Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
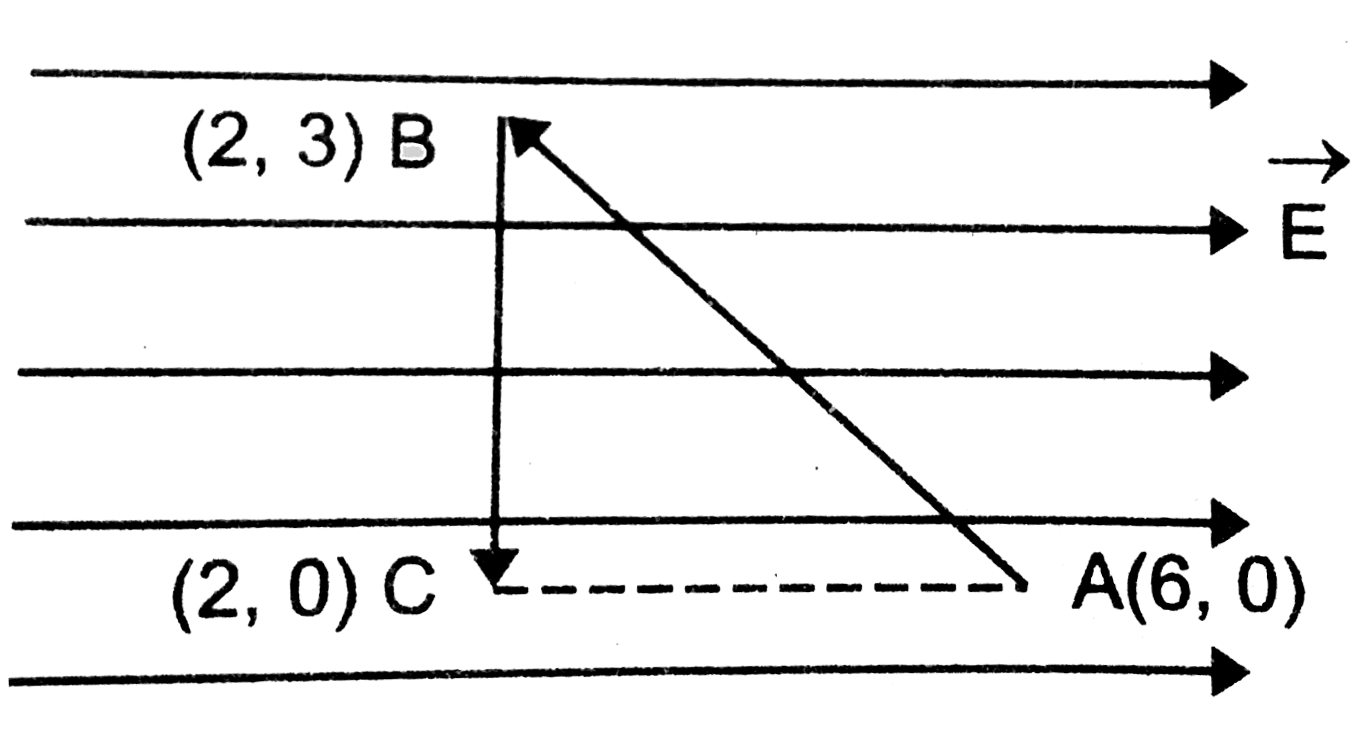
- A test charge q is moved without acceleration from A to C along the p...
Text Solution
|
- A charge +Q at A (see Fig. 3.140) produces electric field E and electr...
Text Solution
|
- Three points A,B,C lie in a uniform electric field E of 5xx10^(3) N//C...
Text Solution
|
- A test charge q is moved without acceleration from A to C along the p...
Text Solution
|
- A test charge q(0) is moved without acceleration from A to C over th...
Text Solution
|
- A and B are two points in an electric field . If the work done in carr...
Text Solution
|
- एक परिक्ष्ण आवेश q को बिना त्वरण के A से B के अनुदिश त्तपश्चता ...
Text Solution
|
- Two point A and B are 2 cm apart and a uniform electric field vec(E ) ...
Text Solution
|
- आरेख (चित्र) में दिखाए अनुसार, किसी विद्युत् क्षेत्र E में, एक परीक्षण...
Text Solution
|