A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
MECHANICAL PROPERTIES OF SOLIDS
NARAYNA|Exercise MULTIPLE ANSWER TYPE|10 VideosMECHANICAL PROPERTIES OF SOLIDS
NARAYNA|Exercise COMPREHENSION TYPE|11 VideosMECHANICAL PROPERTIES OF SOLIDS
NARAYNA|Exercise NCERT BASED QUESTIONS|21 VideosMECHANICAL PROPERTIES OF FLUIDS
NARAYNA|Exercise EXERCISE - III|30 VideosMOTION IN A PLANE
NARAYNA|Exercise Level-II(H.W)|31 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
NARAYNA-MECHANICAL PROPERTIES OF SOLIDS-SINGLE ANSWER TYPE
- A steel rod of cross-sectional area Im^(2) is acted upon by forces as...
Text Solution
|
- A 30.0 kg hammer, moving with speed a 20.0ms^(-1) strikes a steel spik...
Text Solution
|
- When a weight W is hung from one end of a wire of length L (other end ...
Text Solution
|
- A uniform heavy rod of weight W, cross sectional area a and length L i...
Text Solution
|
- A uniform elastic plank moves due to a constant force F(0) applied at...
Text Solution
|
- A pendulum bob of mass m hangs form a massless elastic string. The pot...
Text Solution
|
- The elastic limit of an elevator cable is 2xx10^(9) N//m^(2). The maxi...
Text Solution
|
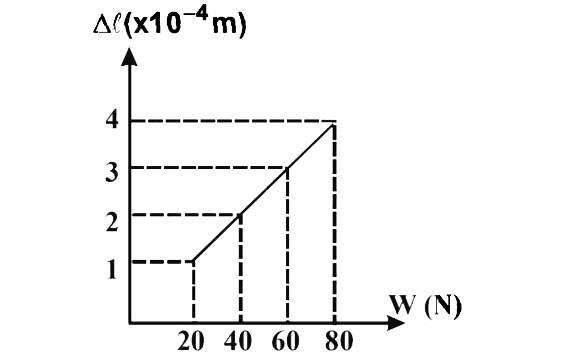
- The adjacent graph shows the estension (Deltal) of a wire of length 1m...
Text Solution
|
- A horizongal rod fixed at one of its ends has lengtht l, rigidly modul...
Text Solution
|
- The following four wires are made of the same material. Which of these...
Text Solution
|
- When temperature of a gas is 20^@C and pressure is changed from p(1)= ...
Text Solution
|
- Two rods of equal cross-sections, one of copper and the other of stee...
Text Solution
|
- A highly rigid cubical block A of small mass M and side L is fixed rig...
Text Solution
|
- In determine of youggn modulus of ealsticity of wire, a force is appli...
Text Solution
|
- Figure shows the graph of elastic potential energy (U) stored versus...
Text Solution
|