A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
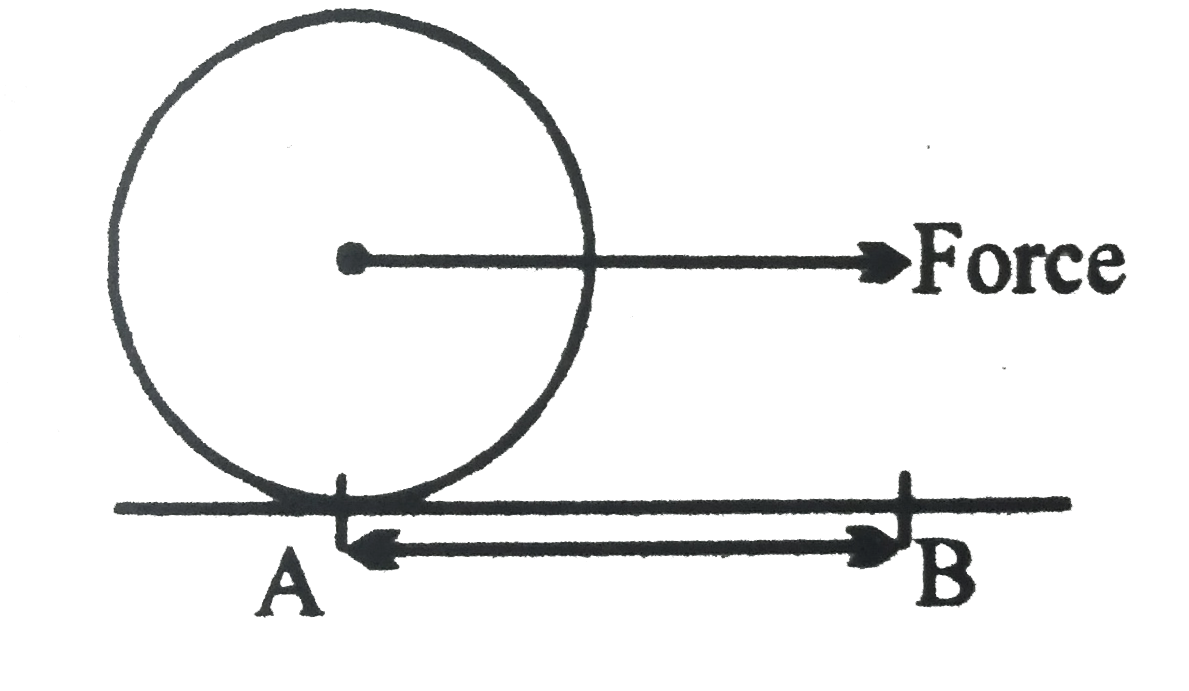
- A disc of circumference s is at rest at a point A on a horizontal surf...
Text Solution
|
- A disc is pulled by a force F acting at a point above the centre of ma...
Text Solution
|
- A disc of circumference s is at rest at a point A on a horizontal surf...
Text Solution
|
- A block 'B' rests on 'A' A rests on a horizontal surface 'C' which is ...
Text Solution
|
- A disc is rolling without sliding on a horizontal surface. Velocity of...
Text Solution
|
- A disc of circumference S stands vertically on a horizontal surface as...
Text Solution
|
- A uniform disc of mass M and radius R initially stands vertically on t...
Text Solution
|
- A coin placed on a horizontal rotating disc, with its centre at 10 cm ...
Text Solution
|
- A circular disc of radius R rolls without slipping along the horizonta...
Text Solution
|
 .
.