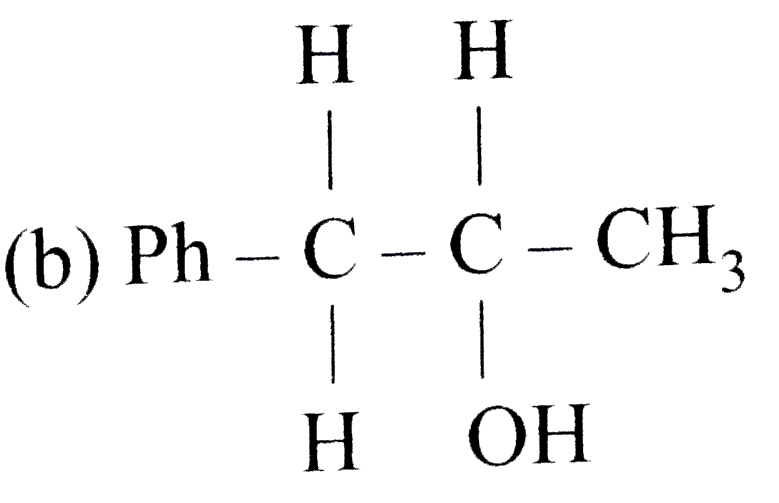
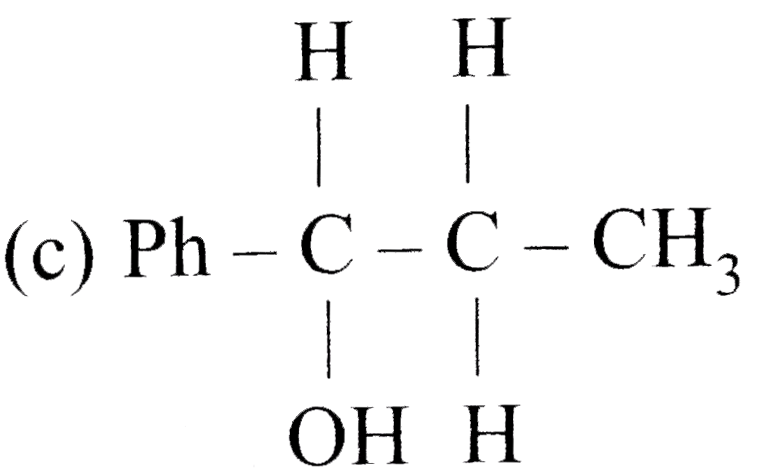A
B
C
D
Text Solution
AI Generated Solution
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
HYDROCARBONS
A2Z|Exercise Method of Preparation of Alkynes|59 VideosHYDROCARBONS
A2Z|Exercise Benzene|23 VideosHYDROCARBONS
A2Z|Exercise Chemical Properties Of Alkanes|97 VideosENVIRONMENTAL CHEMISTRY
A2Z|Exercise Section D - Chapter End Test|30 VideosHYDROGEN
A2Z|Exercise Section D - Chapter End Test|30 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
A2Z-HYDROCARBONS-Methods Of Preparation Of Alkanes
- The only alcohol that can be prepared by the indirect hydration of alk...
Text Solution
|
- Which is the wrong statement about osxy mercuration- demercuration ?
Text Solution
|
- Which of the following alkenes will give anti-markownikoff's product a...
Text Solution
|
- A will have configuration
Text Solution
|
- C CI(3)CH=CH(2) overset(Cl(2)+H(2)O)rarr P, Identify major product ...
Text Solution
|
- CH(2)= CHCH(2)CH=CH(2) overset(NBS)rarr X( Major ),(X) is :
Text Solution
|
- Hence X is
Text Solution
|
- Complete the following reaction
Text Solution
|
- Complete the following reaction
Text Solution
|
- The relative rates of hydrogenation is in the order of
Text Solution
|
- Ph -ch(2)-ch=ch(2)overset(dil H(2)SO(4))rarrX, Identify product 'X' ...
Text Solution
|
- CH(3)CH=CH(2)overset(BD(3) //THF)underset(H(2)O // OH)rarrX,
Text Solution
|
- Product is :
Text Solution
|
- The given reaction, is an example of :
Text Solution
|
- , product X is
Text Solution
|
- An organic compound X(C(6)H(13)Br) is optically active, X on treatment...
Text Solution
|
- When 1-alkyne is treated with Na + Liq. NH(3) and product is reacted w...
Text Solution
|
- Which of the following will not react with an ammoniacal silver nitrat...
Text Solution
|
- The product formed when acetylene is passed through red hot tube is
Text Solution
|
- R-CH(2)-C Cl(2)-R overset(Reag ent)rarrR-C-=C-R The reagent is
Text Solution
|