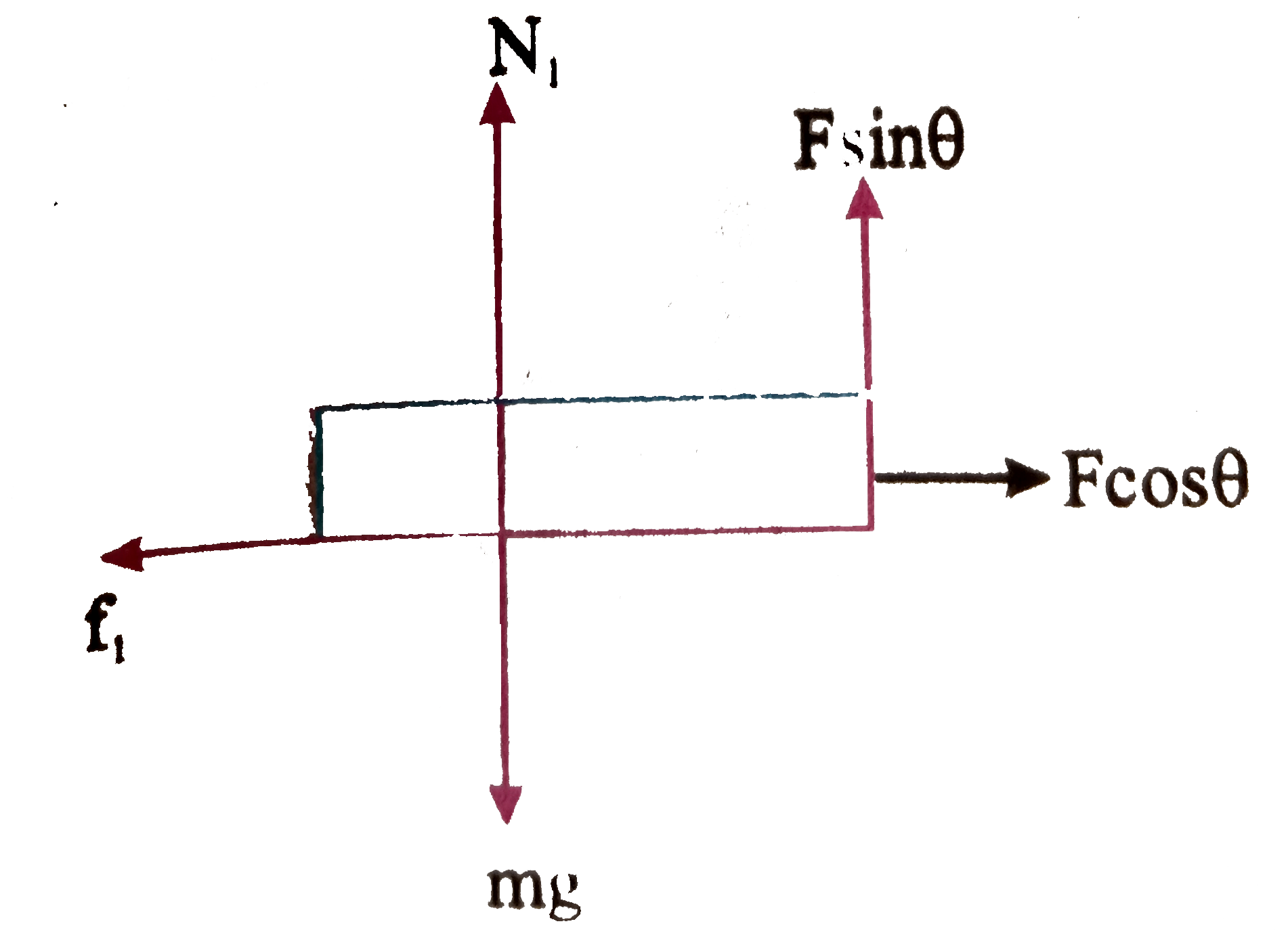
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
NARAYNA-SYSTEM OF PARTICLES-Level-VI
- A wheel of radius R, mass m with an axle of radius r is placed on a ho...
Text Solution
|
- Consider a cylinder of mass M=1 kg and radius R=1 mlying on a rough ho...
Text Solution
|
- Consider a cylinder of mass M=1 kg and radius R=1 mlying on a rough ho...
Text Solution
|
- Consider a cylinder of mass M=1 kg and radius R=1 mlying on a rough ho...
Text Solution
|
- A uniform rod is fixed to a rotating turntable so that its lower end i...
Text Solution
|
- A uniform rod is fixed to a rotating turntable so that its lower end i...
Text Solution
|
- A disc of a mass M and radius R can rotate freely in vertical plane ab...
Text Solution
|
- A disc of mass M and radius R can rotate freely in a vertical plane ab...
Text Solution
|
- A disc of mass M and radius R can rotate freely in a vertical plane ab...
Text Solution
|
- A plank of mass m(1) with a uniform solid sphere of mass m(2) placed o...
Text Solution
|
- A uniform cylinder of radius R is spinned about it axis to the angular...
Text Solution
|
- The pulley shown in figure has a radius 10 cm and moment of inertia 0....
Text Solution
|
- Two solid semi-circular disks fo equal masses m=10 kg collide and stic...
Text Solution
|
- A ball of radius R=20 cm has mass m=0.75 kg and moment of inertia (abo...
Text Solution
|
- A uniform square plate of mass 'm'is supported as shown. If the cable ...
Text Solution
|
- In the figure shown there is a fixed wedge 'W' of inclination theta. A...
Text Solution
|
- In the figure shown a uniform ringh of mass m placed on arough horizon...
Text Solution
|
- A thin rod of mass m and length 2l is placed horizontally and perpendi...
Text Solution
|
- Figure shows an arrangements of masses hanging from a ceilling. In equ...
Text Solution
|
- A right triangular plate ABC of mas m is free to rotate in the vertica...
Text Solution
|