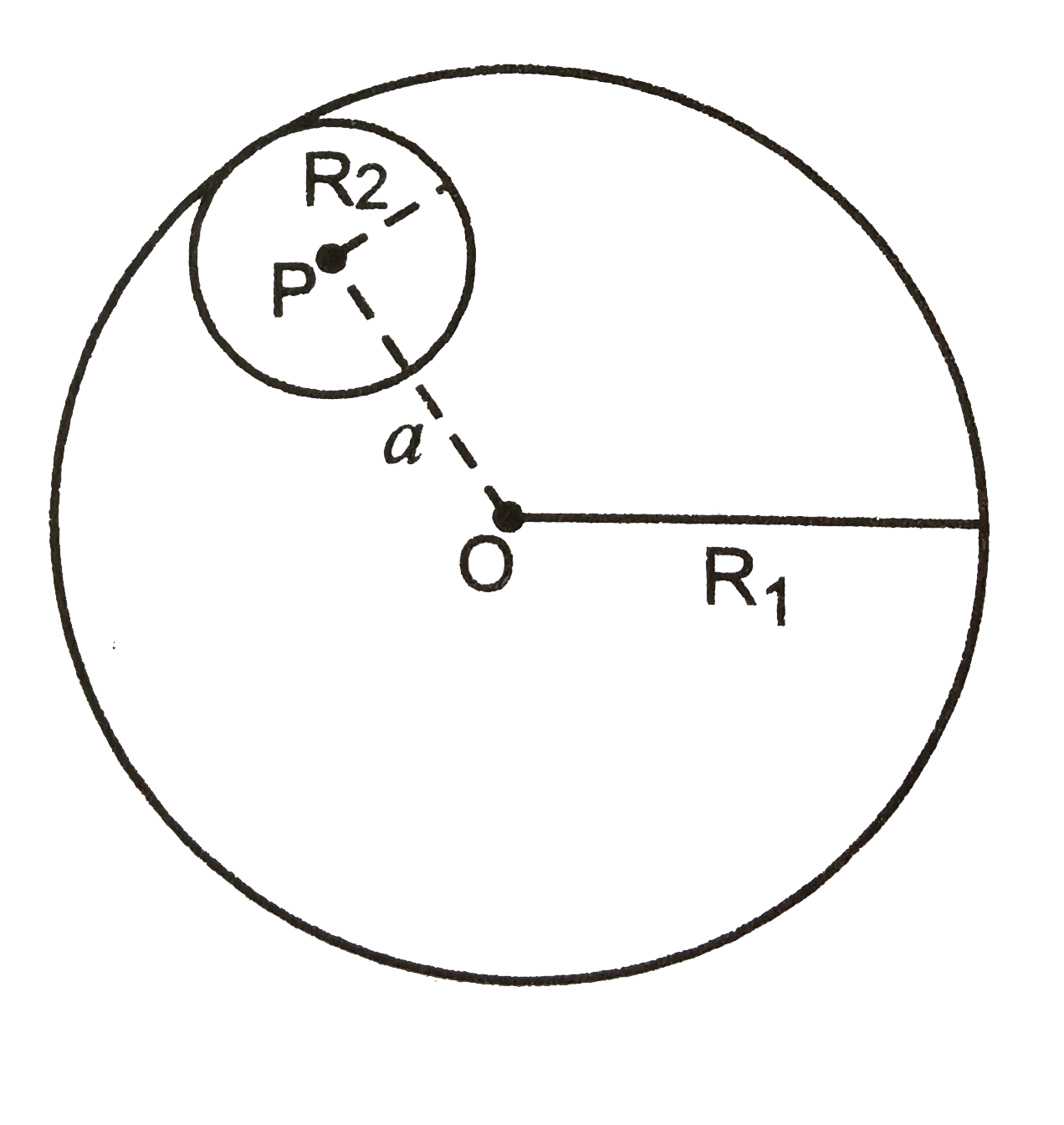
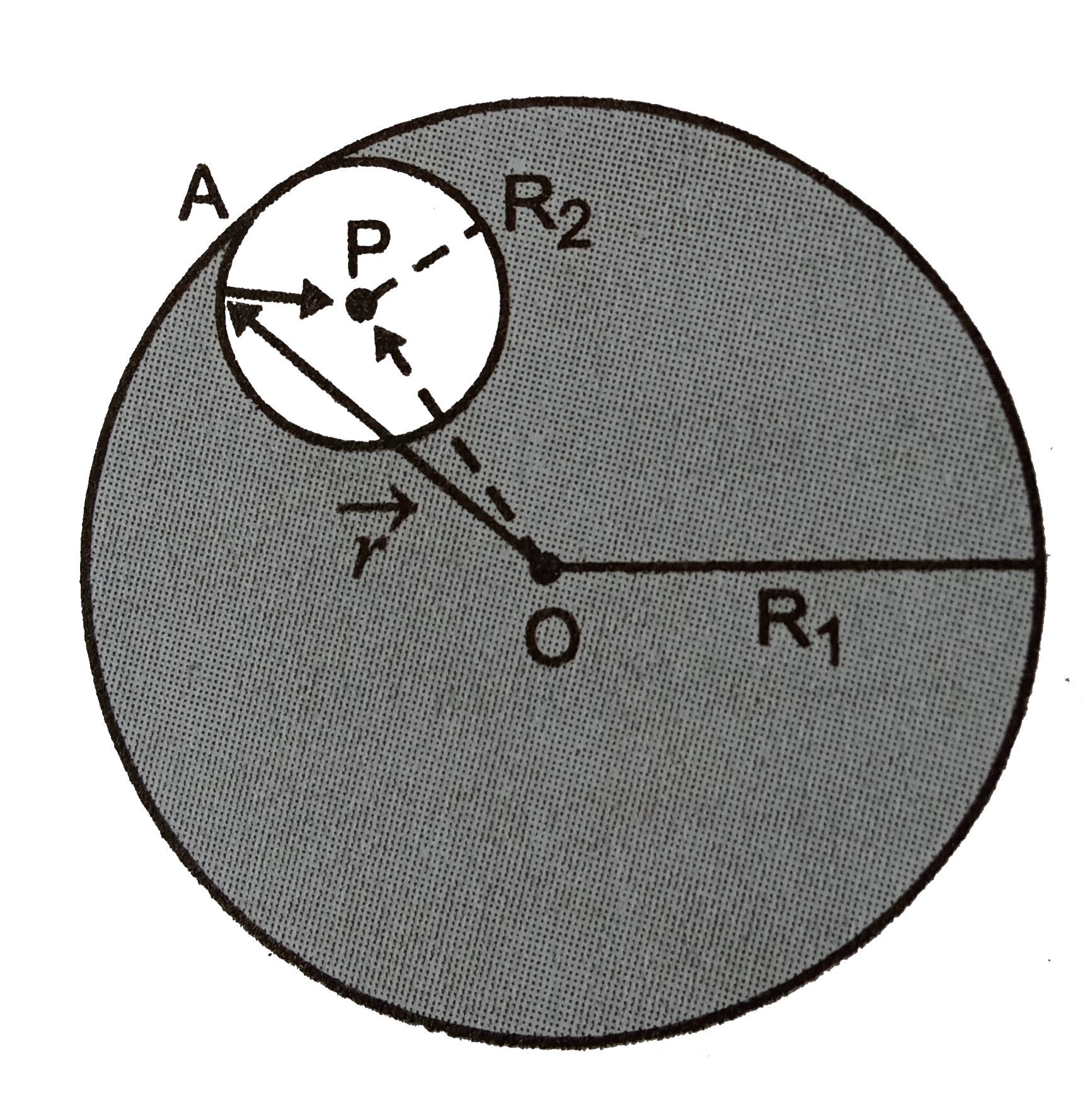
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
ELECTROSTATICS
PRADEEP|Exercise FILL IN THE BLANKS|8 VideosELECTROSTATICS
PRADEEP|Exercise PROBLEMS FOR PRACTICE|8 VideosELECTROSTATICS
PRADEEP|Exercise VALUE BASED QUESTIONS|7 VideosELECTRONIC DEVICES
PRADEEP|Exercise Fill in the Blanks|1 VideosMAGNETIC EFFECT OF CURRENT AND MAGNETISM
PRADEEP|Exercise Competition Focus (Multiple Choice Questions)|2 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
PRADEEP-ELECTROSTATICS-Exercise
- Two path balls carrying eqaul chareges are suspended froom a common ...
Text Solution
|
- Two charges, each equal to q, aer kept at x=-a and x=a on the x-axis. ...
Text Solution
|
- Consider a uniform spherical charge distribution of radius R(1) centr...
Text Solution
|
- A long cylindrical shell carries positive surface charge sigma in the ...
Text Solution
|
- Two point charges +8q and -2q are located at x=0 and x=L respectively....
Text Solution
|
- If potential (in volts) in a region is expressed as V (x, y, z) = 6xy ...
Text Solution
|
- The figure below depict two situations in which two infinitely long st...
Text Solution
|
- Poistive and negative point charges of equal magnitude are kept at (0,...
Text Solution
|
- A thin semi-circular ring of radius r has a positive charge q distribu...
Text Solution
|
- Two charges q(1) and q(2) are placed 30 cm apart, as shown in the figu...
Text Solution
|
- The point charges + q, -2q and + q are placed at point (x = 0, y = a, ...
Text Solution
|
- A thin conducting ring orf radius R is given a chareg +Q, Fig. The el...
Text Solution
|
- Let there be a spherically symmetric charge distribution with charge d...
Text Solution
|
- A thin semi-circular ring of radius r has a positive charge q distribu...
Text Solution
|
- Let P(r)=(Q)/(piR^4)r be the charge density distribution for a solid s...
Text Solution
|
- Two positive charges of magnitude q are placed at the ends of a side (...
Text Solution
|
- Conisder a thin spherical shell of radius R with centre at the origin,...
Text Solution
|
- Charges Q, 2Q and 4Q are uniformly distributed in three dielectric sol...
Text Solution
|
- The electric field in a certain region is acting radially outwards and...
Text Solution
|
- An assmebly of charges +q, -q , +q, -q….. are at positions x = 1 m, ...
Text Solution
|