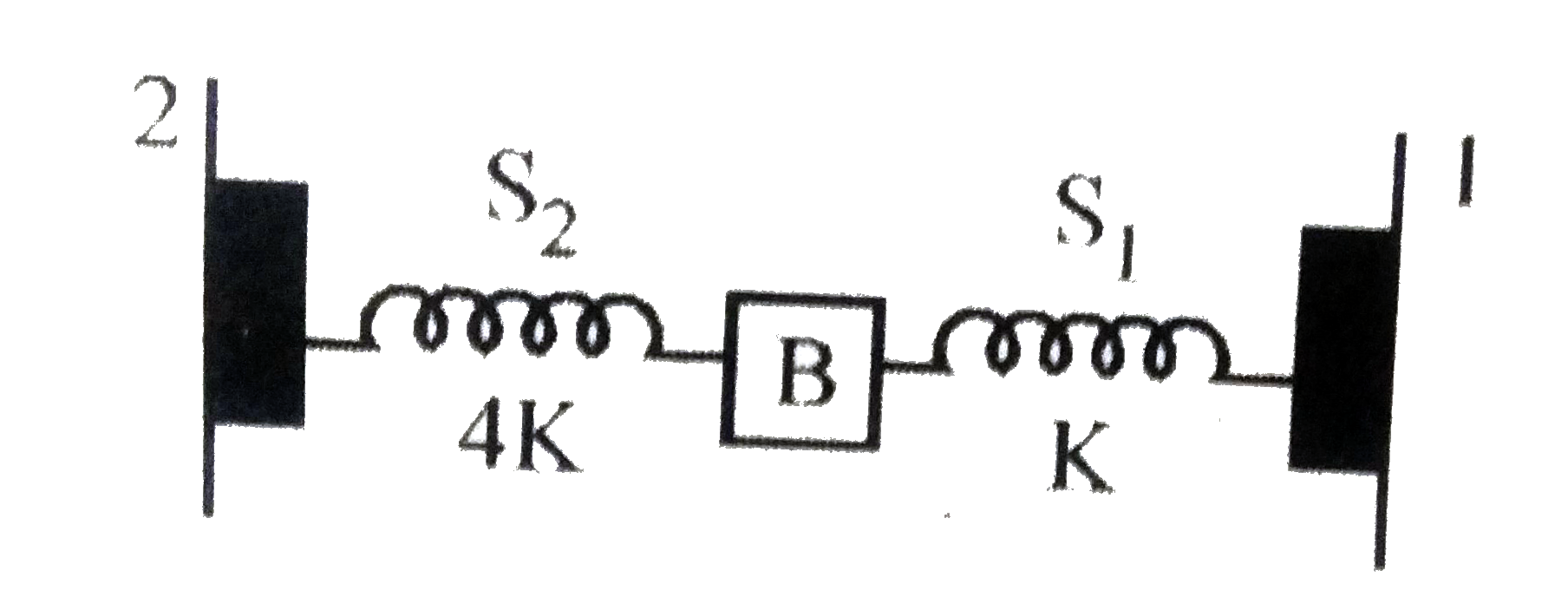A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
MARVEL PUBLICATION-OSCILLATIONS-MCQ
- A mass m suspended from a vertical spring oscillates with a period of ...
Text Solution
|
- A particle at the end of a spring executes simple harmonic motion with...
Text Solution
|
- A block of mass m, attacted to a string of spring constant k, oscillat...
Text Solution
|
- The force constants of two springs areK(1) and K(2). Both are stretche...
Text Solution
|
- Two springs of force constants K(1) " and " K(2) are connected to a ma...
Text Solution
|
- A block A of mass m is placed on a frictionless horizontal surface. An...
Text Solution
|
- Two masses m1 and m2 are suspended together by a massless spring of co...
Text Solution
|
- A block (B) is attached to two unstriched sprig S(1) and S(2) with spr...
Text Solution
|
- A wooden block performs SHM on a frictionless surface with frequency, ...
Text Solution
|
- Two similar springs P and Q have spring constant K(P) and K(Q) such th...
Text Solution
|
- A mass m is suspended separately by two different spring of spring con...
Text Solution
|
- The graph shown was obtained from experimental measurements of the per...
Text Solution
|
- The displacement-time graph of a particle executing simple harmonic mo...
Text Solution
|
- The graph of l against T for a simple pendulum is
Text Solution
|
- The period (T) of a simple pendulum is measured for different length (...
Text Solution
|
- For a particle executing simple harmonic motion, the displacement x is...
Text Solution
|
- Figure shows the displacement time graphs of two simple harmonic motio...
Text Solution
|
- A particle executing linear SHM has velocities v(1) " and " v(2) at di...
Text Solution
|
- If the metal bob of a simple pendulum is replaced by a wooden bob, the...
Text Solution
|
- Two particles perform linear simple harmonic motion along the same pat...
Text Solution
|