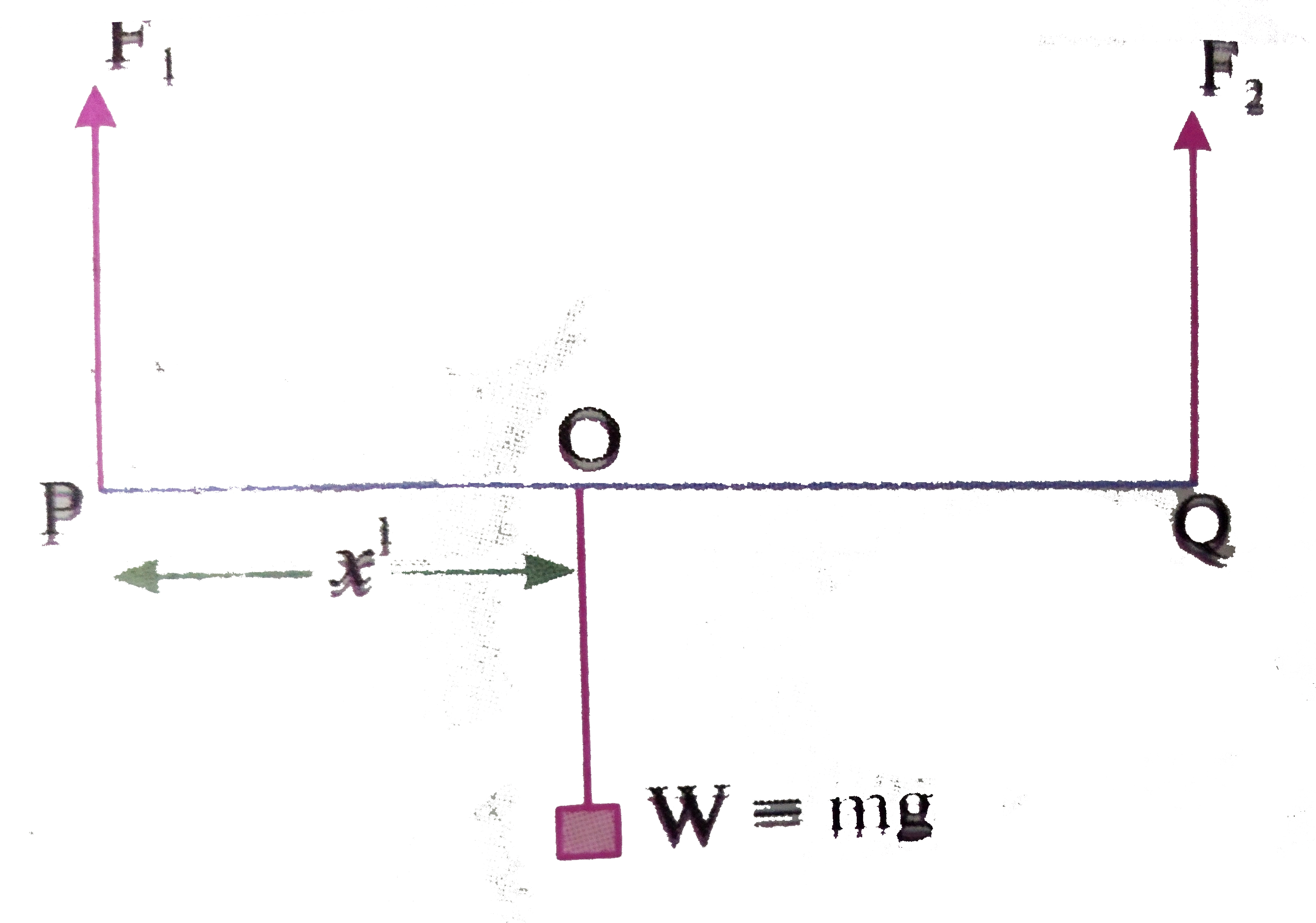Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
NARAYNA-MECHANICAL PROPERTIES OF SOLIDS-LEVEL-II (H.W)
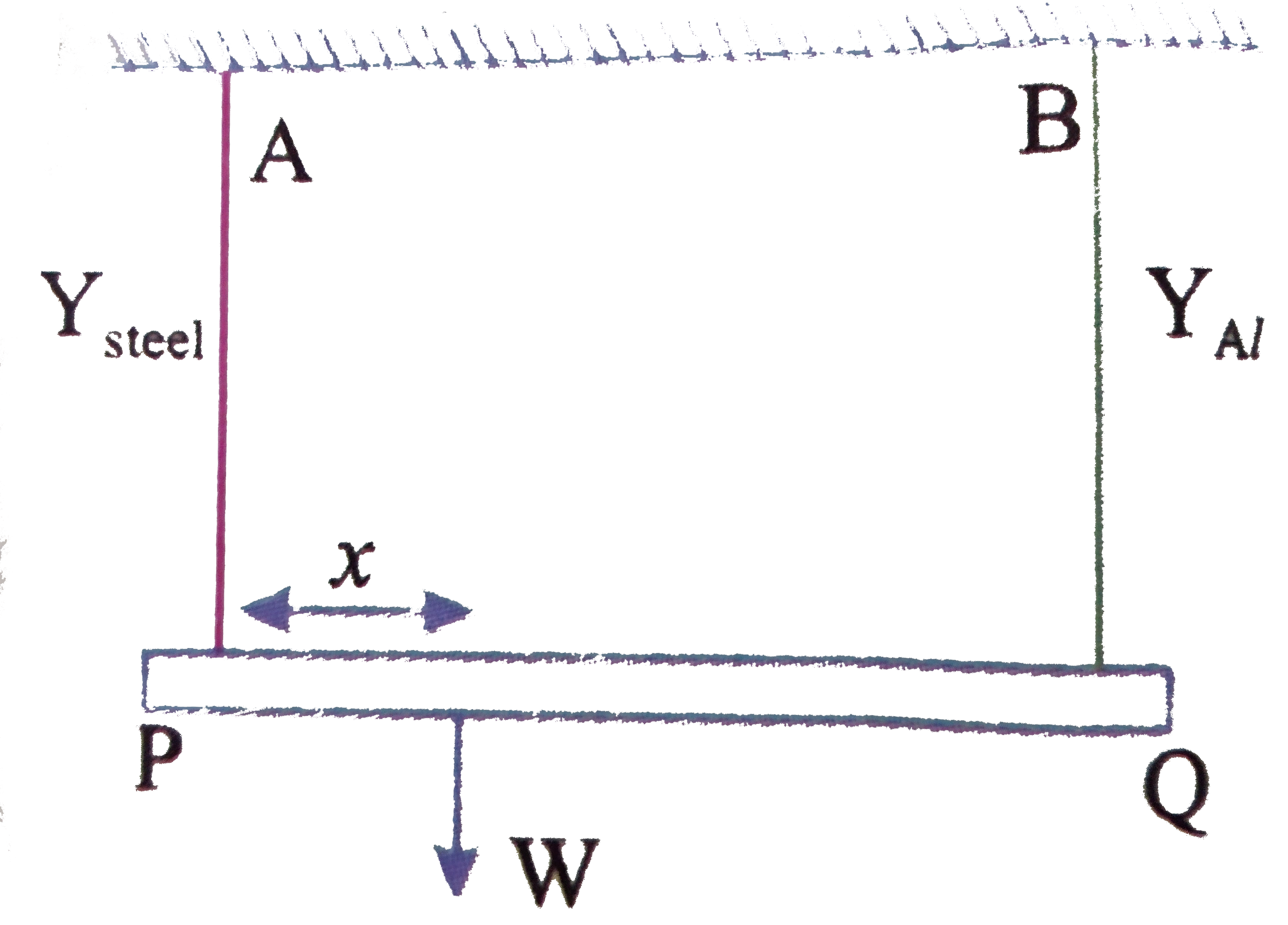
- A rod PQ of length 1.05m having negligible mass is supported at its e...
Text Solution
|
- One end of uniform wire of length L and of weight W is attached rigidl...
Text Solution
|
- A 20kg load is suspended from the lower end of a wire 10cm long and 1...
Text Solution
|
- A Steel wire is 1m long and 1mm^(2) in area of cross-section. If it ta...
Text Solution
|
- A wire of length 1 m and radius 1mm is subjected to a load. The extens...
Text Solution
|
- A stress of 10^(6) N//m^(2) is required for breaking a material. If t...
Text Solution
|
- A wire can be broken by 400kg.wt. The load required to break the wi...
Text Solution
|
- A copper wire and an aluminium wire has lenghts in the ratio 3:2 di...
Text Solution
|
- There are two wires of same material. Their radii and lengths are bot...
Text Solution
|
- Two rods of different materials having coefficient of thermal expansio...
Text Solution
|
- A piece of copper wire has twice the radius of a piece of steel wire....
Text Solution
|
- A tangential force of 2100N is applied on a surface area 3xx10^(-6) m^...
Text Solution
|
- A uniform pressure P is exerted by an external agent on all sides of a...
Text Solution
|
- A solid sphere of radius R made of a material of bulk modulus K is sur...
Text Solution
|
- Find the change in density of water in occean at depth of 700m below...
Text Solution
|
- When a rubber ball of volume v, bulk modulus K is at a depth h in wat...
Text Solution
|
- A fractinal change in volume of oil is i percent . When a pressure f 2...
Text Solution
|
- When a wire of length 10m is subjected to a force of 100N along its le...
Text Solution
|
- The posisson's ratio of material is 0.4. If a force is applied to a wi...
Text Solution
|
- A wire having a length L and cross- sectional area A is suspended at o...
Text Solution
|
- Two wires of same material and same diameter have lenghts in the rati...
Text Solution
|