Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
- A uniform ring is rotating about vertical axis with angular velocity o...
Text Solution
|
- A ring of radius r is rotating about a vertical axis along its diamete...
Text Solution
|
- A conducting circular ring is rotated with angular velocity omega abou...
Text Solution
|
- A uniform ring is rotating about vertical axis with angular velocity o...
Text Solution
|
- A thin circular ring of mass M and radius R is rotating about its axis...
Text Solution
|
- A uniform ring is rotating about vertical axis with angular velocity o...
Text Solution
|
- A thin circular ring of mass m and radius R is rotating about its axis...
Text Solution
|
- A ring of radius r is rotating about a vertical axis along its diamete...
Text Solution
|
- A ring of radius r is rotating about a vertical axis along its diamete...
Text Solution
|
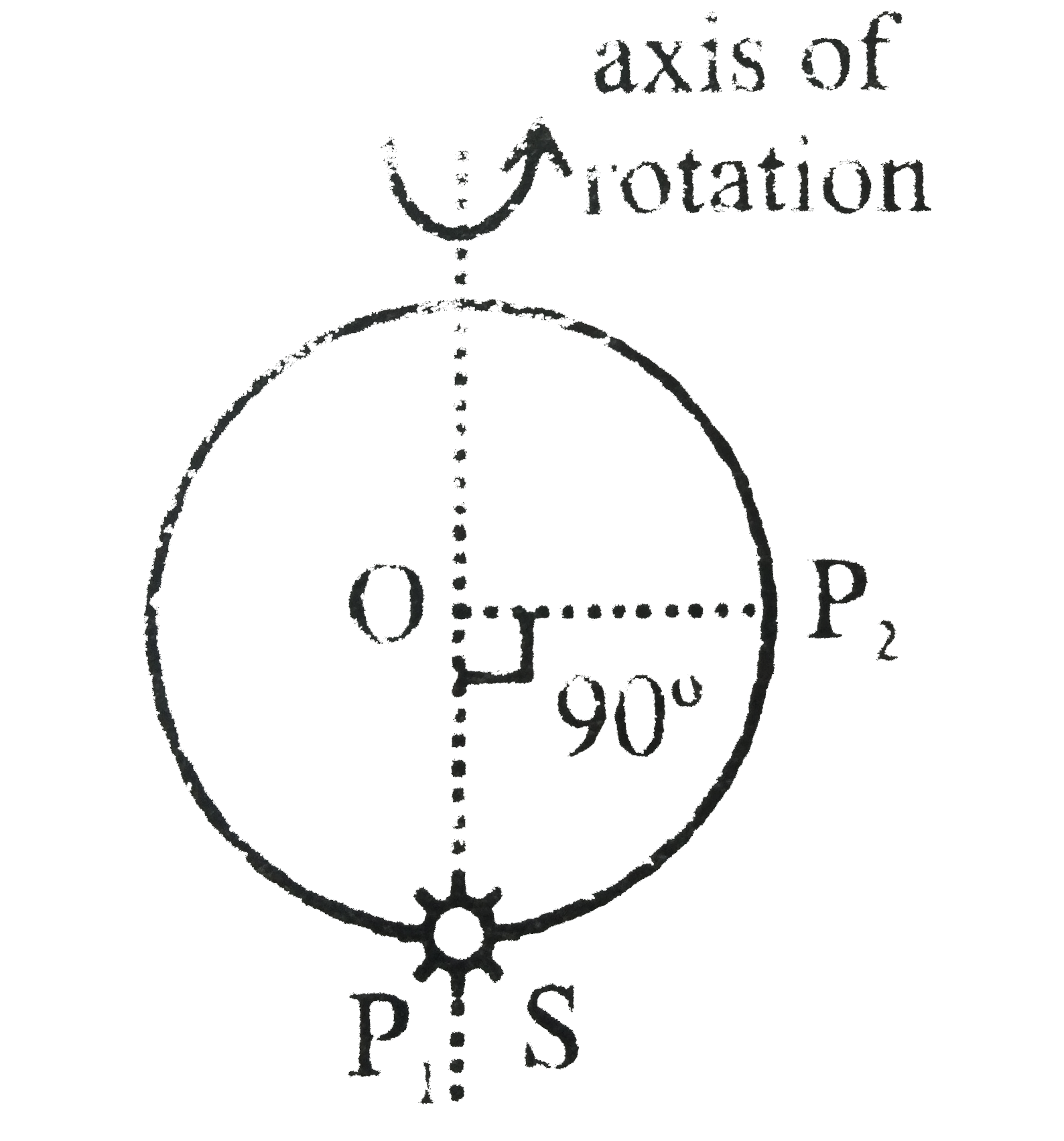 .
.