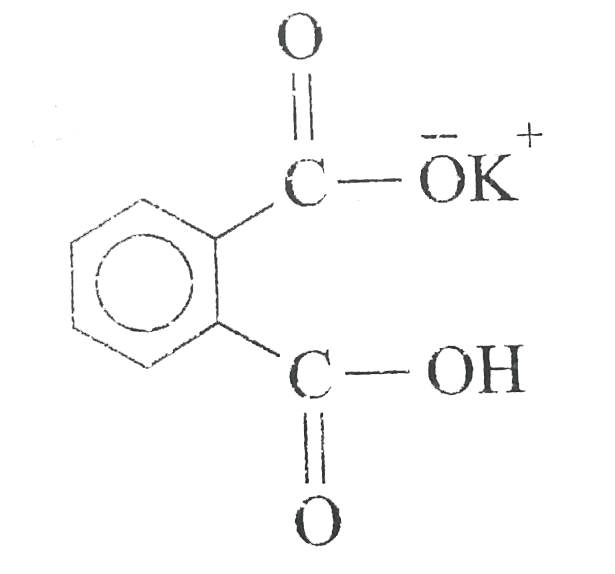
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
R SHARMA-SOLUTIONS-QUESTION BANK (Building the knowledge)
- Molarity of K^(+) ions in 0.33 M potassium sulphate aqueous solution i...
Text Solution
|
- In the laboratory we often measure the volume of one solution that is ...
Text Solution
|
- Solutions of accurately known concentrations are called
Text Solution
|
- A solution is 0.150 mole fraction glucose (C(6)H(12)O(6)) and 0.850 mo...
Text Solution
|
- When an aqueous solution containing a nonvolatile solute freezes,
Text Solution
|
- The main ingredient of automobile antifreeze mixtures is
Text Solution
|
- The vapor pressure of acetone at 20^(@)C is 185 torr. When 1.2 g of a ...
Text Solution
|
- Consider separate solutions of 0.500 M C(2)H(5)OH(aq),0.100 M Mg(3)(PO...
Text Solution
|
- A compound H(2)X with molar mass of 80 g is dissolved in a solvent hav...
Text Solution
|
- The molarity of a solution obtained by mixing 750 mL of 0.5 (M) HCl wi...
Text Solution
|
- The degree of dissociation (alpha) of a weak electrolyte, A(x)B(y) is ...
Text Solution
|
- Ethylene glycol is used as an antifreeze in a cold cliamate Mass of et...
Text Solution
|
- The vapour pressure of water at 20^(@) is 17.5 mmHg. If 18 g of glucos...
Text Solution
|
- At 80^@C, the vapour pressure of pure liquid A is 520 mm Hg and that o...
Text Solution
|
- 25 mL of a solution of barium hydroxide on titration with 0.1 "molar" ...
Text Solution
|
- To neutralize completely 20 mL of 0.1M aqueous solution of phosphorus ...
Text Solution
|
- How many grams of a dibasic acid (mol. Mass 200) should be present in ...
Text Solution
|
- The vapour pressure of benzene at a certain temperature is 640 mm Hg. ...
Text Solution
|
- If solution containing 0.15 g of solute dissolved in 15 g of solvent b...
Text Solution
|
- The vapour pressure of a solvent decreased by 10 mm of Hg when a non-v...
Text Solution
|