Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
CP SINGH-ALTERNATING CURRENT-EXERCISES
- In a series LCR circuit with an AC source, R = 300 Omega, C = 20 muF, ...
Text Solution
|
- The peak voltage in a 220 V AC source is
Text Solution
|
- An alternating emf given by V = V(0) sin omegat has peak value 10 volt...
Text Solution
|
- The average emf during the positive half cycle of an ac supply of peak...
Text Solution
|
- The rms value of an ac of 50Hz is 10A. The time taken by an alternatin...
Text Solution
|
- An ac ammeter is used to measure currnet in a circuit. When a given di...
Text Solution
|
- The rms value of the emf given by E = 8 sin omegat + 6 sin 2omegat .
Text Solution
|
- An AC is given by the equation i=i(1)cos omegat+i(2)sin omegat. The r....
Text Solution
|
- A direct current of 5 amp is superimposed on an alternating current I=...
Text Solution
|
- An AC source is rated 220 V, 50 Hz. The average voltage is calculated ...
Text Solution
|
- The magnetic field energy in an inductor changes from maximum value to...
Text Solution
|
- An AC source producing emf epsilon = epsilon0 [cos(100 pi s^(-1)) t ...
Text Solution
|
- What reading would you expact of a square-wave current, suitching rapo...
Text Solution
|
- The heat produced in a given resistor in a given time by the sinusoida...
Text Solution
|
- An alternating current having peak value 14 A is used to heat a metal ...
Text Solution
|
- An alternating voltage V =200sqrt2 sin 100 t where V is in volt and t ...
Text Solution
|
- What is the r.m.s. value of an alternating current which when passed t...
Text Solution
|
- A constant current of 2.8 A exists in a resistor. The rms current is
Text Solution
|
- Choose the currect option .
Text Solution
|
- The rms value of potential difference V shown in the figure is
Text Solution
|
- Which one of the follwing represents the variation of capacitive react...
Text Solution
|
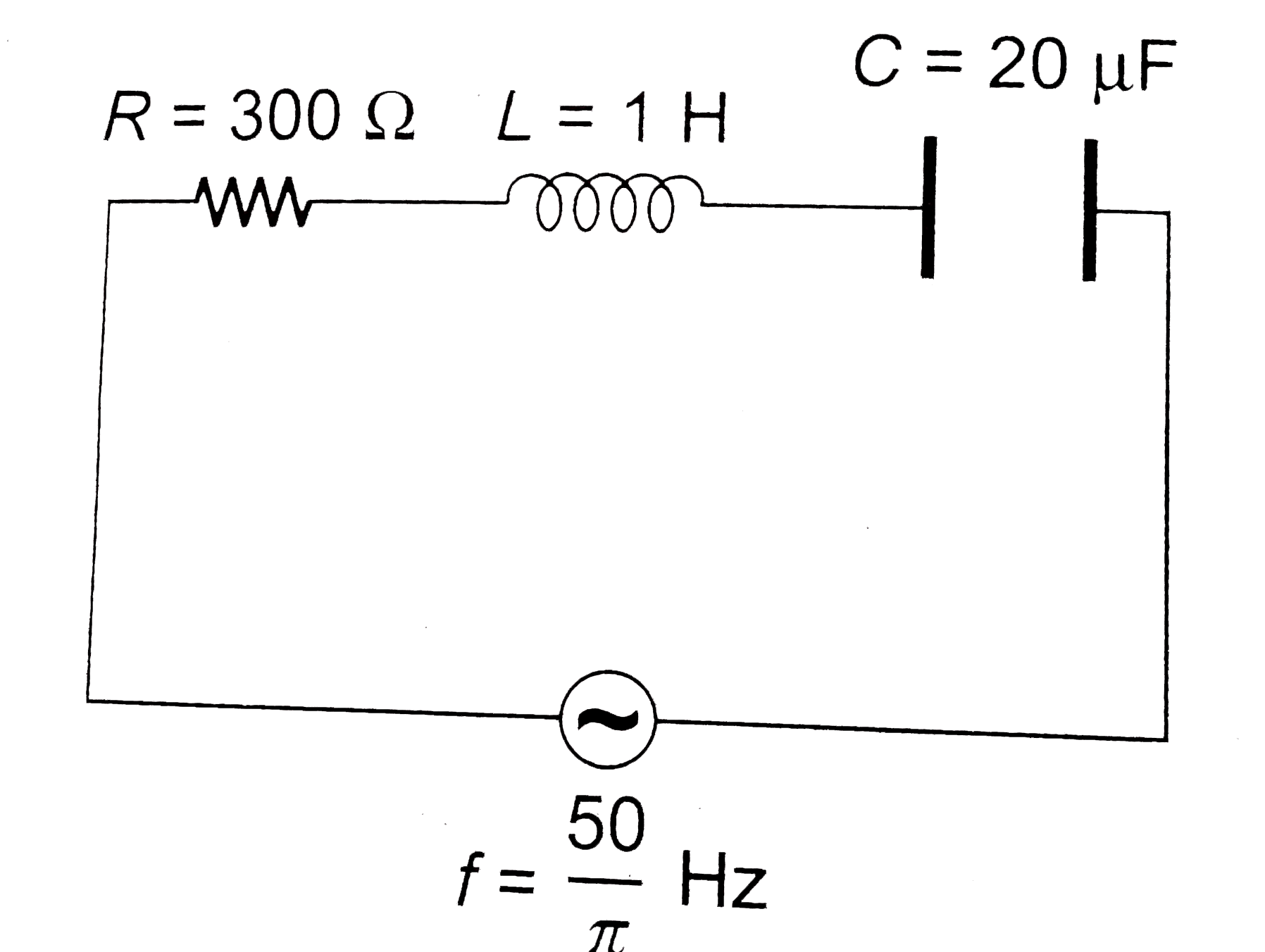 .
.