Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
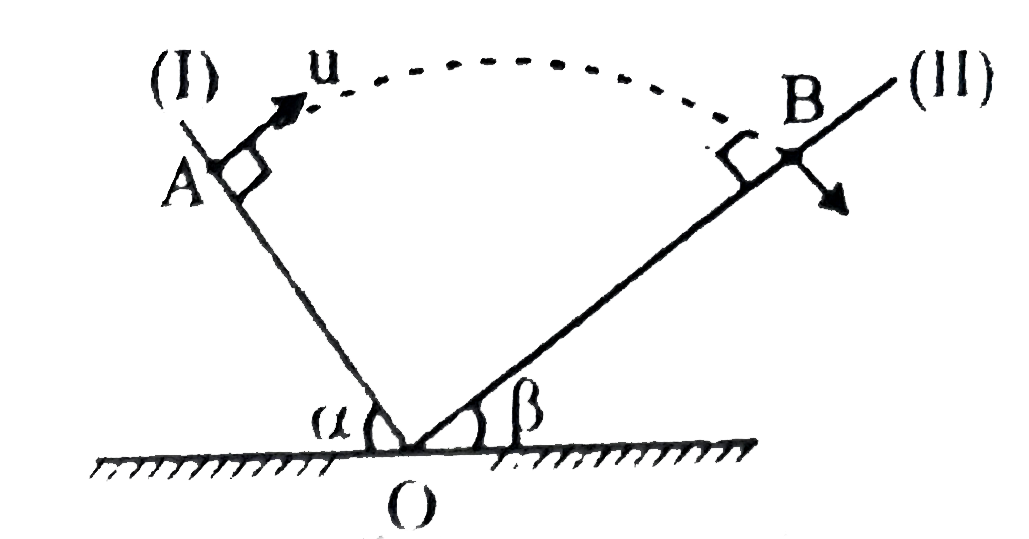
- Two inclined planes (I) and (II) have inclination alpha and beta respe...
Text Solution
|
- Two inclined planes OA and OB having inclination (with horizontal) 30^...
Text Solution
|
- Two inclined planes (I) and (II) have inclination alpha and beta respe...
Text Solution
|
- Two inclined planes OA and OB of inclinations alpha and beta equal to ...
Text Solution
|
- A particle is projected from point A perpendicular to inclined plane w...
Text Solution
|
- A particle is projected with velocity "u" in horizontal direction as s...
Text Solution
|
- A particle is projected with velocity "u" in horizontal direction as s...
Text Solution
|
- Two inclined planes OA and OB intersect in a horizontal plane having t...
Text Solution
|
- Two inclined planes OA and OB intersect in a horizontal plane having t...
Text Solution
|