Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
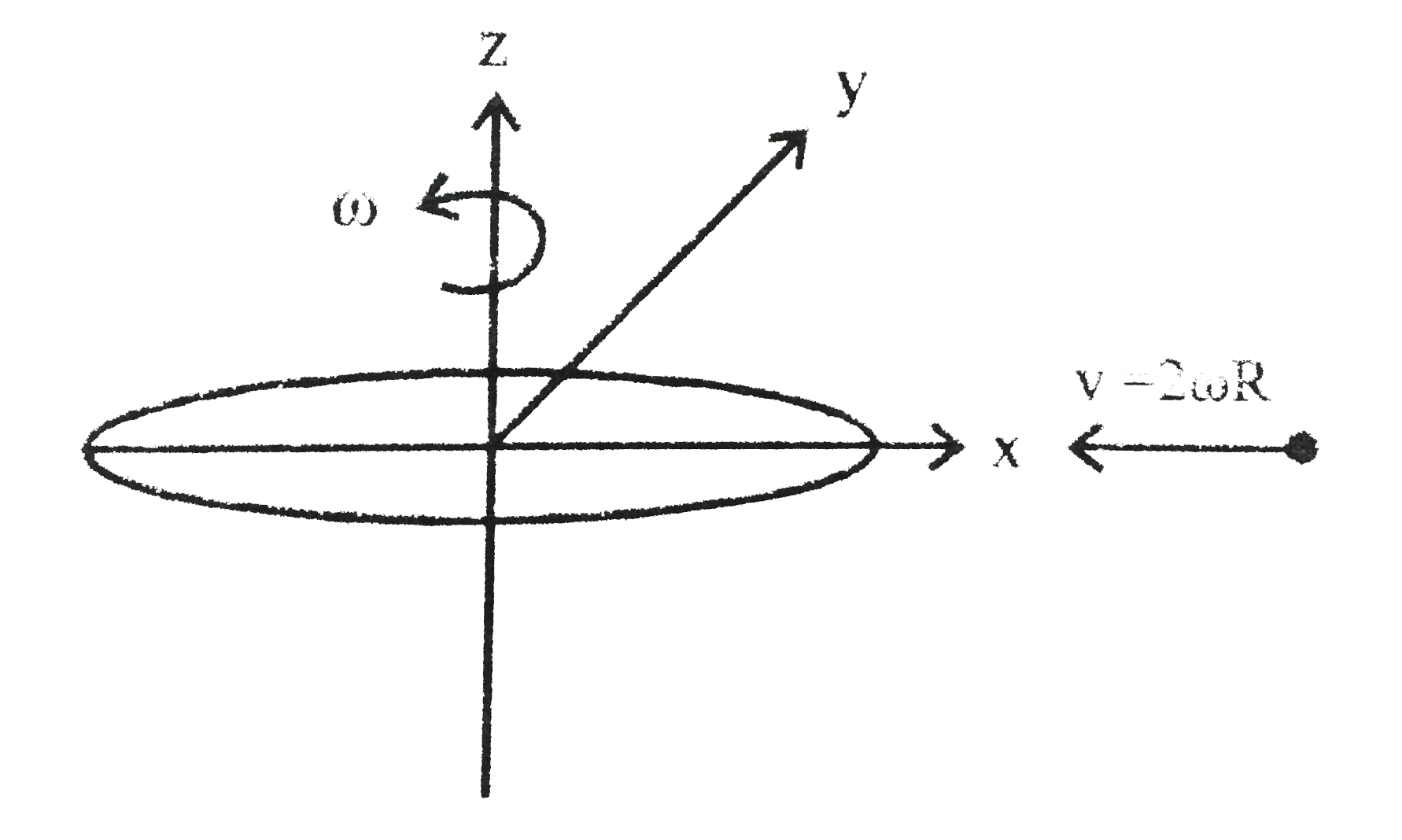
- A uniform dis of mass m and radius R rotates about a fixed vertical ax...
Text Solution
|
- A uniform disc of mass m and radius R rotates about a fixed vertical a...
Text Solution
|
- A uniform disc of mass m and radius R rotates about a fixed vertical a...
Text Solution
|
- A uniform disc of mass m and radius R rotates about a fixed vertical a...
Text Solution
|
- A uniform dis of mass m and radius R rotates about a fixed vertical ax...
Text Solution
|
- A uniform circular disc of radius R is rotating about its own axis wit...
Text Solution
|
- A thin uniform circular disc of mass M and radius R is rotating in a h...
Text Solution
|
- A uniform disc of radius a and mass m, is rotating freely with angular...
Text Solution
|
- A thin uniform circular disc of mass M and radius R is rotating in a h...
Text Solution
|