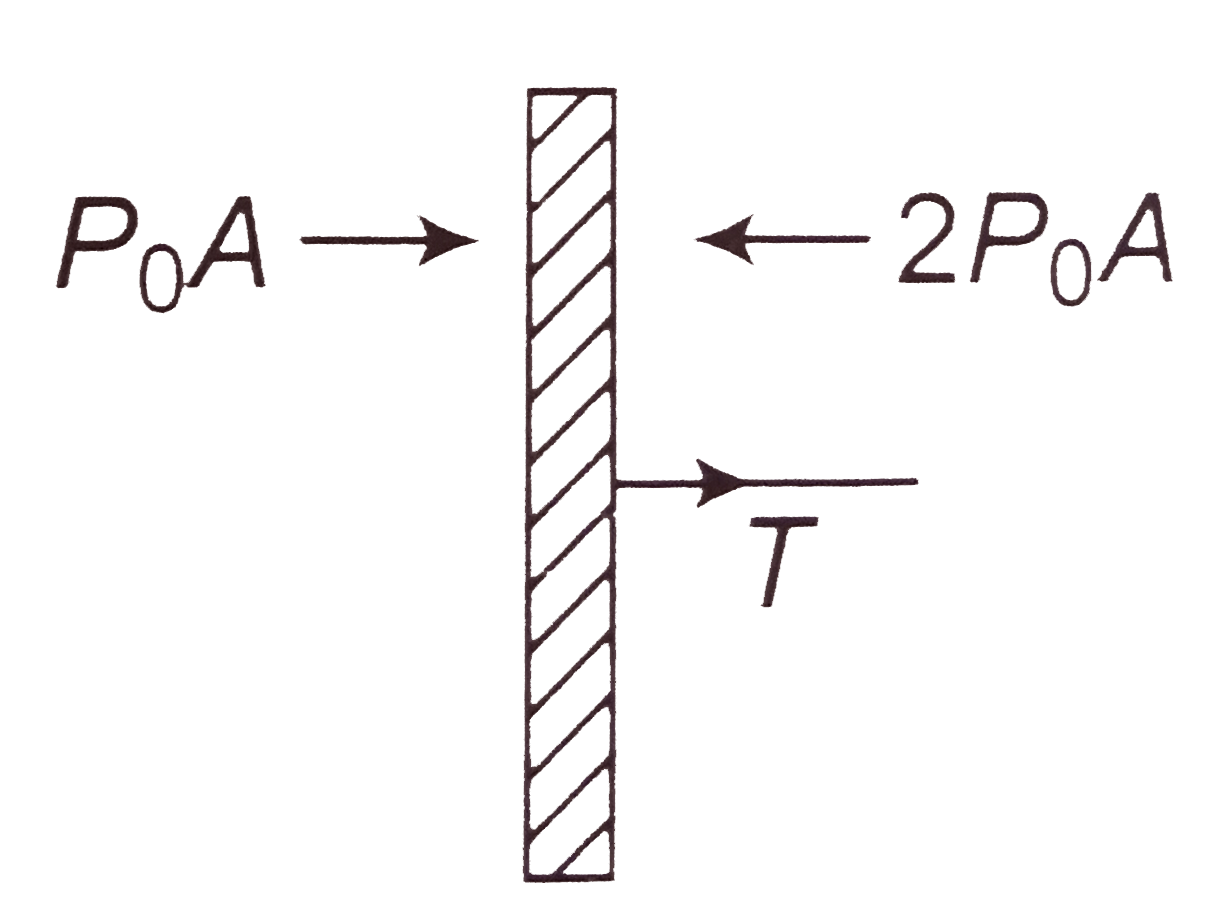A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
CP SINGH-LAWS OF THERMODYNAMICS-EXERCISE
- A cyclic process is shown on the P-T diagram. Which of the curve shown...
Text Solution
|
- A gas is contained in a metallic cylinder fitted with a piston.The pis...
Text Solution
|
- A cylindrical tube of uniform cross-sectional area A is fitted with tw...
Text Solution
|
- The latent heat of vaporisation of water is 2240 J/gm. If the work don...
Text Solution
|
- When 1g of water at 0^@C and 1xx10^5(N)/(m^2) pressure is converted in...
Text Solution
|
- A vessel containing 5 litres of a gas at 0.8 m pressure is connected t...
Text Solution
|
- A thermally insulated container is divided into two parts by a screen....
Text Solution
|
- Each molecule of a gas has f degrees of freedom. The ratio gamma for t...
Text Solution
|
- The molar heat capacity of a gas at constant volumes is CV. If n moles...
Text Solution
|
- Let (Cv) and (Cp) denote the molar heat capacities of an ideal gas at ...
Text Solution
|
- The molar heat capacity for an ideal gas cannot
Text Solution
|
- If for a gas, (R)/(CV)=0.67, the gas is
Text Solution
|
- For hydrogen gas Cp-Cv=a and for oxygen gas Cp-Cv=b,Cp and Cv being mo...
Text Solution
|
- If for hydrogen sp-sv=a and oxygen sp-sv=b, where sp and sv refer to s...
Text Solution
|
- The ratio (Cp)/(Cv)=gamma for a gas. Its molecular weight is M. Its sp...
Text Solution
|
- Cp is always greater than Cv for a gas, which of the following stateme...
Text Solution
|
- If one mole of a monatomic gas (gamma=5/3) is mixed with one mole of a...
Text Solution
|
- A mixture of n1 moles of monoatomic gas and n2 moles of diatomic gas h...
Text Solution
|
- When an ideal diatomic gas is heated at constant pressure, the fractio...
Text Solution
|
- A gas, for which gamma is (4)/(3) is heated at constant pressure. The ...
Text Solution
|