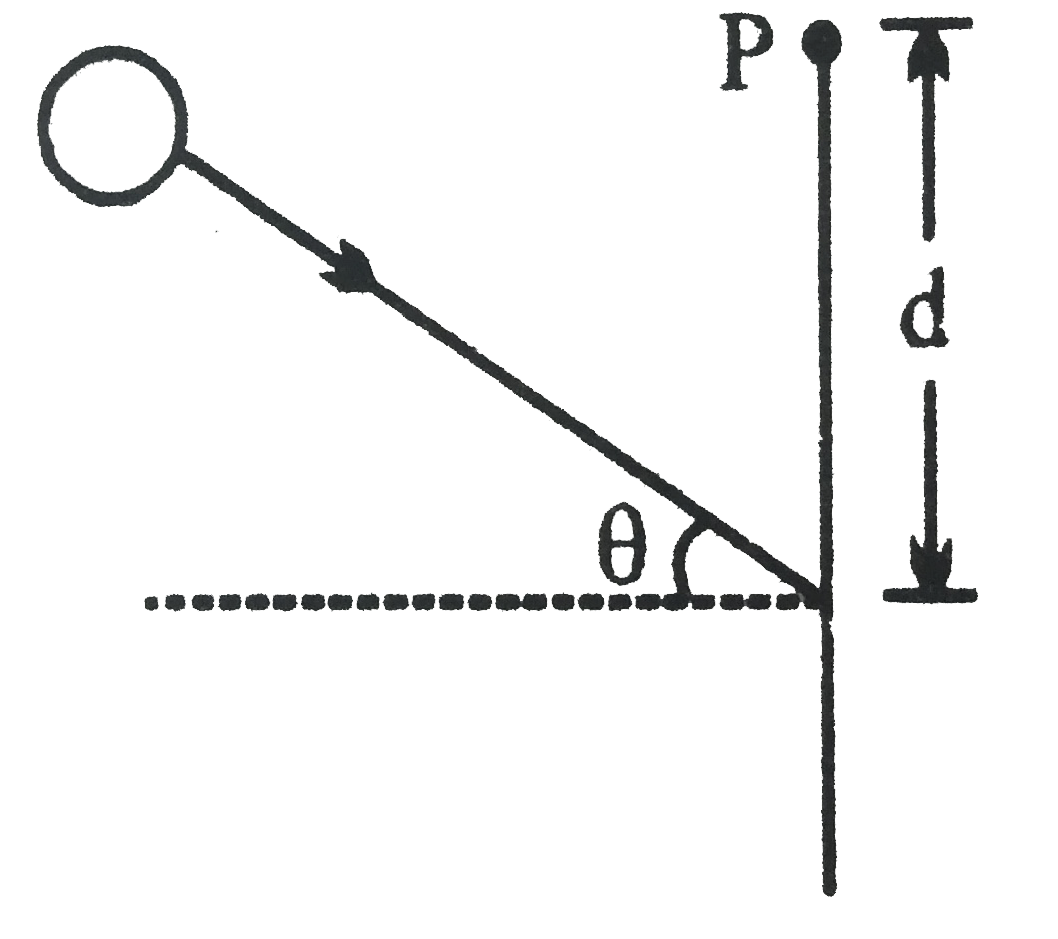 .
.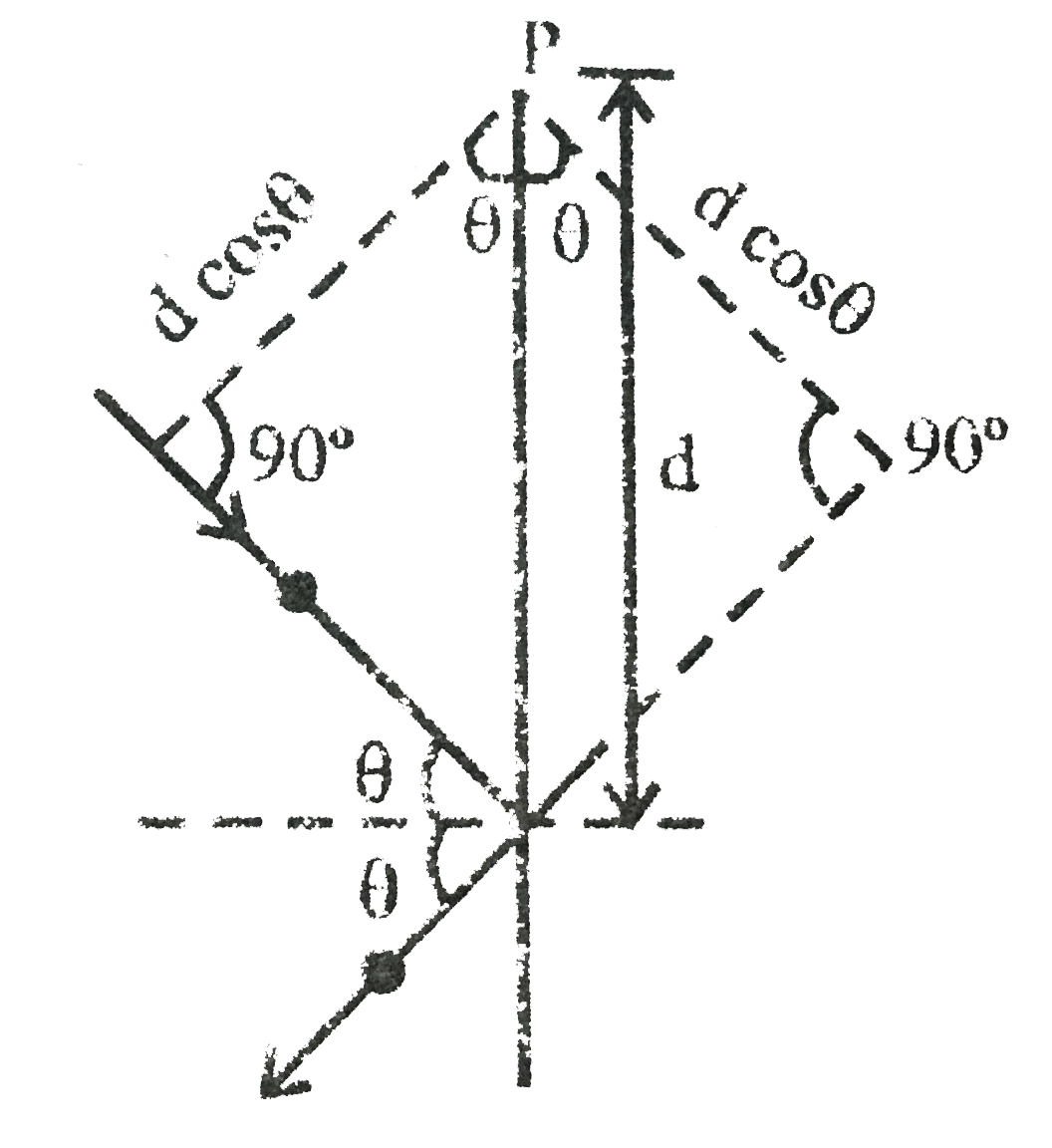 .
.