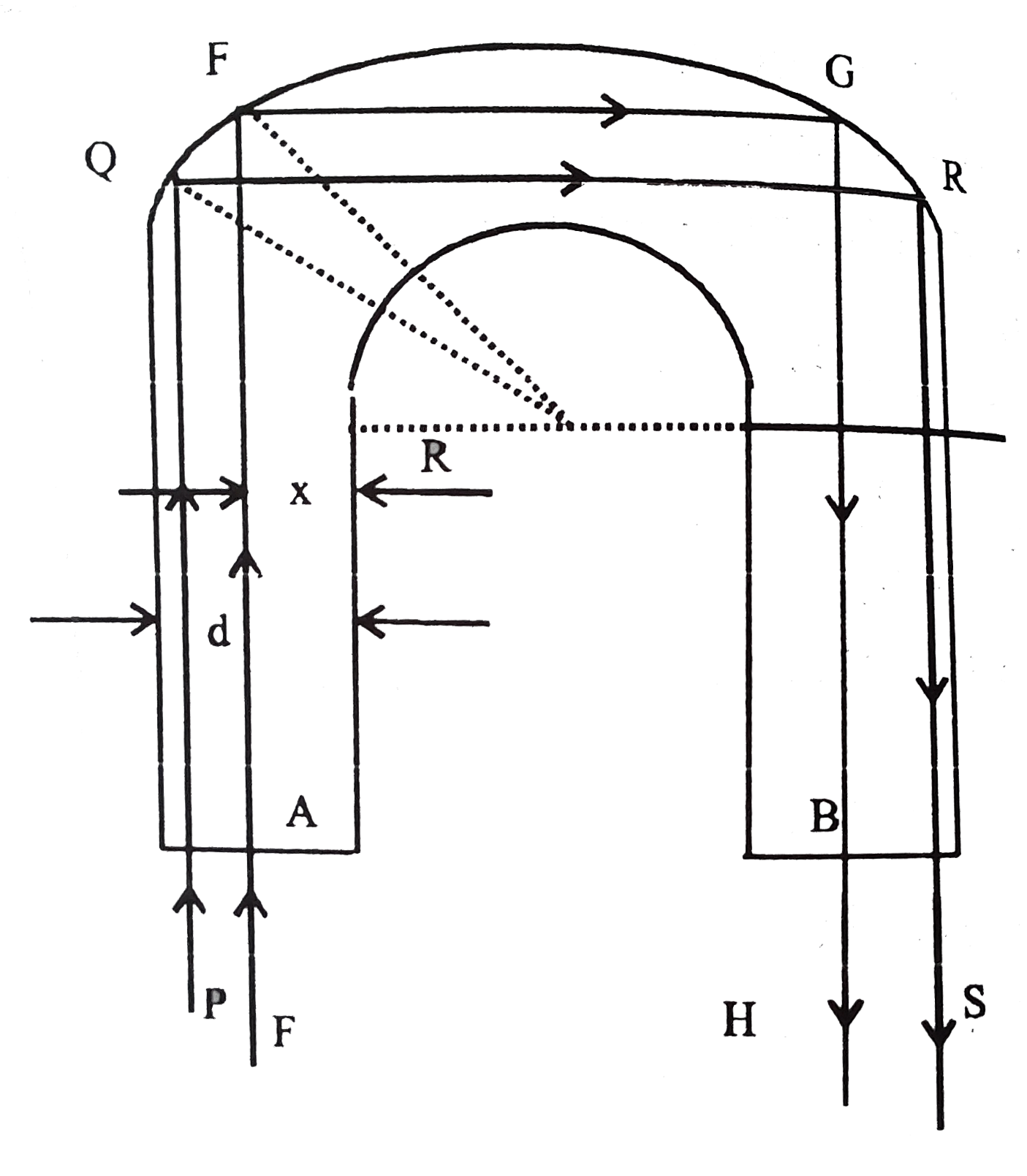
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
- A glass rod having square cross-section is bent into the shape as show...
Text Solution
|
- A glass rod having square cross-section is bent into the shape as show...
Text Solution
|
- What should be the value of refractive index n of a glass rod placed ...
Text Solution
|
- A rod of glass ( mu = 1.5) and of square cross section is bent into t...
Text Solution
|
- A rod made of glass (mu = 1.5) and of square cross-section is equal is...
Text Solution
|
- Consider a tank made of glass (refractive index 1.5) with a thick bott...
Text Solution
|
- A portion of a straight glass rod of diameter 2 cm and refractive inde...
Text Solution
|
- A glass prism of refractive index 1.5 is placed in water of refractive...
Text Solution
|
- Consider a tank made of glass (refractive index 1.5) with a thick bott...
Text Solution
|