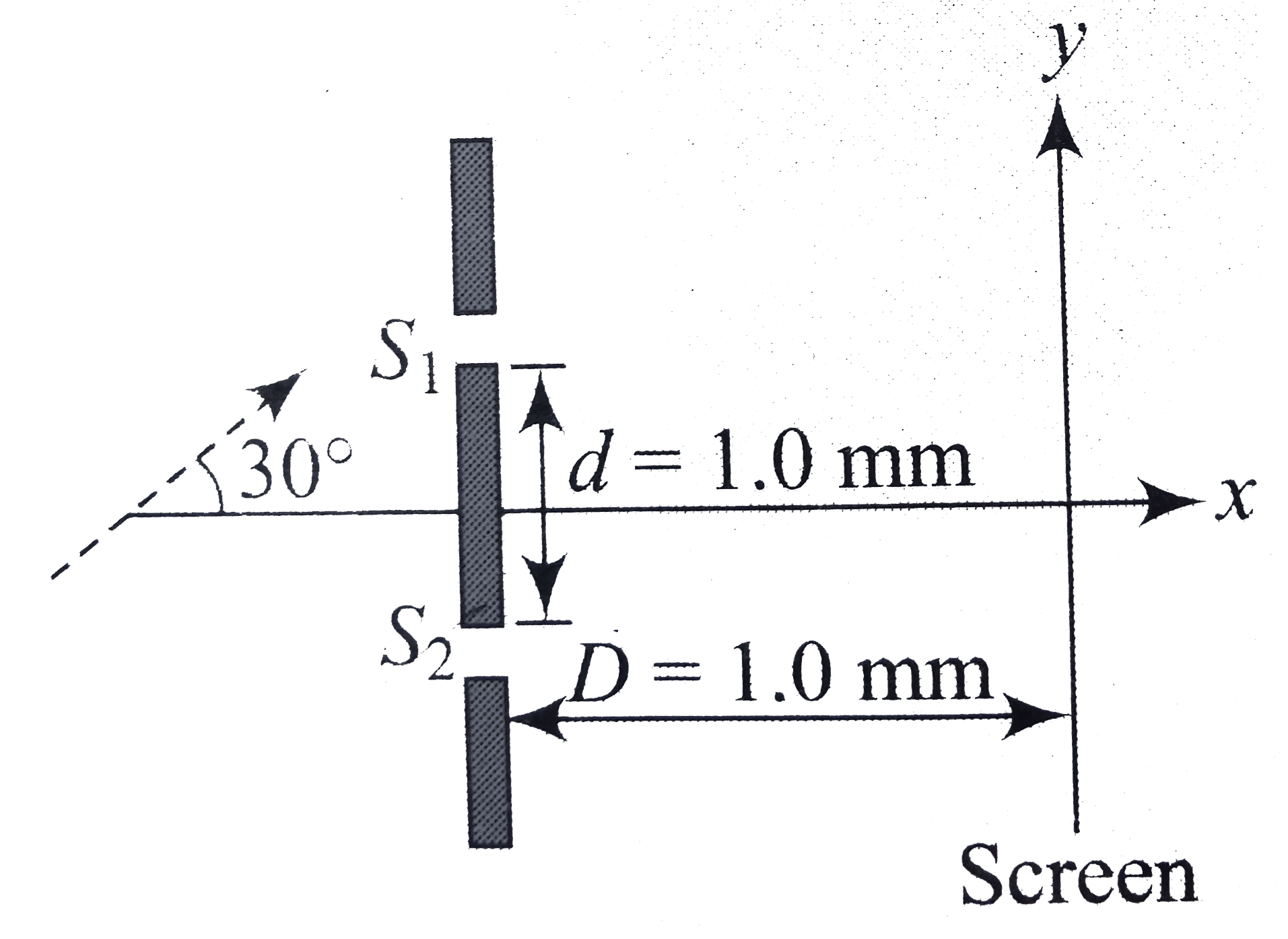Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
- A coherent parallel beam of microwaves of wavelength lambda = 0.5 mm f...
Text Solution
|
- A parallel beam of monochromatic light is used in a Young's double sli...
Text Solution
|
- A coherent parallel beam of microwaves of wavelength lambda = 0.5 mm f...
Text Solution
|
- A coherent parallel beam of microwaves of wavelength lambda = 0.5 mm f...
Text Solution
|
- The distance between two slits in a YDSE apparatus is 3mm. The distanc...
Text Solution
|
- A parallel light beam of wavelength 6000Å passes through a slit 0.2 mm...
Text Solution
|
- The distance between two slits in a YDSE apparatus is 3mm. The distanc...
Text Solution
|
- In a Young's double slit experiment, the slit separation d is 0.3 mm a...
Text Solution
|
- lamda =0.5 mm तरंगदैर्ध्य की सूक्ष्मतरंगो का एक कलासम्बद्ध समान्तर पुं...
Text Solution
|