Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
- When an electron moves from A to B along and electric field line as s...
Text Solution
|
- The work done in carrying a charge of 5 mu C form a point A to a point...
Text Solution
|
- When an electron moves from A to B along and electric field line as s...
Text Solution
|
- The work done in carrying an electron from point A to a point B in an ...
Text Solution
|
- 15 joule of work has to be done against an existing electric field to ...
Text Solution
|
- In figure two points A and B are located in a region of electric field...
Text Solution
|
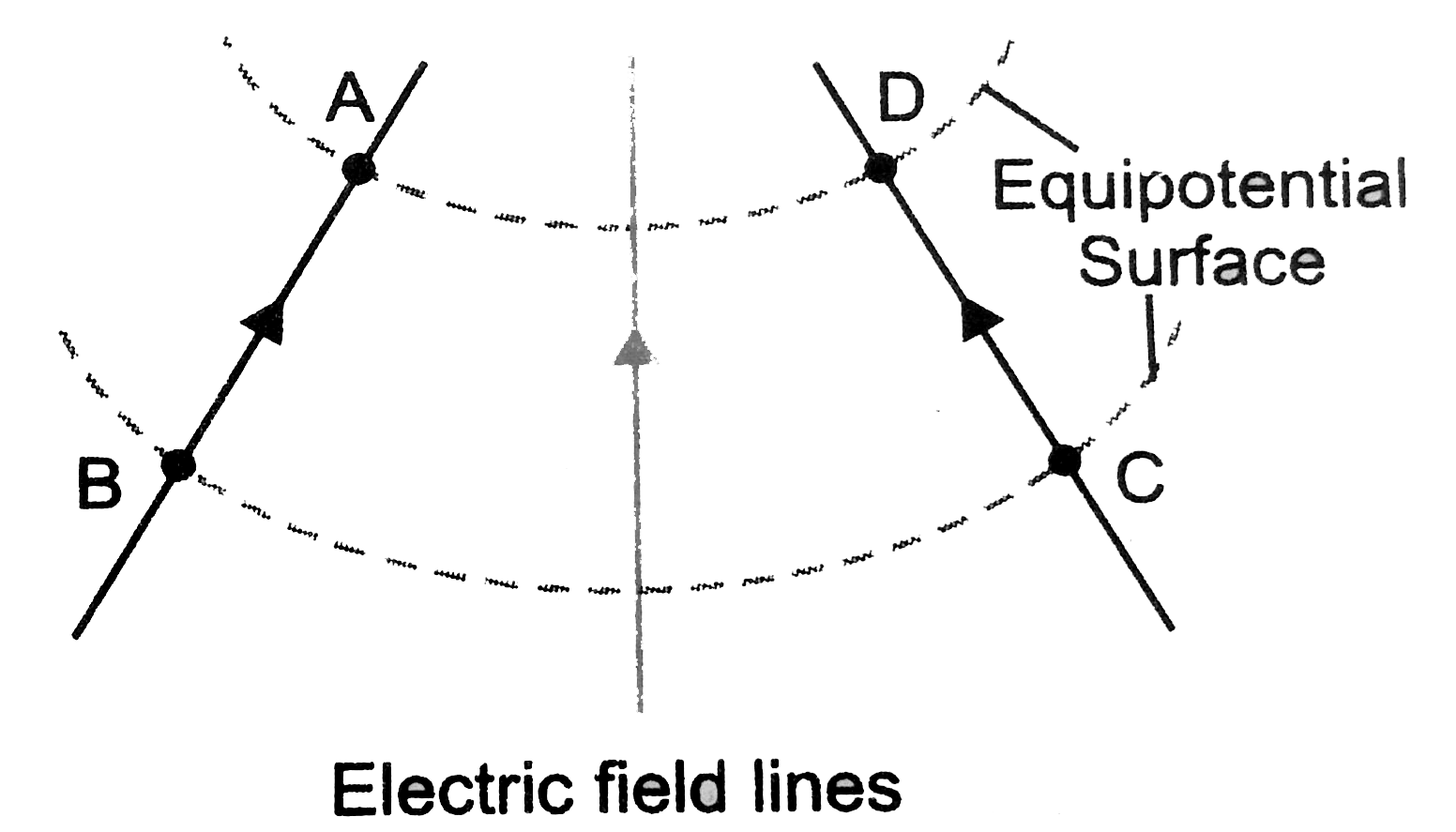
- Figure shows four points A, B, C and D in uniform electric field vec(E...
Text Solution
|
- एक वैद्युत यात्रा में एक इलेक्ट्रॉन को बिन्दु A से B तक ले जाने में कि...
Text Solution
|
- समरूप विधुत क्षेत्र में R त्रिज्या का वृत्त बनाया गया है वृत्त की पर...
Text Solution
|