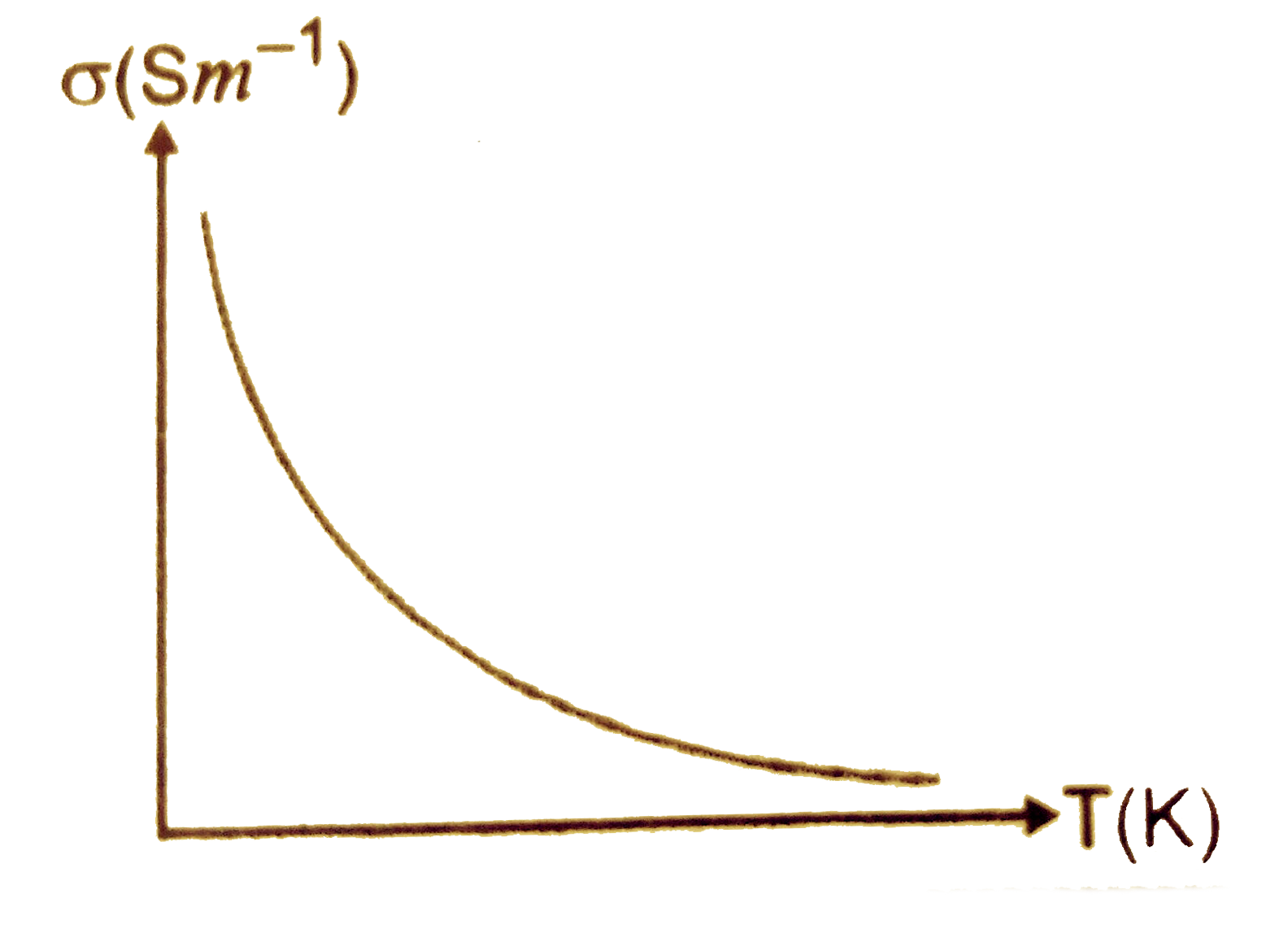
Conductivity of a metallic conductor is
`sigma = 1/rho = (n e^(2)tau)/m`
For a metal, the number density of electrons n is fixed. When temperature of metal increases, the amplitude of vibrations of the atoms or ions of the metal conductor increases. As a result of it, the collision of electrons with atoms/ions become more frequnet, consequnetly, the relaxation time `tau` decreases. It means, conductivity of a metallic conductor decreases with the increases of temperature, as shown in figure