Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
ELECTRODYNAMICS
IE IRODOV, LA SENA & SS KROTOV|Exercise Conductors And Dielectrics In An Electric Field|47 VideosELECTRODYNAMICS
IE IRODOV, LA SENA & SS KROTOV|Exercise Electric Capacitance - Energy Of An Electric Field|46 VideosELECTRICITY AND MAGNETISM
IE IRODOV, LA SENA & SS KROTOV|Exercise All Questions|6 VideosELECTROMAGNETISM
IE IRODOV, LA SENA & SS KROTOV|Exercise All Questions|24 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
IE IRODOV, LA SENA & SS KROTOV-ELECTRODYNAMICS-Motion Of Charged Particle In Magnetic Field
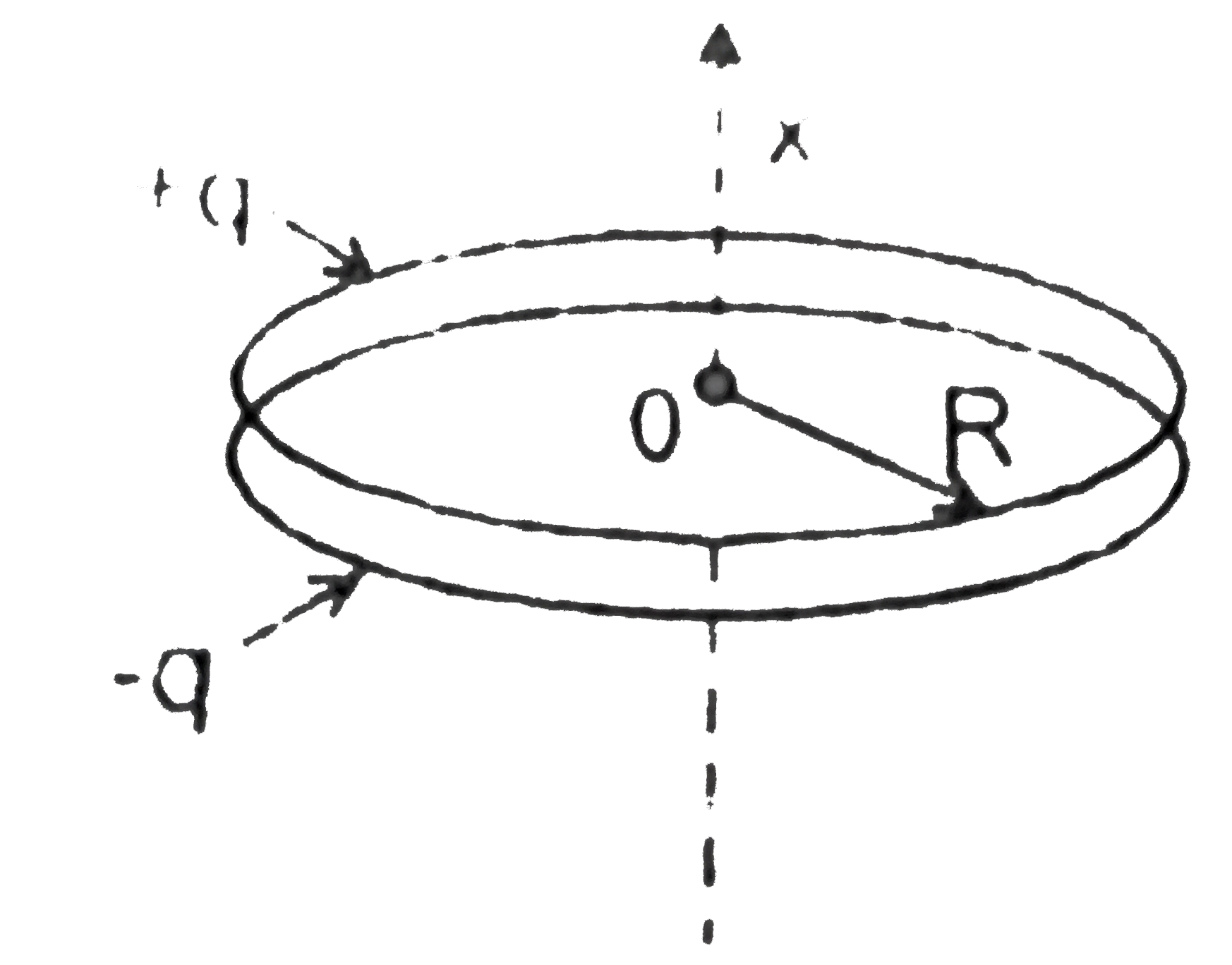
- Two coaxial rings, each of radius R, made of thin wire are separated b...
Text Solution
|
- At the moment t = 0 on electron leaves one plate of a parallel-plate ...
Text Solution
|
- A proton accelarted by a potential differnce V gets into the unifrom...
Text Solution
|
- A particle with specific charge q//m moves rectilinerarly due to an ...
Text Solution
|
- An electron starts moving in a unifrom electric fied of strength E ...
Text Solution
|
- Determine the accelration of a relativistic electron moving along ...
Text Solution
|
- At the moment t = 0 a relativsitic proton files with a velocity v(...
Text Solution
|
- A proton accelarted by a potential differnce V = 500 kV fieles throug...
Text Solution
|
- A charged particle moves along a circle of radius r = 100 mm in a u...
Text Solution
|
- A relativistic particle with charge q and rest mass m, moves along a...
Text Solution
|
- Up to what values of kinetic energy does the period of revolution of ...
Text Solution
|
- An electron accelerated by a potnetial difference V = 1.0 kV moves i...
Text Solution
|
- A slightly divergent beam of non-relatistic charged particles accele...
Text Solution
|
- A non-relativistic electron originates at a point A lying on the axi...
Text Solution
|
- From the surface of a round wire of radius a carrying a direct cur...
Text Solution
|
- A non-relativistic charged particle files through the electric field o...
Text Solution
|
- Unifrom electric and magnetic fields with strength E and induction B...
Text Solution
|
- A narrow beam of identical ions with specific charge q//m, possessin...
Text Solution
|
- A non-relativistic protons beam passes without diviation through t...
Text Solution
|
- Non-relativistic protons move rectinearly in the region of space whe...
Text Solution
|
- A beam of non-relatitivistic chagred particles moves without deviatio...
Text Solution
|