Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
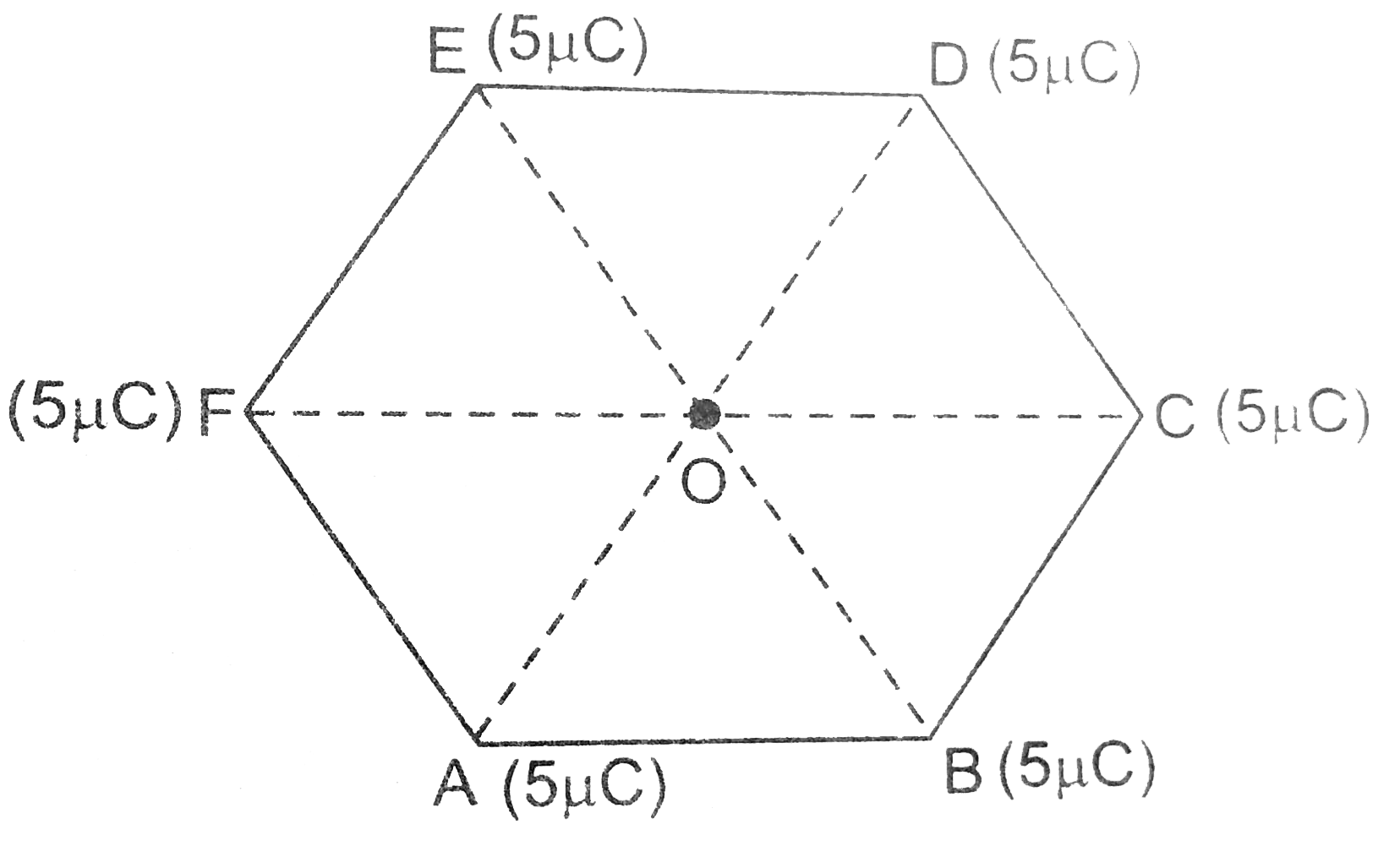
- A regular hexagon of side 10 cm has a charge 5 muC at each of its ver...
Text Solution
|
- Find the potential energy of a charge q(0) placed at the centre of reg...
Text Solution
|
- 10 cm भुजा वाले एक सम-षट्भुज के प्रत्येक शीर्ष पर 1 mu C का आवेश है । ...
Text Solution
|
- 10 सेमी भुजा वाले एक सम - षटभुज के प्रत्येक शीर्ष पर 5 muC का आवेश है ...
Text Solution
|
- A hexagon of side 8 cm has a charge 4 muC at each of its vertices. The...
Text Solution
|
- 10 cm भुजा वाले एक सम - षट्भुजा के प्रत्येक शीर्ष पर 5 muC का...
Text Solution
|
- A regular hexagon of side 5 cm has charge 10 mu C at each of its vetic...
Text Solution
|
- A regular hexagon of side 10 cm has a charge 5 muC at each of its ver...
Text Solution
|
- A hexagon of side 'a' has a charge 'q' at each of its vertices. The el...
Text Solution
|