Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
NARAYNA-NEWTONS LAWS OF MOTION-PASSAGE TYPE QUESTION
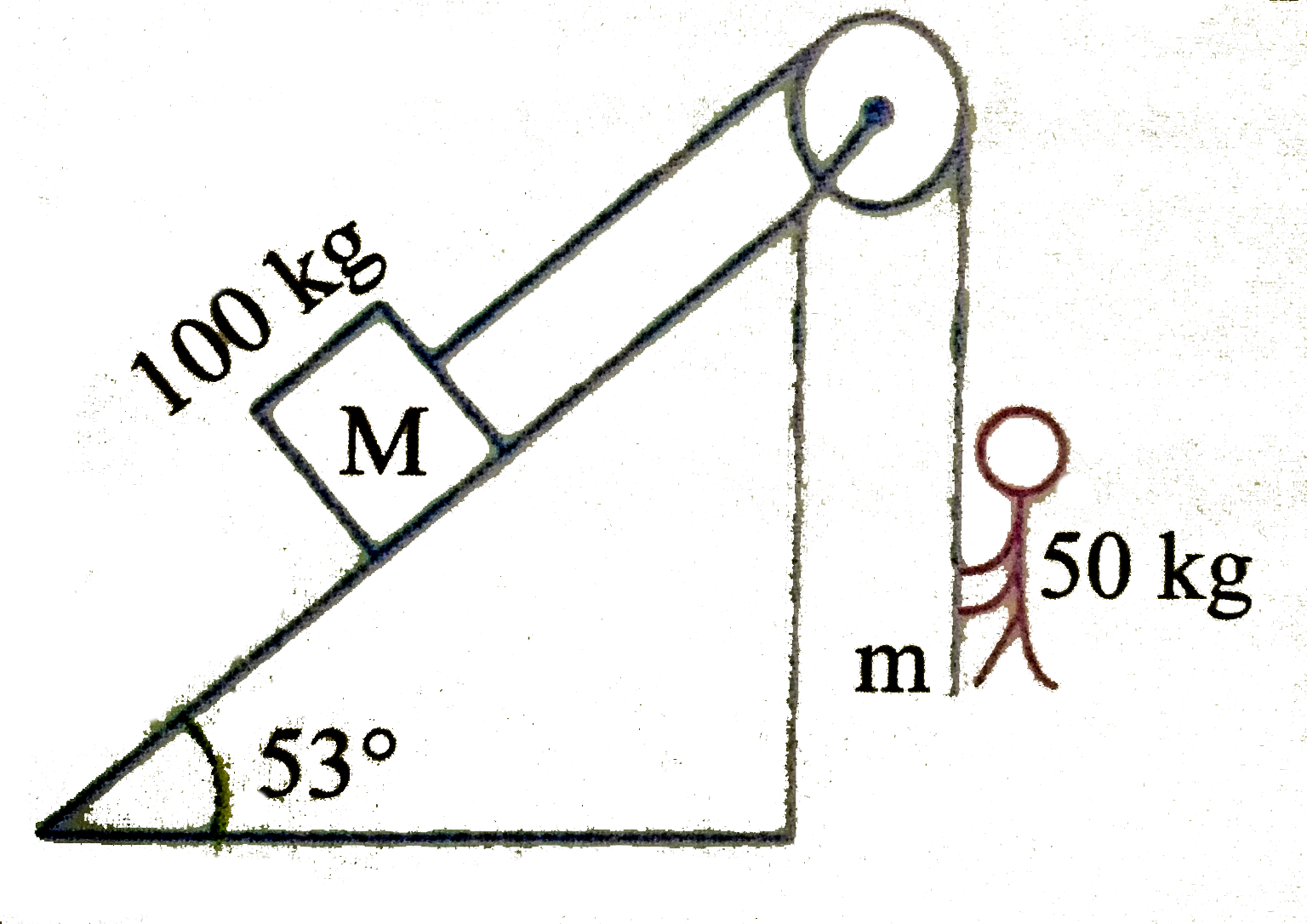
- By what acceleration the boy must go up so that 100kg block remains st...
Text Solution
|
- A shot putter with a mass of 80kg pushes the iron ball of mass of 6kg ...
Text Solution
|
- A shot putter with a mass of 80kg pushes the iron ball of mass of 6kg ...
Text Solution
|
- A shot putter with a mass of 80kg pushes the iron ball of mass of 6kg ...
Text Solution
|
- Two blocks m(1) and m(2) are allowed to move without friction. Block m...
Text Solution
|
- Two blocks m(1) and m(2) are allowed to move without friction Block m(...
Text Solution
|
- Two blocks m(1) and m(2) are allowed to move without friction Block m(...
Text Solution
|
 .
.