A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
TRANSMISSION OF HEAT
NARAYNA|Exercise NCERT BASED QUESTIONS|5 VideosTRANSMISSION OF HEAT
NARAYNA|Exercise SINGLE ANSWER QUESTIONS Passage|1 VideosTRANSMISSION OF HEAT
NARAYNA|Exercise LEVEL-III (C.W)|1 VideosTHERMODYNAMICS
NARAYNA|Exercise Exercise|187 VideosUNITS AND MEASUREMENTS
NARAYNA|Exercise STATEMENT TYPE QUESTION|23 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
NARAYNA-TRANSMISSION OF HEAT-LEVEL- (C.W)
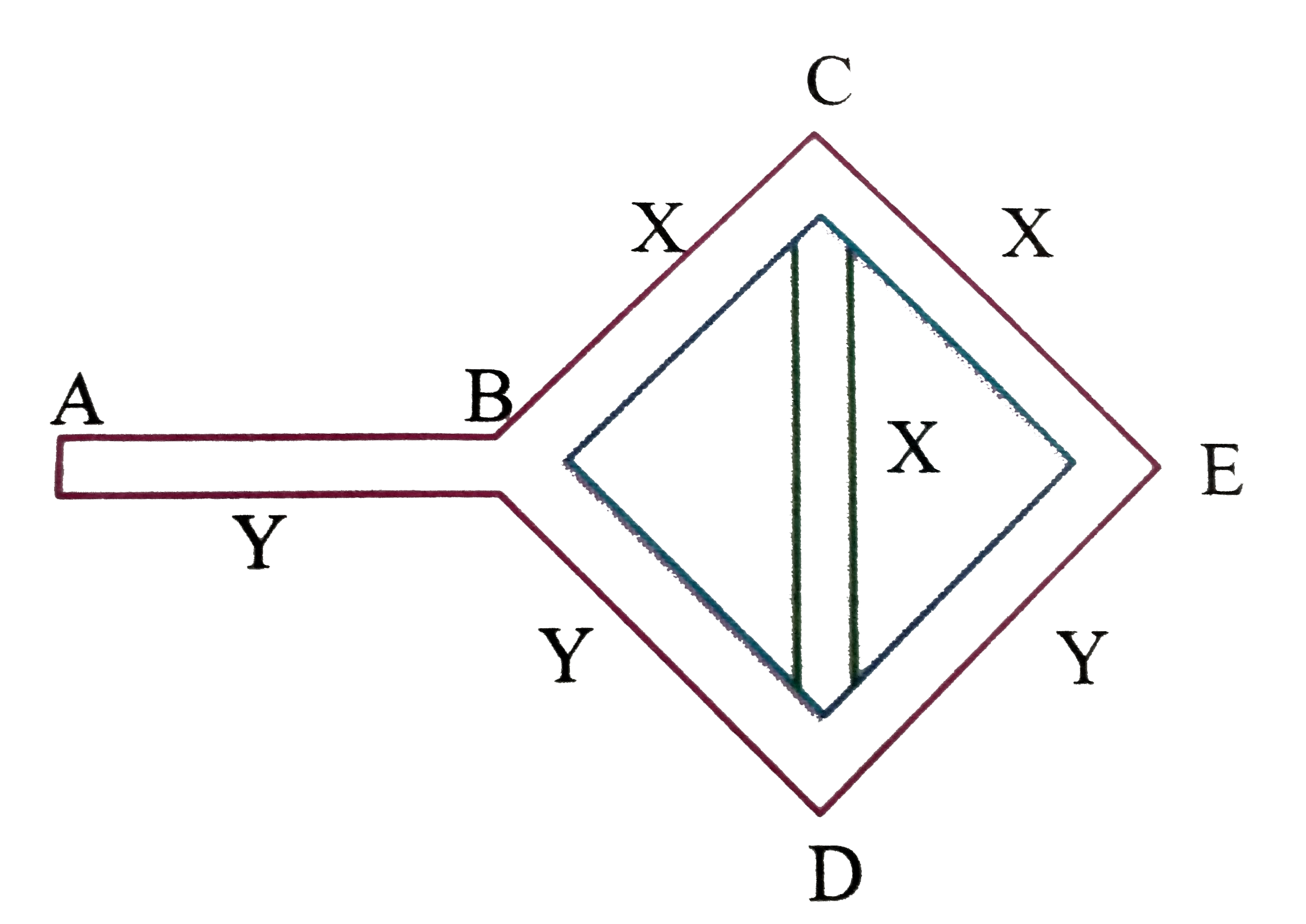
- Three rods of material 'x' and three rods of materialy are connected a...
Text Solution
|
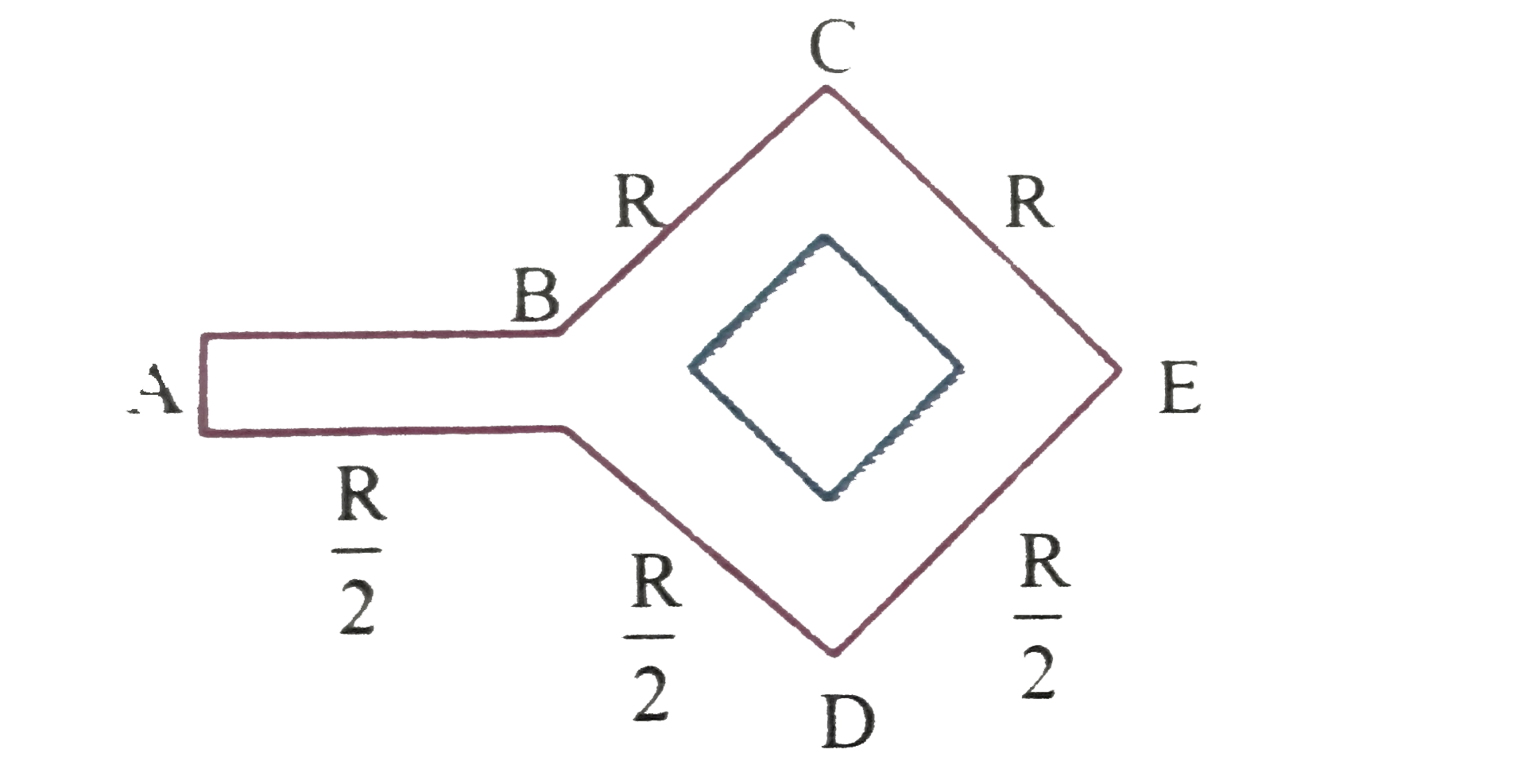
- A cylinder of radius R made of a material of thermal conductivity K(1)...
Text Solution
|
- Water is being boiled in a flat bottomed kettle placed on a stove The ...
Text Solution
|
- A point source of heat of power P is placed at the centre of a spheric...
Text Solution
|
- The temperature of the two outer surfaces of a composite slab, consist...
Text Solution
|
- A and B are two points on uniform metal ring whose centre is O The ang...
Text Solution
|
- Two ends of a conducting rod of varying cross-section are maintained a...
Text Solution
|
- Three rods of same dimensions are arranged as shown in Fig. They have ...
Text Solution
|
- A boiler is made of a copper plate 2.4mm thick with an inside coating ...
Text Solution
|
- Ice starts forming in lake with water at 0^(@)C and when the atmospher...
Text Solution
|
- A long metallic bar is carrying heat from one of its ends to the other...
Text Solution
|
- The temperature drop through each layer of a two layer furnace wall is...
Text Solution
|
- The wall with a cavity consists of two layers of brick separated by a ...
Text Solution
|
- A ring consisting of two parts ADB and ACB of same conductivity k carr...
Text Solution
|
- Two metallic spheres S1 and S2 are made of the same material and have ...
Text Solution
|
- The temperature of an spherical isolated black body falls from T(1) an...
Text Solution
|
- A star behaves like a perfectly black body emitting radiant energy The...
Text Solution
|
- A sphere of density 'd' specific heat capacity 'c' and radius 'r' is h...
Text Solution
|
- Assuming the Sun to be a spherical body of radius R at a temperature o...
Text Solution
|
- The spectral emissive power E(lambda) for a body at temperature T(1) i...
Text Solution
|
 .
. .
.