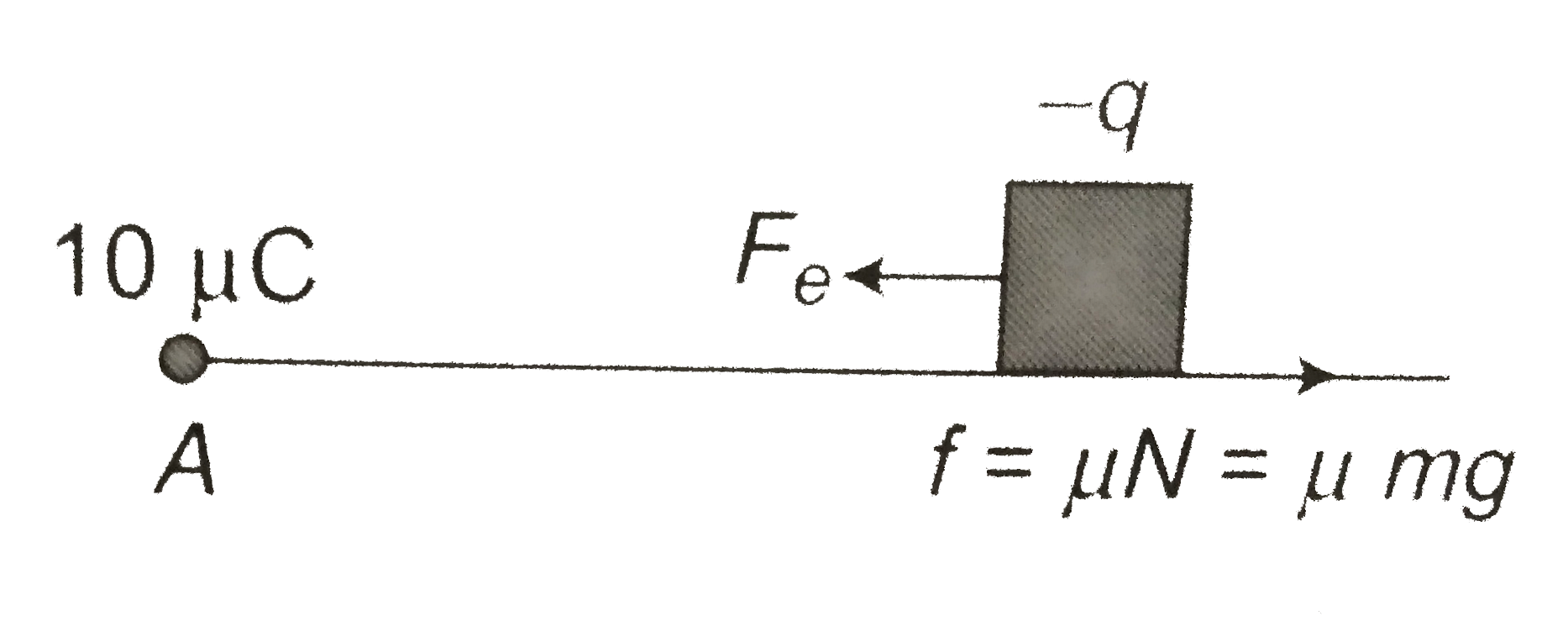Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
CP SINGH-ELECTROSTATICS-Exercises
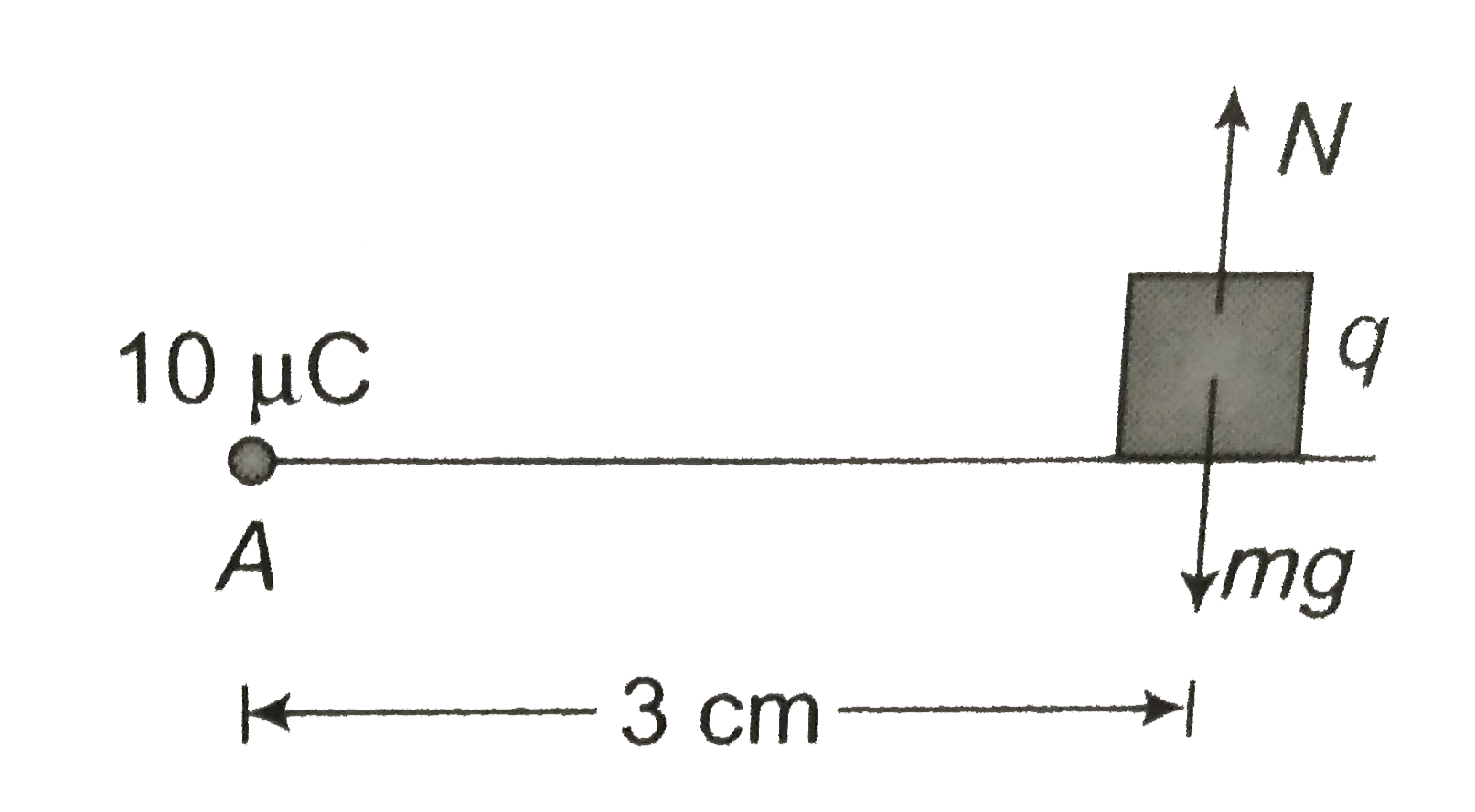
- A particle A having a charge 10 mu C is held fixed on a horizontal sur...
Text Solution
|
- Which of the following is correct regarding electric charge ? (i) If...
Text Solution
|
- When 10^(14) electrons are removed from a neutral metal sphere , the c...
Text Solution
|
- The ratio of the electric force between two electrons to the gravitati...
Text Solution
|
- Find the ratio of the magnitude of the electric force to the grativati...
Text Solution
|
- Two insultating small spheres are rubbed against each other and placed...
Text Solution
|
- Two particles having charge Q(1) and Q(2) , when kept at a certain dis...
Text Solution
|
- Two point charge +2 C and +6 C repel each other with a force of 12 N ....
Text Solution
|
- Two identical metals balls with charges +2Q and -Q are separated by so...
Text Solution
|
- Two positive point charges are 3 m apart their combined charge is 20 m...
Text Solution
|
- Charge Q is divided into two parts which are then kept some distance a...
Text Solution
|
- Force of attraction between two point charges Q and -Q separated by d...
Text Solution
|
- Two charges are at a distance d apart. If a copper plate (conducting m...
Text Solution
|
- Five balls numbered 1,2,3,4,and 5 are suspended using separated thread...
Text Solution
|
- Equal charges q are placed at the four corners A,B,C,Dof a square of l...
Text Solution
|
- Two spherical conductors B and C having equal radii and cayying equal ...
Text Solution
|
- Two positive ions , each carrying a charge q , are separated by a dist...
Text Solution
|
- Two point charges +4q and +q are placed at a distance L apart. A thir...
Text Solution
|
- Two point charges q(1) = +2 C and q(2) = - 1C are separated by a dista...
Text Solution
|
- A charge q is placed at the centre of the line joining two equal charg...
Text Solution
|
- In the previous question , if e = electronic charge , the minimum mag...
Text Solution
|