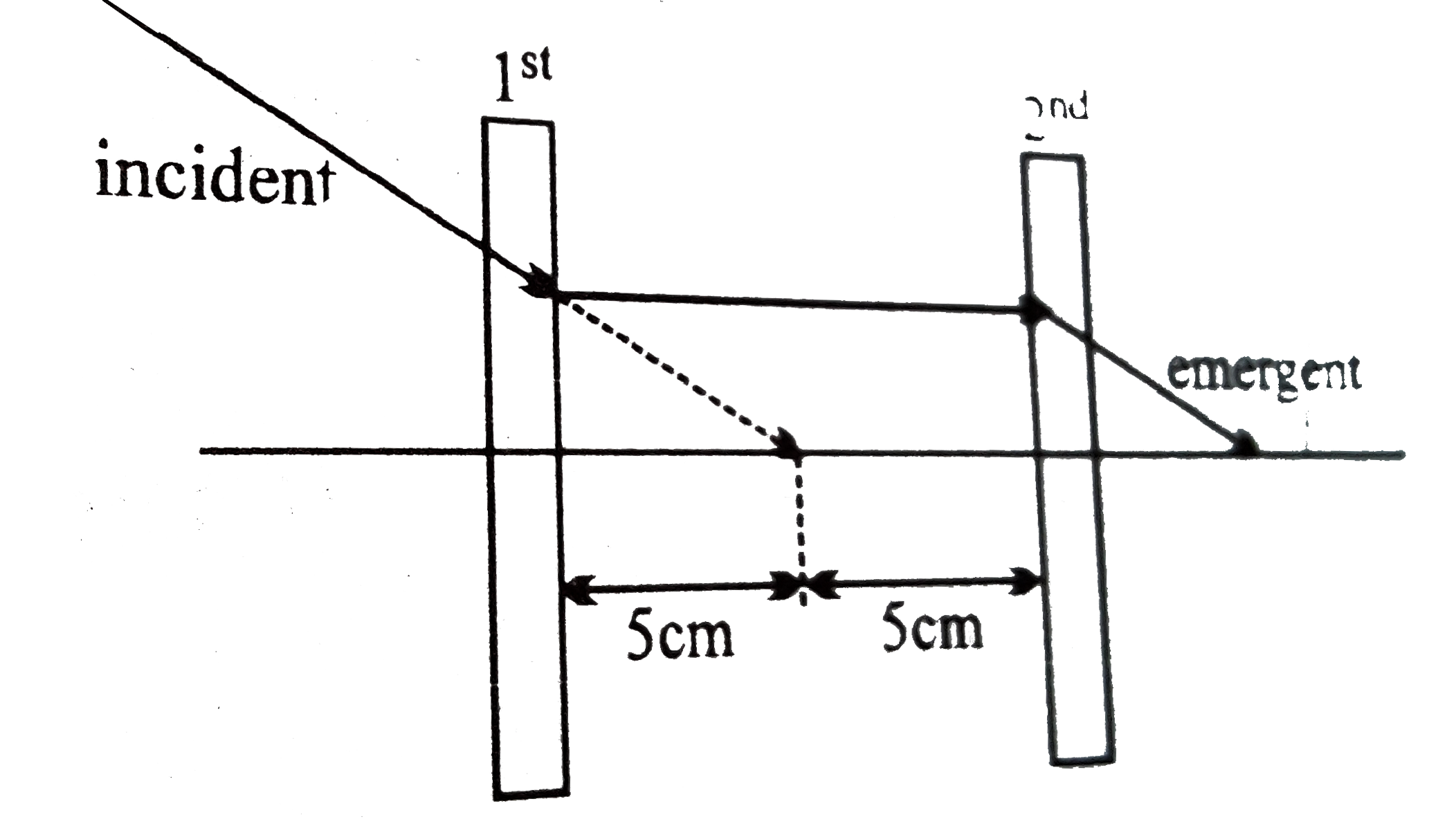
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
- Look at the ray diagram shown ,what will be th focal length of th e1^(...
Text Solution
|
- Assertion: Ray of light passing through optical centre of a lens goes ...
Text Solution
|
- A ray of light AO is incident on a diverging lens as shown in figure. ...
Text Solution
|
- Which of the following ray diagrams is correct for the ray of light in...
Text Solution
|
- Draw the path of light ray passing through a prism. Label angle of inc...
Text Solution
|
- From the ray diagram shown in Fig. calculte the focal length of concav...
Text Solution
|
- A ray of light is incident on a prism as shown in fig. Find the total ...
Text Solution
|
- A lens does not produce any deviation of a ray of light passing throug...
Text Solution
|
- Name the part of a lens through which a ray of light passes without su...
Text Solution
|