A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
CP SINGH-NEET PREVIOUS YEAR-Solved Questions
- At what height from the surface of earth the gravitation potential and...
Text Solution
|
- The ratio of escape velocity at earth (v(e)) to the escape velocity at...
Text Solution
|
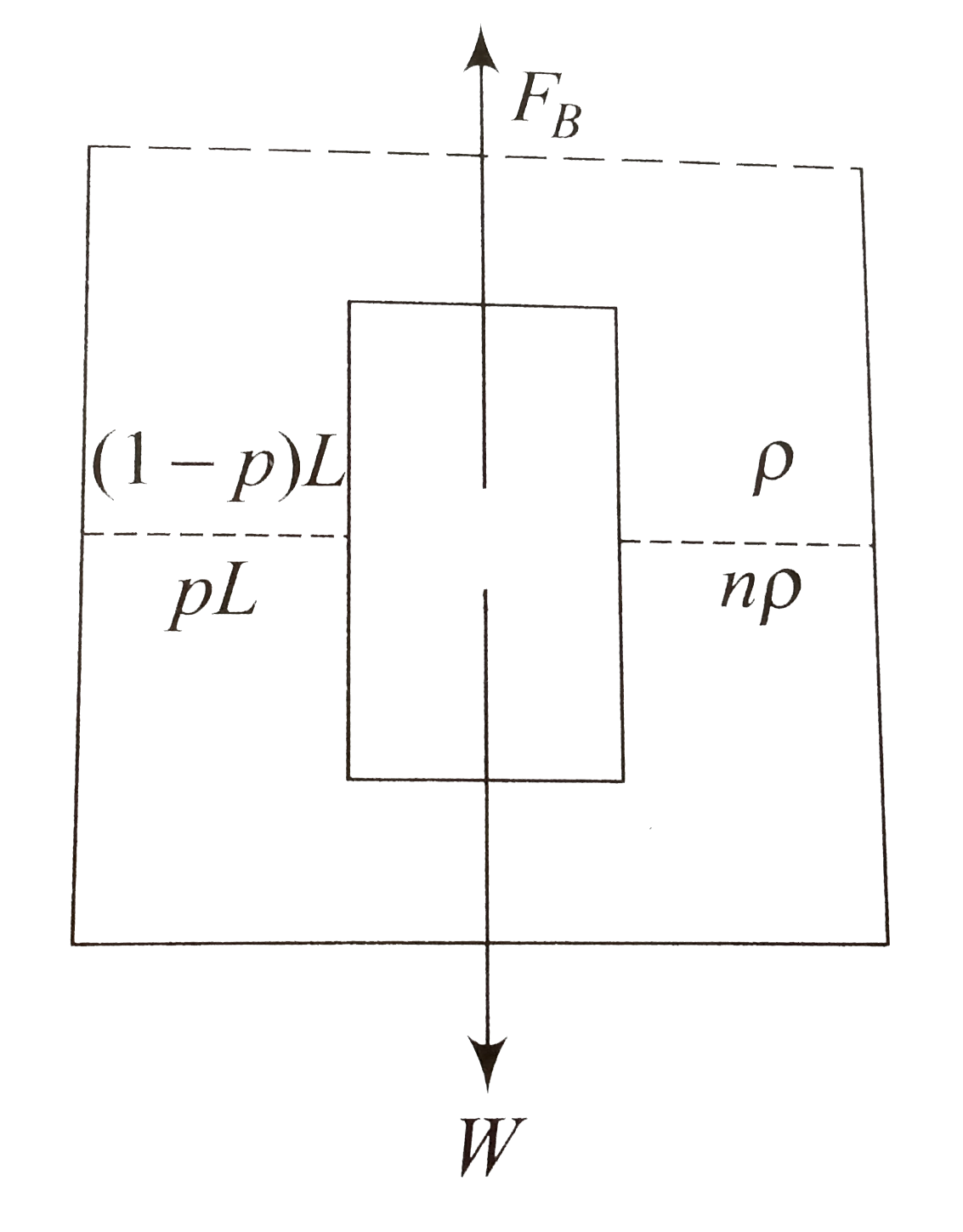
- Two non-mixing liquids of densities rho and (n gt1) are put in a cont...
Text Solution
|
- A uniform rope of legnth L and mass m1 hangs vertically from a rigid s...
Text Solution
|
- An air column, closed at one end and open at the other resonates with ...
Text Solution
|
- A siren emitting a sound of frequency 800 Hz moves away from an observ...
Text Solution
|
- Coefficient of linear expansion of brass and steel rods are alpha(1) a...
Text Solution
|
- The molecules of a given mass of a gas have rms velocity of 200 m//s a...
Text Solution
|
- A piece of ice falls from a height h so that it melts completely. Only...
Text Solution
|
- A gas is compressed isothermally to half its initial volume. The same ...
Text Solution
|
- A refrigerator works between 4^(@)C and 30^(@)C. It is required to rem...
Text Solution
|
- A black body is at a temperature of 5760 K. The energy of radiation em...
Text Solution
|
- A physical energy of the dimension of length that can be formula cut o...
Text Solution
|
- Preeti reached the metro station and found that the escalator was not ...
Text Solution
|
- The x and y coordinates of the particle at any time are x=5t-2t^(2) an...
Text Solution
|
- Two block A and B of masses 3m and m respectively are connected by a m...
Text Solution
|
- A spring of force constant k is cut into lengths of ratio 1 : 2 : 3. T...
Text Solution
|
- Consider a drop of rain water having mass 1 g falling from a height of...
Text Solution
|
- One end of string of length l is connected to a particle on mass m and...
Text Solution
|
- Two astronauts are floating in gravitational free space after having l...
Text Solution
|