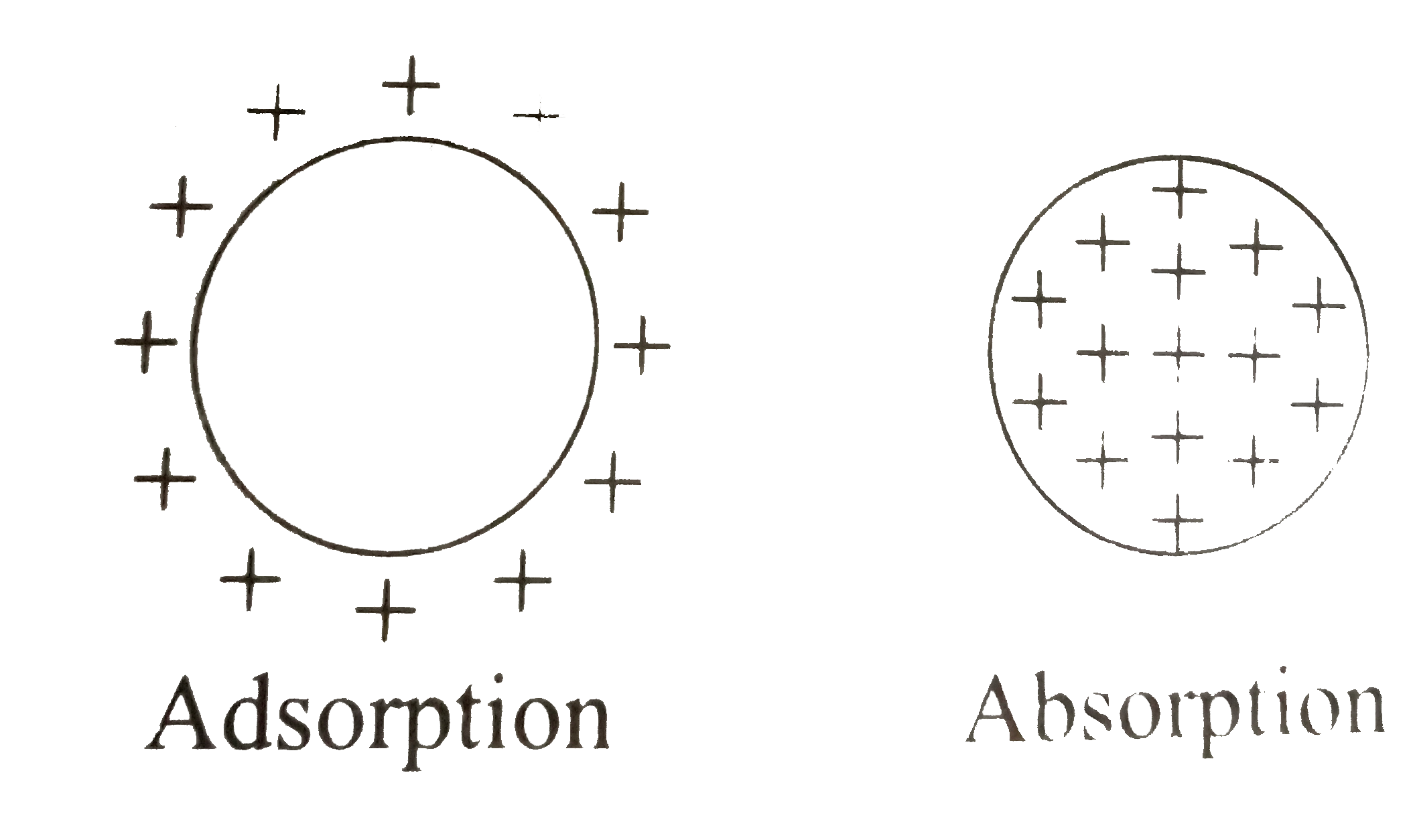
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
R SHARMA-SURFACE CHEMISTRY-Archives
- The term adsorption refers strictly to the existence of an concentrati...
Text Solution
|
- The coagulation value in millimoles per litre of the electrolyes used ...
Text Solution
|
- Which one of the following chargcterisitic is associated with adsorpt...
Text Solution
|
- Which property of colloids is not dependent on the change on colloidal...
Text Solution
|
- Which of the following statements of correct for the spontaneous adsop...
Text Solution
|
- In frenudlich adsorption isotherm, the value of 1//n is
Text Solution
|
- Which one of the following statements is incorrect about enzyme catal...
Text Solution
|
- The ease of adsorption of the hydrated alkali metal ions om ion-exchan...
Text Solution
|
- The protcting power of lyophilic colloidal solution is expressed in te...
Text Solution
|
- If x is the amount of adsorbate and m is the amount of adsorbent, whic...
Text Solution
|
- The Langmuir adsorption isotherm is deduced using the assumption.
Text Solution
|
- A plt of log X/m vs. log P for the adsorption of a gasd on a solid giv...
Text Solution
|
- Which one of the following forms micells in aqueous solution above cer...
Text Solution
|
- which of the following forms cationic micelles above certain concentra...
Text Solution
|
- Which of the following statements about the zeolites is false?
Text Solution
|
- According to the adsorption theory of catalysis the speed of the react...
Text Solution
|
- Position of nonpolar and parts in micells is
Text Solution
|
- Which is not correct regarding the adsorption of a gas on surface of a...
Text Solution
|
- The method usually employed for the precipitation of a colloidal solut...
Text Solution
|