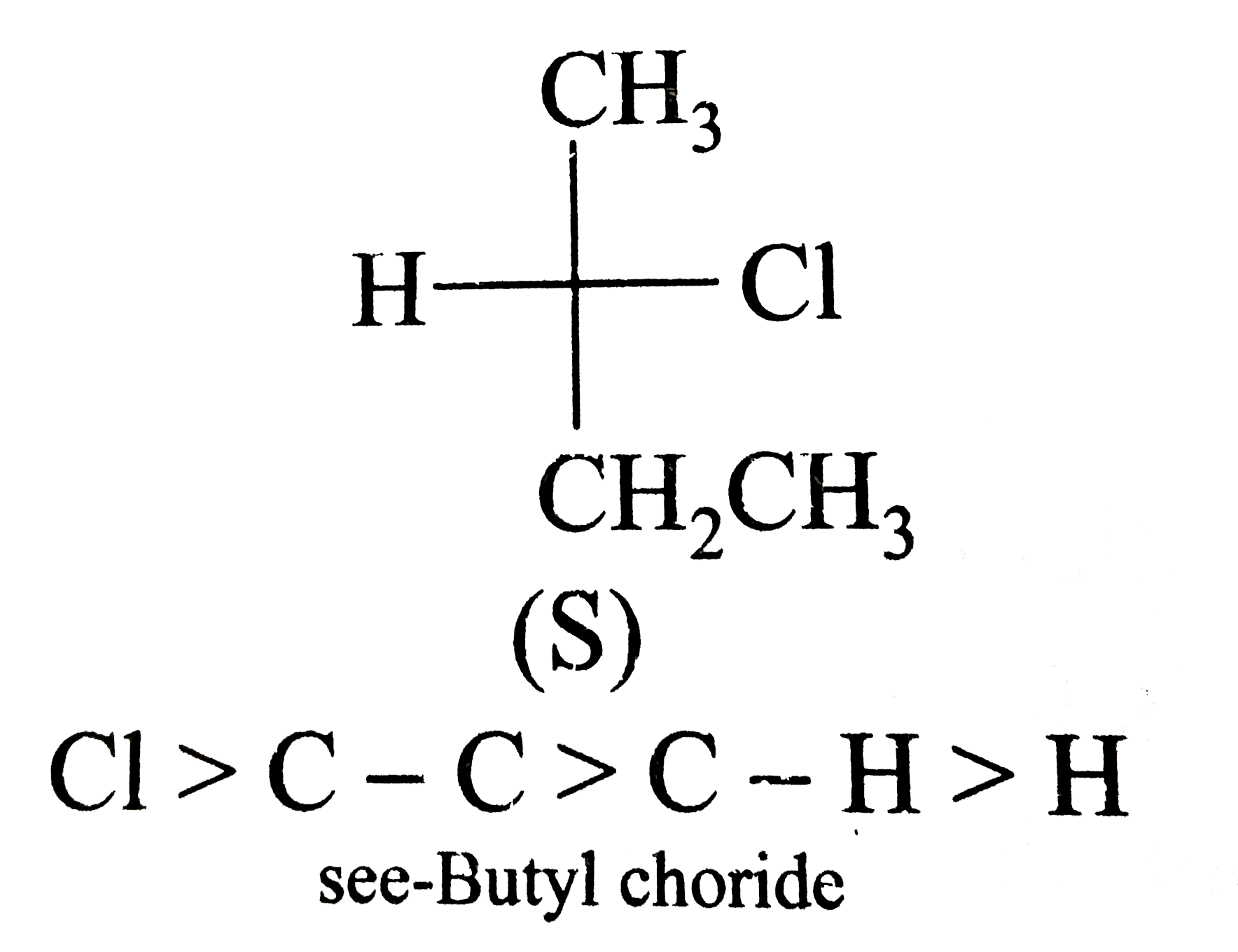
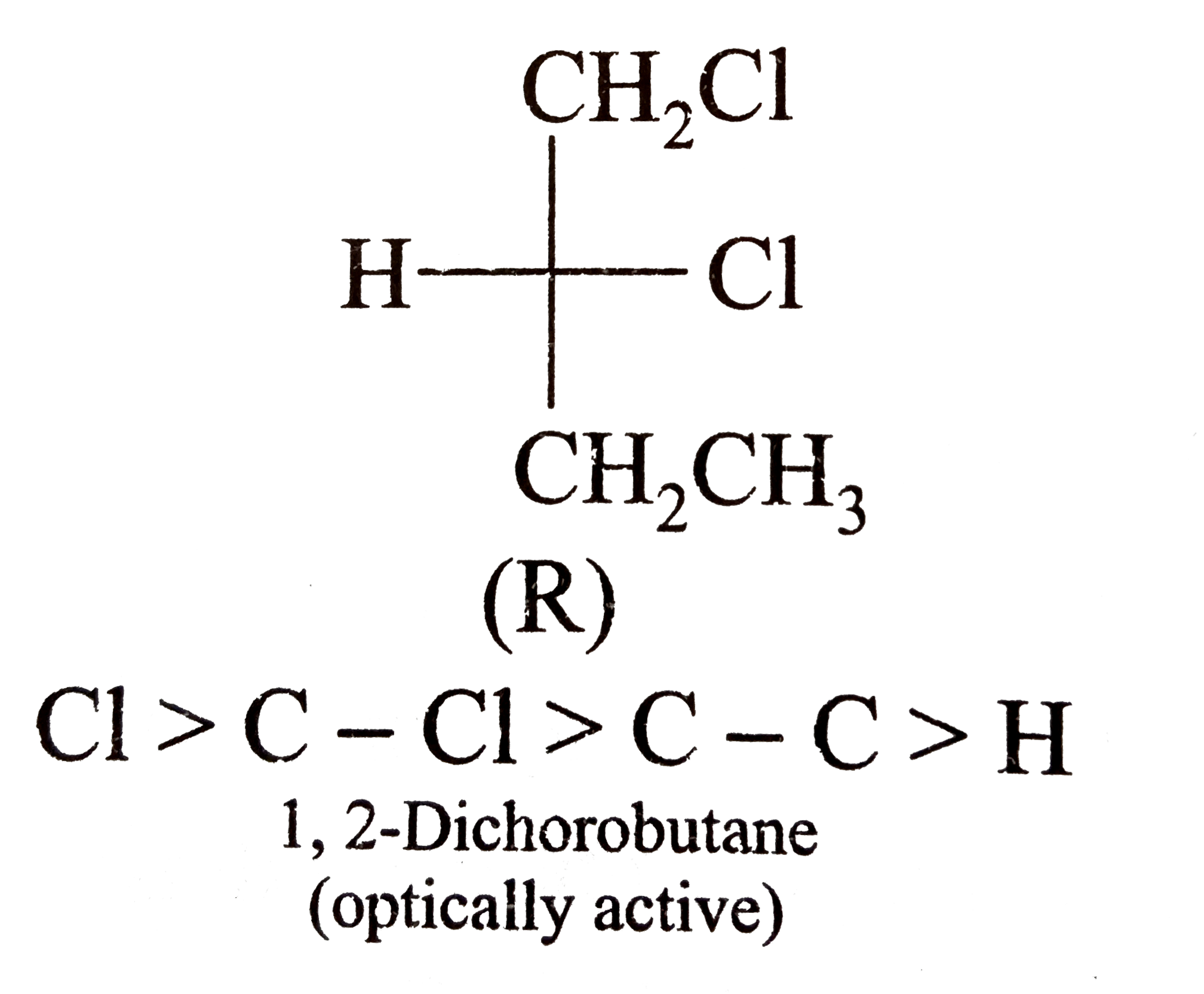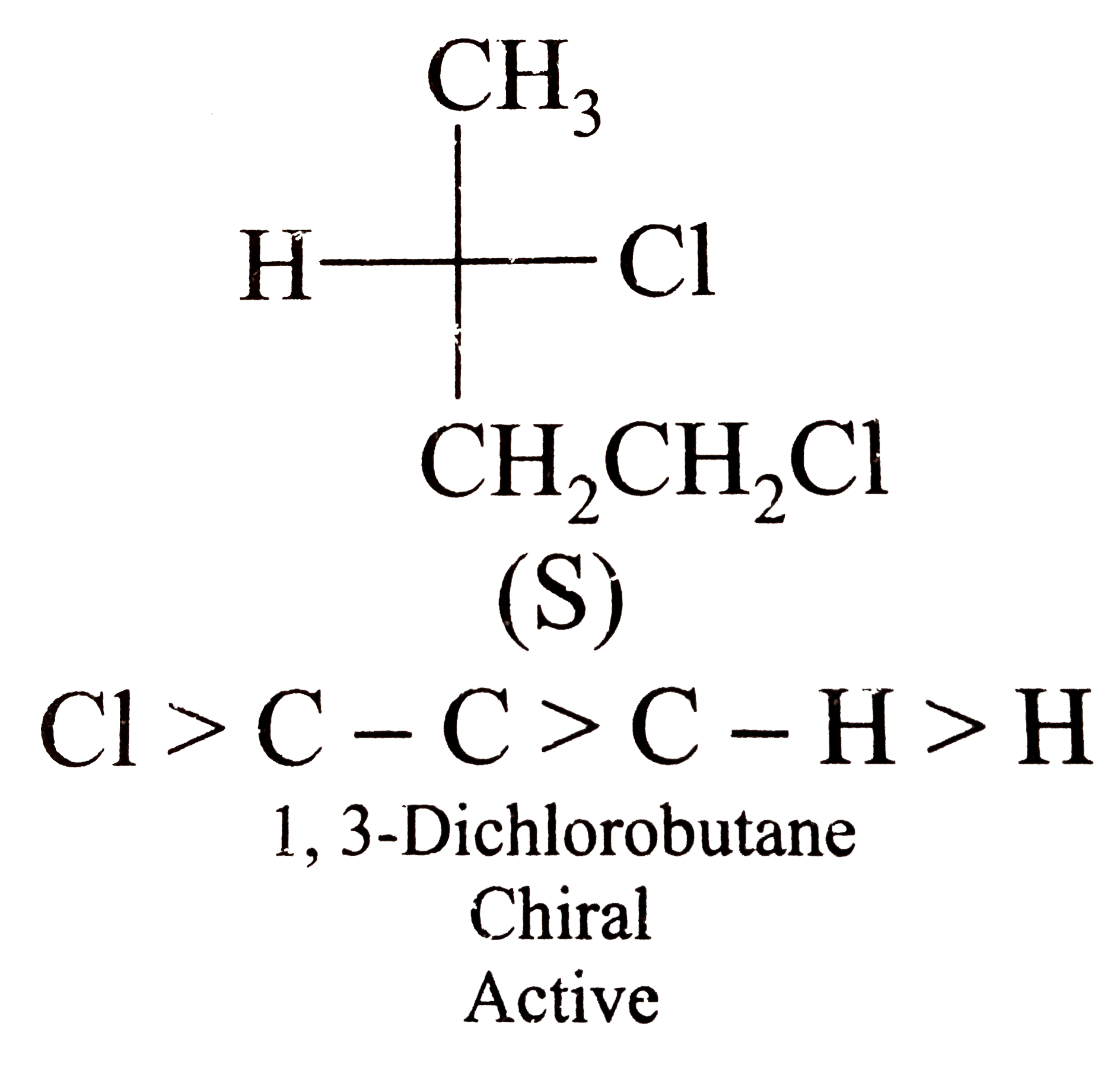A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
R SHARMA-STEREOCHEMISTRY-Level III
- Consider the following configurations (A),(B),(C ) and (D) (A) ...
Text Solution
|
- Consider the following configuration (A),(B) and (C ). (A) Whic...
Text Solution
|
- The chemical properties of enantiomer are the same towards achiral (...
Text Solution
|
- Which fo the following stereosimers represent meso compounds?
Text Solution
|
- (S)-sec Buty1 chloride is subjected to free-radical chlorination follo...
Text Solution
|
- Cyclohexene on reaction with Br(2)in C CI(4) yields
Text Solution
|
- Consider the following reaction sequence The final product (III)...
Text Solution
|
- trans-But-2-ene reacts with cold dilute KMnO(4) solution to yield
Text Solution
|
- trans-But-2-ene reacts with D(2) in the presence of Ni as catayst. The...
Text Solution
|
- Geometrical isomerism is exihibited by
Text Solution
|
- The smallest ketone and its next homologue are reacted with H(2)NOH to...
Text Solution
|
- Which of the following Fischer's projection formula is identical to D-...
Text Solution
|
- Among the following four structures I to IV C(2)H(5)-overset(CH(3))o...
Text Solution
|
- The number of isomers for the compound with moelecular formula C(2)BrC...
Text Solution
|
- Give the IUPAC name of the alkene
Text Solution
|
- When NH(2)OH reacts with an usymmetrical ketone then numver of product...
Text Solution
|
- The name of the formed is
Text Solution
|
- The absolute configuartion of the configuration compound is
Text Solution
|
- The prefixes syn and anti are used to denote
Text Solution
|
- The number of optical isomers of the compound CH(3)CHBrCHBrCOOH is
Text Solution
|