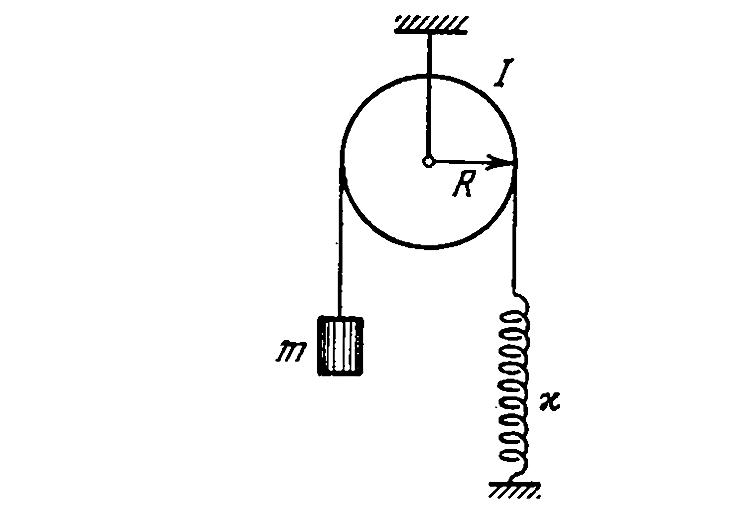Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
OSCILLATIONS AND WAVES
IE IRODOV, LA SENA & SS KROTOV|Exercise Electric Oscillations|56 VideosOSCILLATIONS AND WAVES
IE IRODOV, LA SENA & SS KROTOV|Exercise Elastic Waves|39 VideosOPTICS
IE IRODOV, LA SENA & SS KROTOV|Exercise Exercise|2 VideosPHYSICAL FUNDAMENTALS OF MECHANICS
IE IRODOV, LA SENA & SS KROTOV|Exercise Relativistic Mechanics|49 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
IE IRODOV, LA SENA & SS KROTOV-OSCILLATIONS AND WAVES-Electromagnetic Waves, Radiation
- Find the frequency of small oscillations of the arrangement illustrate...
Text Solution
|
- An electromagnetic wave of frequency v=3.0 MHz passes from vacuum into...
Text Solution
|
- A plane electromagnetic wave falls at right angles to the surface of a...
Text Solution
|
- A plane electromagnetic wave of frequency v=10 MHz propagates in a poo...
Text Solution
|
- A plane electromagentic wave E=E(m) cos ( omegat - kr) propagates in ...
Text Solution
|
- A plane electromagentic wave E=E(m)cos ( omegat-kr) where E(m) E(m) e(...
Text Solution
|
- A plane electromagnetic wave E=E(m) cos ( omega t-kx) propagating in v...
Text Solution
|
- Proceeding from Maxwell's equation shown that in the case of a plane e...
Text Solution
|
- Find the mean Plynting vector ( : S: ) of a plane electromagnetice wa...
Text Solution
|
- A plane harmonic electromagnetic wave with plane polarization propagat...
Text Solution
|
- A ball of radius R=50 cm is located in a non- magnetic medium with per...
Text Solution
|
- A standing electromagnetic wave with electric component E=E(m) cos kx....
Text Solution
|
- A standing electromagnetic wave E=E(m) cos kx. Cosomegat is sustained ...
Text Solution
|
- A parallel - plate air capacitor whose electrodes are shaped as dis...
Text Solution
|
- An alternating sinusoidal current of frequency omega=1000s^(-1) flows ...
Text Solution
|
- A parellel-plate capacity whose electrodes are shaped as round disc is...
Text Solution
|
- A current I flows along a straight conductor with round cross-section....
Text Solution
|
- Non-relativistic protons accelerated by a potential difference U from ...
Text Solution
|
- A current flowing in the winding of a long straight solenoid is increa...
Text Solution
|
- Fig. illustrates a segment of a double line carrying direct current wh...
Text Solution
|
- The enegry is transferred form a source of constant voltage V to a con...
Text Solution
|