Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
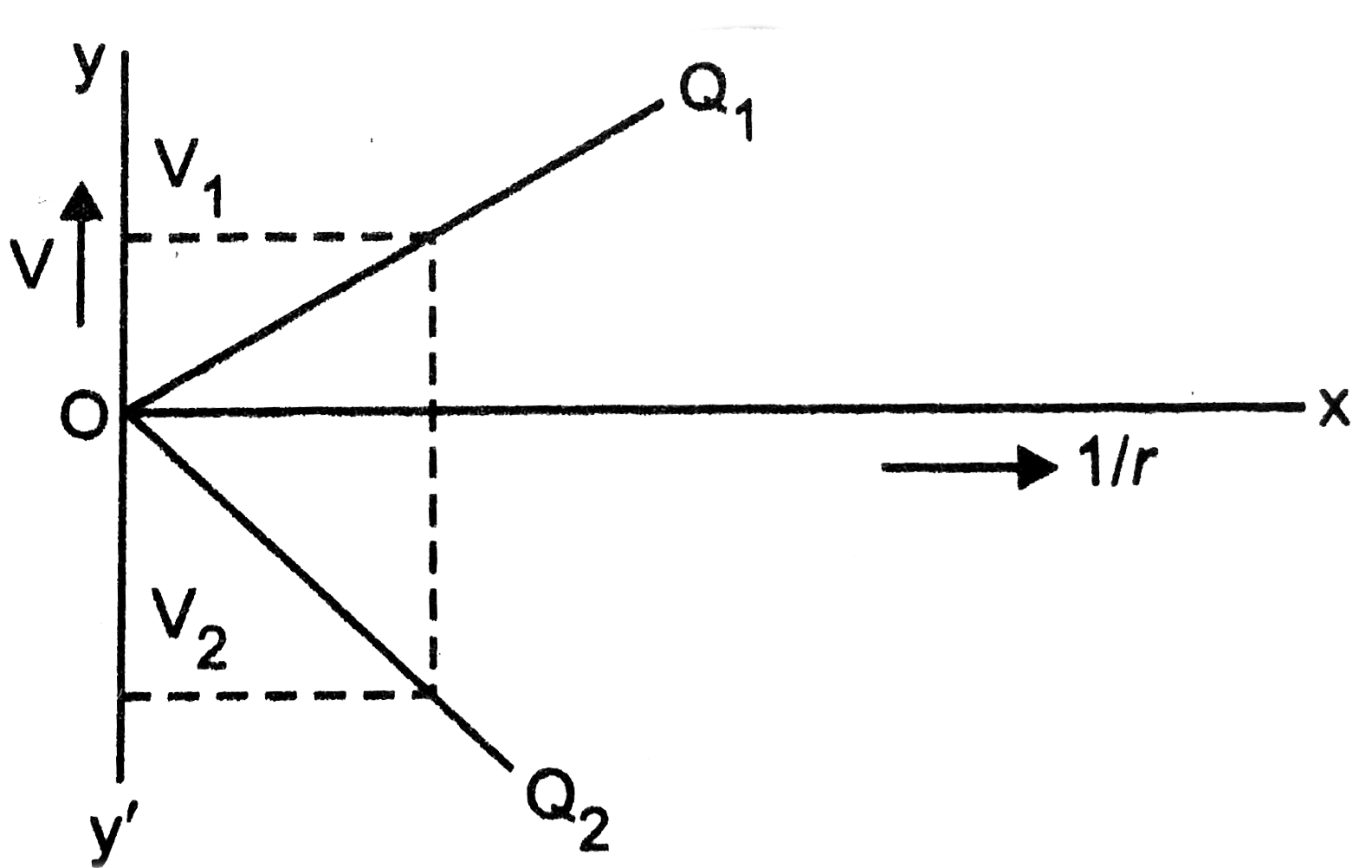
- Fig.1 shows the variation of electric potential V with 1//r, where r i...
Text Solution
|
- Two charge Q(1)=18muC and Q(2)=-2 mu C are separted by a distance R, a...
Text Solution
|
- Assertion: Two charges q(1) and q(2) are placed at separation r . Then...
Text Solution
|
- Figure shows the electirc field lines for two point charges separat...
Text Solution
|
- Fig.1 shows the variation of electric potential V with 1//r, where r i...
Text Solution
|
- Two concentric spherical shells of radii R and 2R are given charges Q...
Text Solution
|
- Two large , parallel conducting plates X and Y , kept close to each ot...
Text Solution
|
- Find out potential energy of the two point charge system having charge...
Text Solution
|
- दो आवेशों q(1) तथा q(2) के बीच लगने वाला कूलॉम बल, F=(q(1)q(2))/(r^(2)...
Text Solution
|