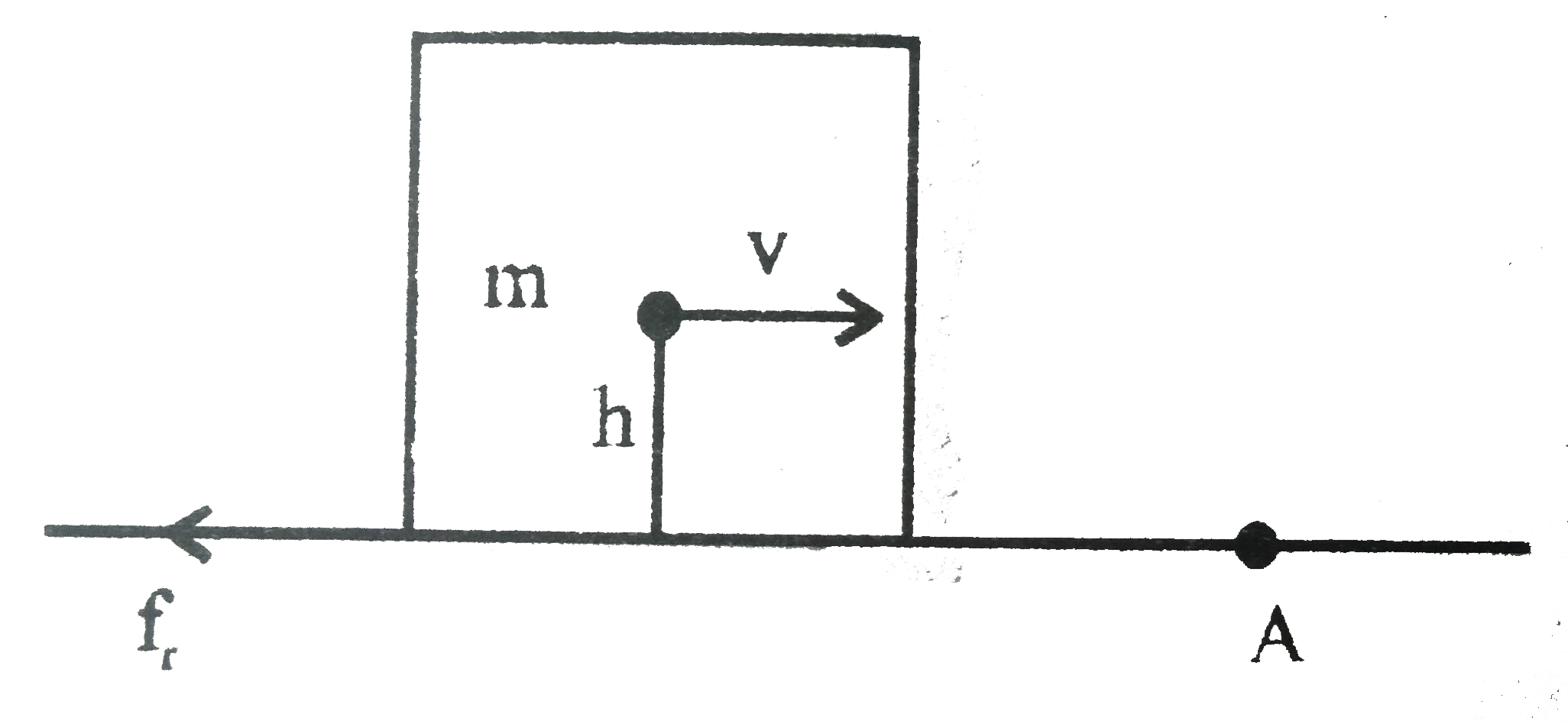
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
- A block of mass m moves on a horizontal rough surface with initial vel...
Text Solution
|
- A block of mass M is being pulley along horizontal surface .The coeffi...
Text Solution
|
- A block of mass m moves on a horizontal rough surface with initial vel...
Text Solution
|
- A bullet of mass m moving with velocity upsilon(1) strikes a suspended...
Text Solution
|
- A homogenous block of mass m, width b and height h is resting on a rou...
Text Solution
|
- m द्रव्यमान का एक गुटका M द्रव्यमान के एक त्रिभुजाकार गुटक पर रखा हुआ ...
Text Solution
|
- A block of mass M is using on a rough horizontal surface. muR is the c...
Text Solution
|
- What is the value of applied force ‘F’ which is exerted at an angle th...
Text Solution
|
- A block of mass M is kept on a smooth horizontal surface. Another bloc...
Text Solution
|