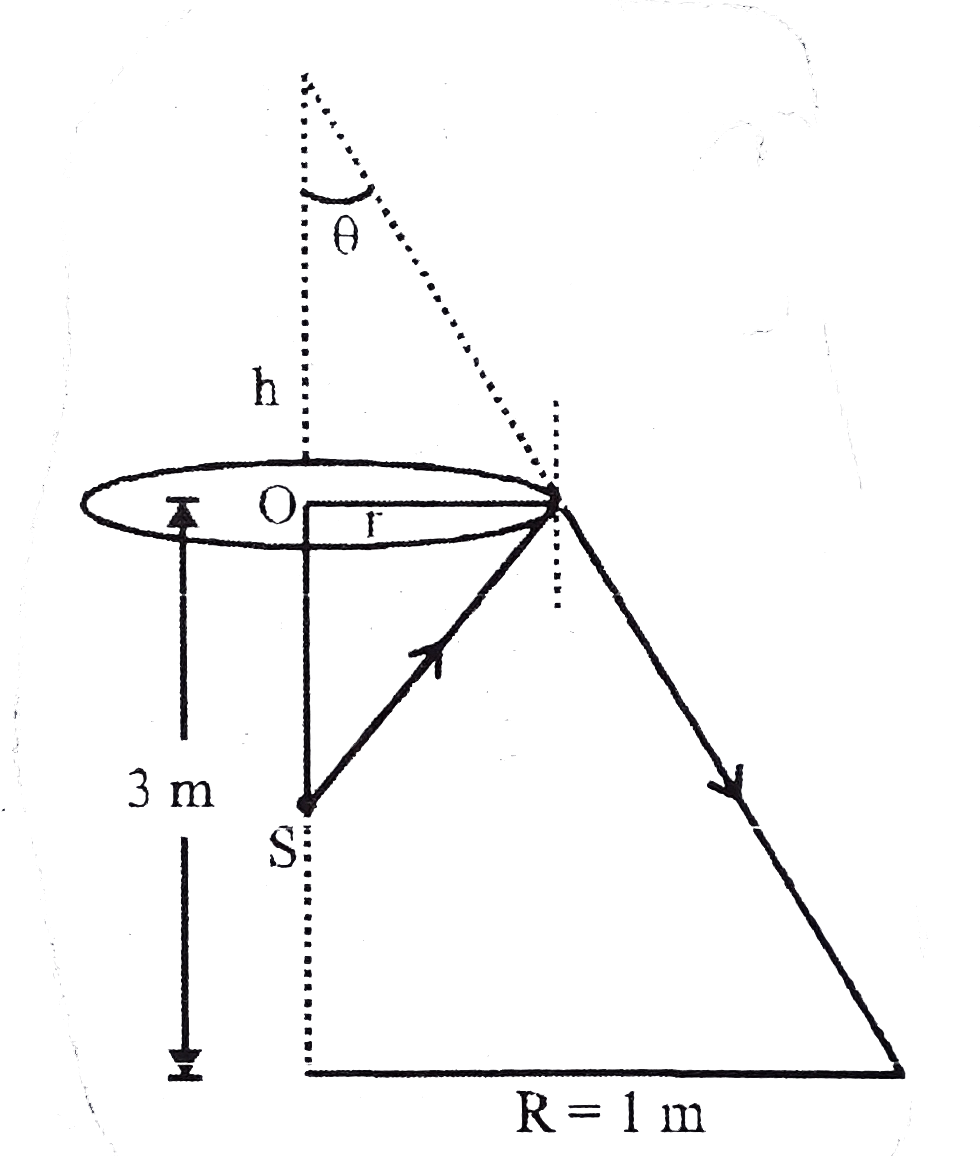
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
- A plane mirror of circular shape with radiusr=20cmis fixed to the ceil...
Text Solution
|
- A bulb is hanging over a table. At which portion of the table is the i...
Text Solution
|
- A particle moves in a circular path of radius 5 cm in a plane perpendi...
Text Solution
|
- A plane mirror of circular shape with radiusr=20cmis fixed to the ceil...
Text Solution
|
- A lamp is hanging along the axis of a circular table of radius r. At w...
Text Solution
|
- A concave mirror of radius of curvature R has a circular outline of ra...
Text Solution
|
- A point light source illuminates a screen the, maximum illuminance bei...
Text Solution
|
- A lamp is hanging along the axis of a circular table of radius r. at w...
Text Solution
|
- An object is placed at a distance of 20 cm from a convex mirror of rad...
Text Solution
|