Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
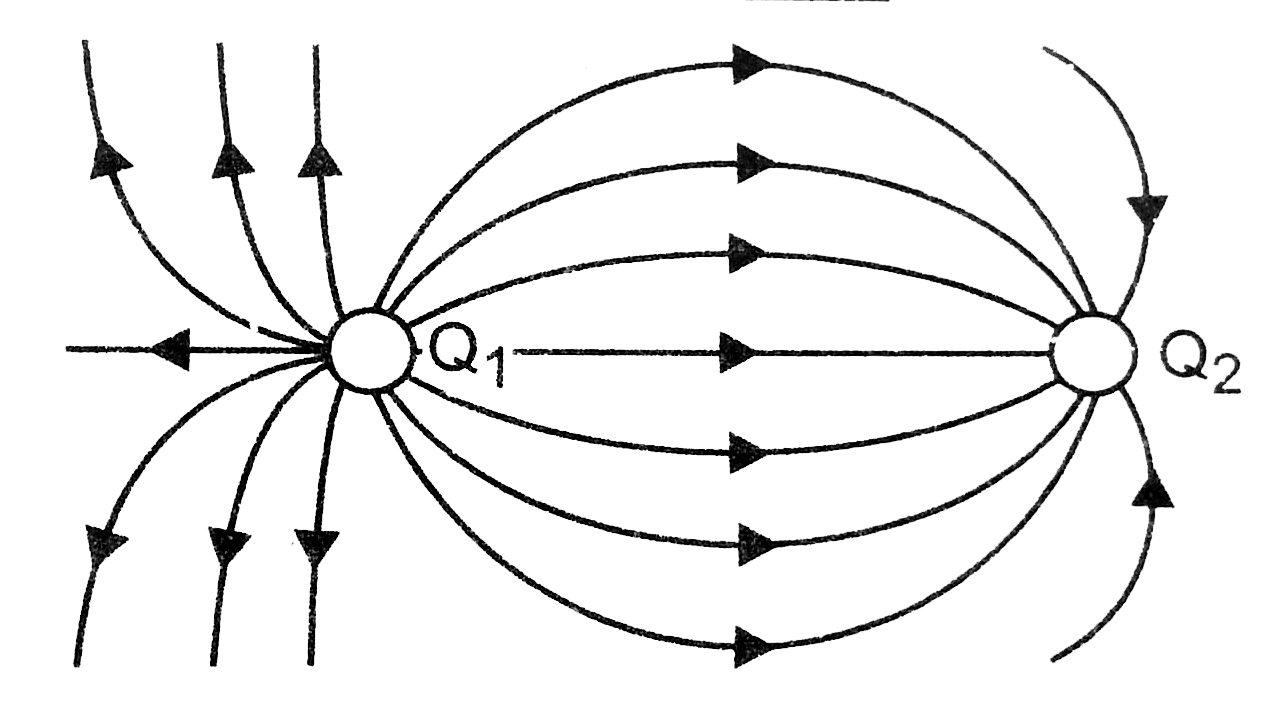
- A few electric field lines for a system of two charges Q(1) and Q(2) f...
Text Solution
|
- A few electric field lines for a system of two charges Q1 and Q2 fixed...
Text Solution
|
- The field lines for two point charges shown in fig. (i) Is the fie...
Text Solution
|
- Two charges q(1) and q(2) are kept on x-axis and electric field at di...
Text Solution
|
- The given figure gives electric line of force due to two charges q(1) ...
Text Solution
|
- Fig.1 shows the variation of electric potential V with 1//r, where r i...
Text Solution
|
- A few electric field lines for a system of two charges Q(1) and Q(2) f...
Text Solution
|
- The electric lines of force of two point charges are shown in fig. W...
Text Solution
|
- A few electric field lines for a system of two charges Q(1) and Q(2) f...
Text Solution
|