Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
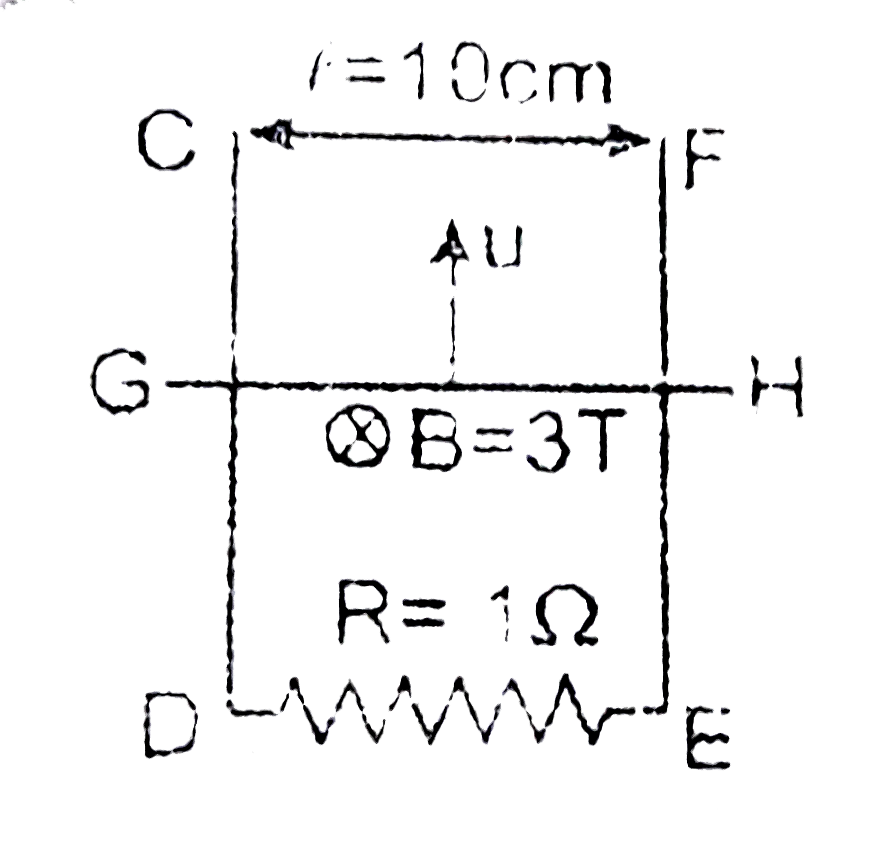
- In the figure, CDEF is a fixed conducting smooth frame in vertical pla...
Text Solution
|
- The collar A is free to slide along the smooth shaft B mounted in the ...
Text Solution
|
- A conducting frame abcd is kept in a vertical plane. A conducting rod ...
Text Solution
|
- CDEF is a fixed conducting smooth frame in vertical plane. A conductin...
Text Solution
|
- A conducting frame is placed in a horizontal plane as shown in the fig...
Text Solution
|
- A rod of mass m and resistance r is placed on fixed, resistanceless, s...
Text Solution
|
- In the figure, CDEF is a fixed conducting smooth frame in vertical pla...
Text Solution
|
- In the figure shown 'PQRS' is a fixed resistanceless conducting frame ...
Text Solution
|
- The velocity of end 'A' of rigid rod placed between two smooth vertica...
Text Solution
|