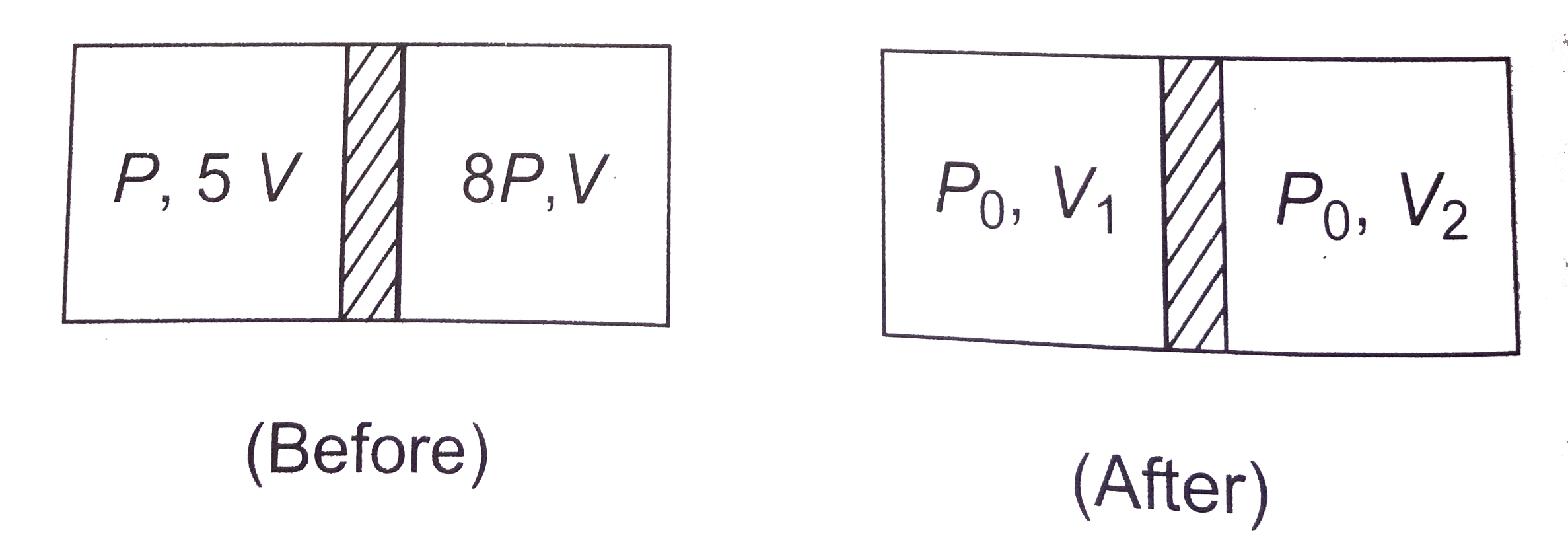Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
CP SINGH-LAWS OF THERMODYNAMICS-EXERCISE
- A piston divides a closed gas cylinder into two parts. Initially the p...
Text Solution
|
- The first law of thermodynamics incorporates are concept (i) conserv...
Text Solution
|
- The work done in the process AB is
Text Solution
|
- (i) DeltaW(AB)=5P0V0 (ii) DeltaW(BC)=0 (iii) DeltaW(CA)=-2P0V0 (...
Text Solution
|
- Consider the process on a system shown in figure. During the process, ...
Text Solution
|
- Consider two processes on a system as shown in figure. The volumes in...
Text Solution
|
- A system can be taken from the initial state p(1),V(1) to the final st...
Text Solution
|
- In the figure given two processes A and B are shown by which a thermod...
Text Solution
|
- Refer to figure in previous question, DeltaU(1) and DeltaU(2) be the c...
Text Solution
|
- Refer to figure DeltaU(1) and DeltaU(2) be the changes in internal ene...
Text Solution
|
- In a given process on an ideal gas, dW=0 and dQlt0. Then for the gas
Text Solution
|
- Consider the following two statements. (A) If heat is added to a syst...
Text Solution
|
- In a process on a system, the initial pressure and volume are equal to...
Text Solution
|
- The pressure p and volume V of an ideal gas both increase in a process...
Text Solution
|
- The state of a thermodynamic system is represented by
Text Solution
|
- Which of the following is not a thermodynamical function
Text Solution
|
- If Q, E and W denote respectively the heat added, change in internal e...
Text Solution
|
- For free expansion of the gas, which of the following is true?
Text Solution
|
- A system is given 300 calories of heat and it does 600 joules of work....
Text Solution
|
- In thermodynamic process, pressure of a fixed mass of a gas is changes...
Text Solution
|
- A perfect gas goes from a state A to another state B by absorbing 8 × ...
Text Solution
|