Let a cell of emf `epsilon` be connected between points A and B. Let the currents in the various branches be as shown in figure
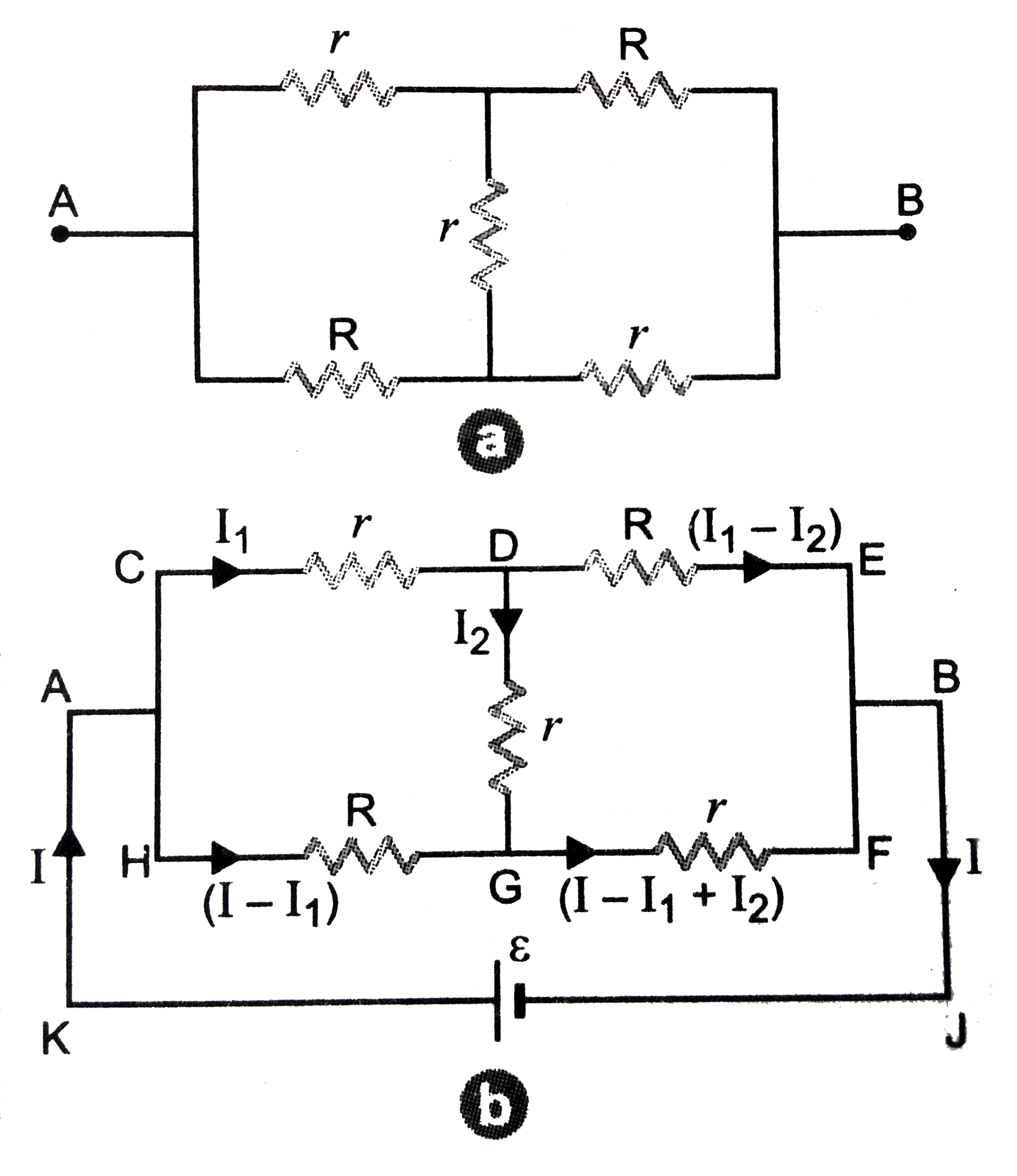
.
Applying Kirchhoff's Second Rule to loop KACDEBJK
`I_(1) r + (I_(1)-I_(2)) R= epsilon`
or `I_(1)(r +R) - I_(2)R = epsilon`....(i)
For loop CDGHC, we get
`I_(1) r + I_(2) r - (I - I_(1))R= 0`
`I_(1)(r+R)+I_(2) r = IR`....(ii)
For loop DEFGD, we get
`(I_(1) - I_(2))R - (I - I_(1) +I_(2)) r - I_(2) r= 0`
`I_(1)(R+ r)- I_(2)(R +2 r)= Ir`....(iii)
Solving equations (ii) and (iii), we get
`I_(1)= (R +r)/(R +3r) I and I_(2) = (R-r)/(R+3r) I`
Putting values in (i), we get
`((R+r)/(R+3r)) I (r+R)- ((R-r)/(R+3r)) IR= epsilon`
or `((3 r R+r^(2))/(R+3r))I=epsilon`
Equivalent resistance between A and B
`R_(eq) = epsilon/I=(3 r R +r^(2))/(R+3r) = (r (3+r))/((R +3r))`