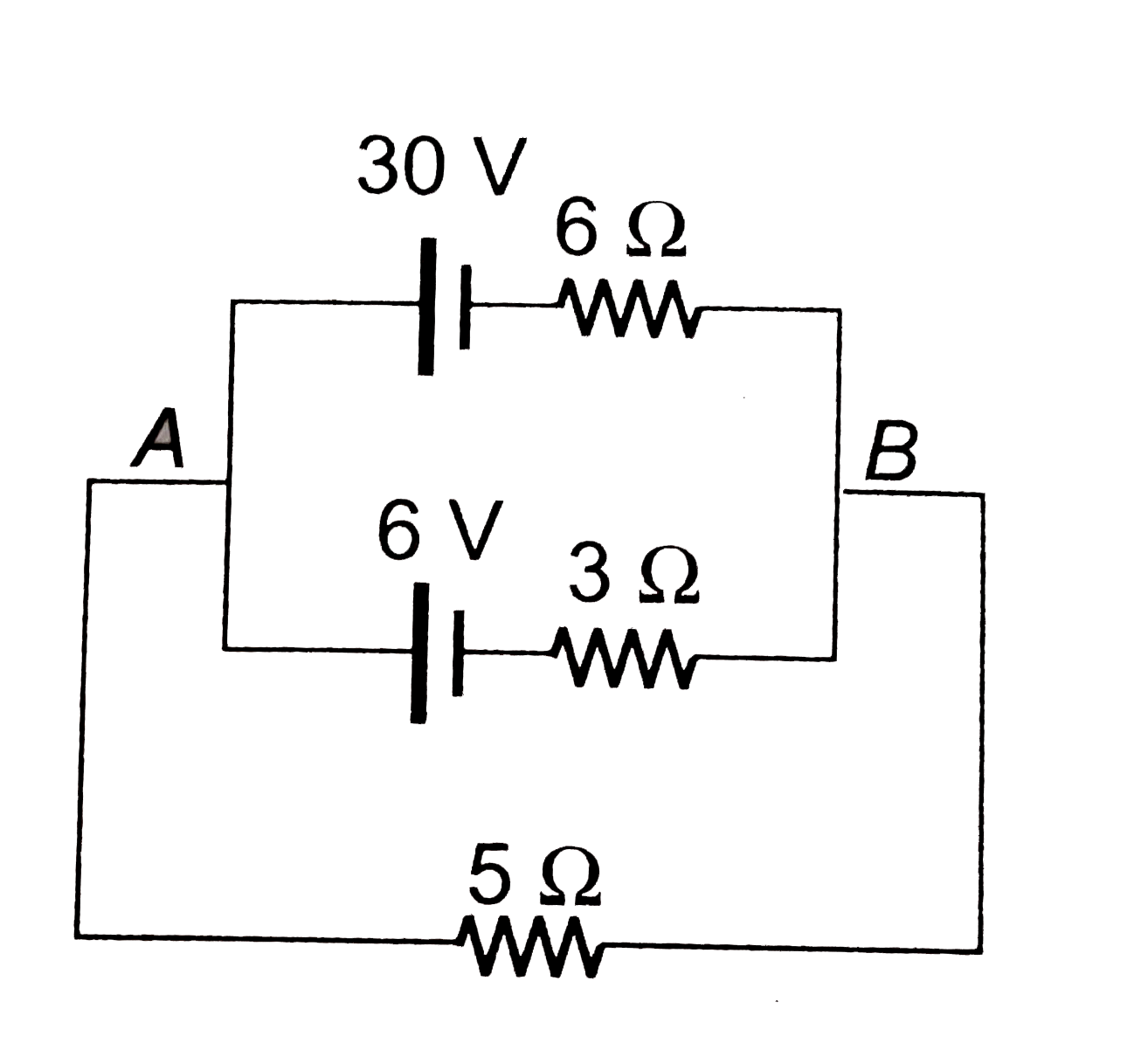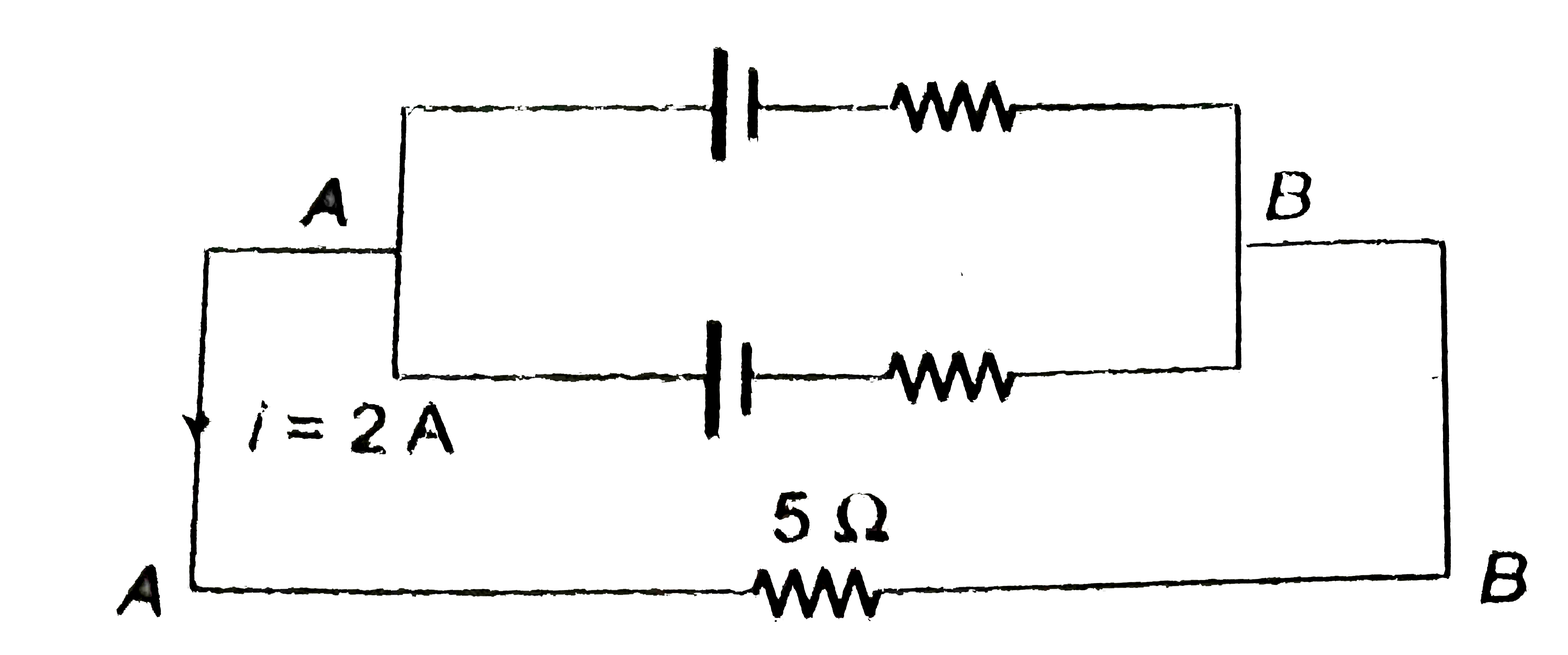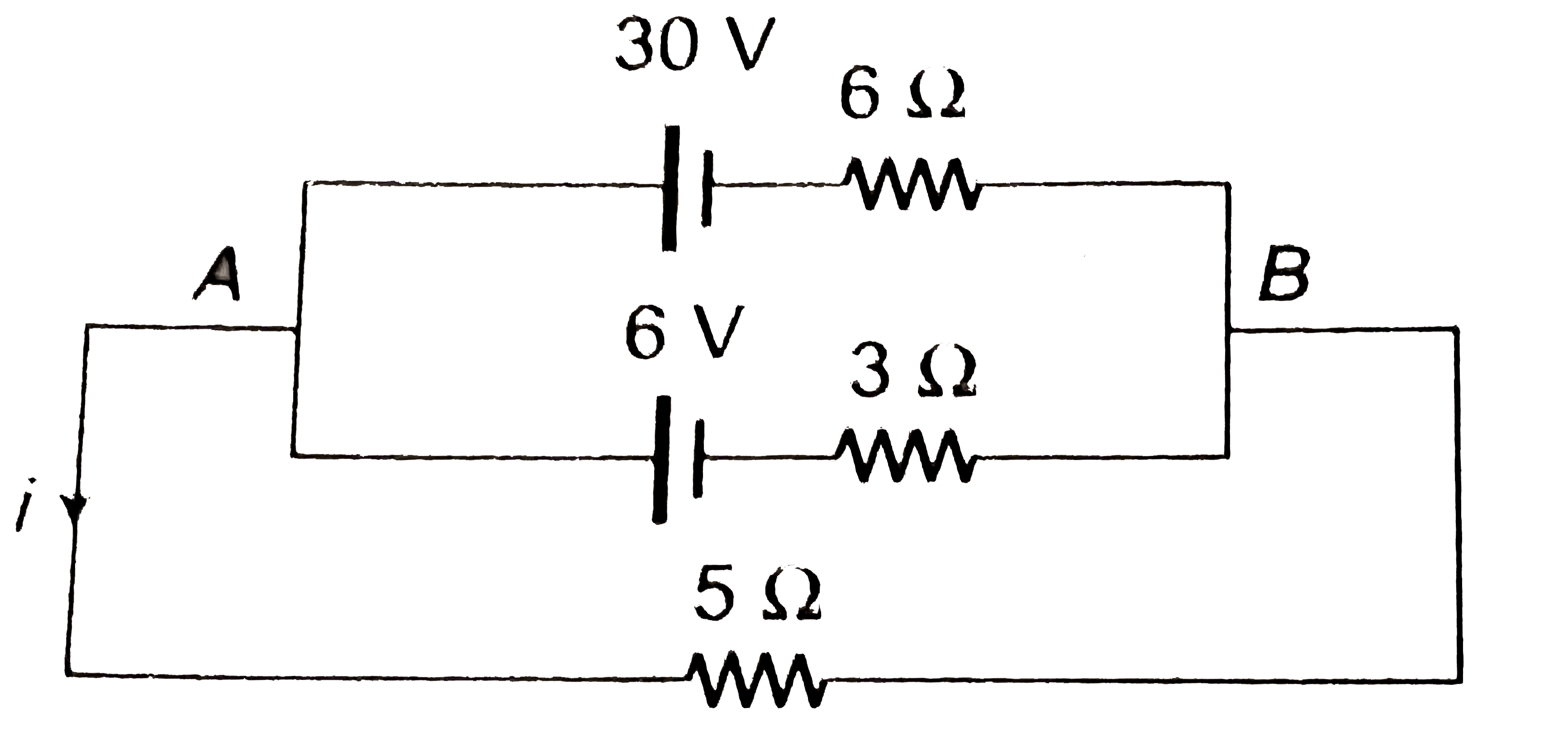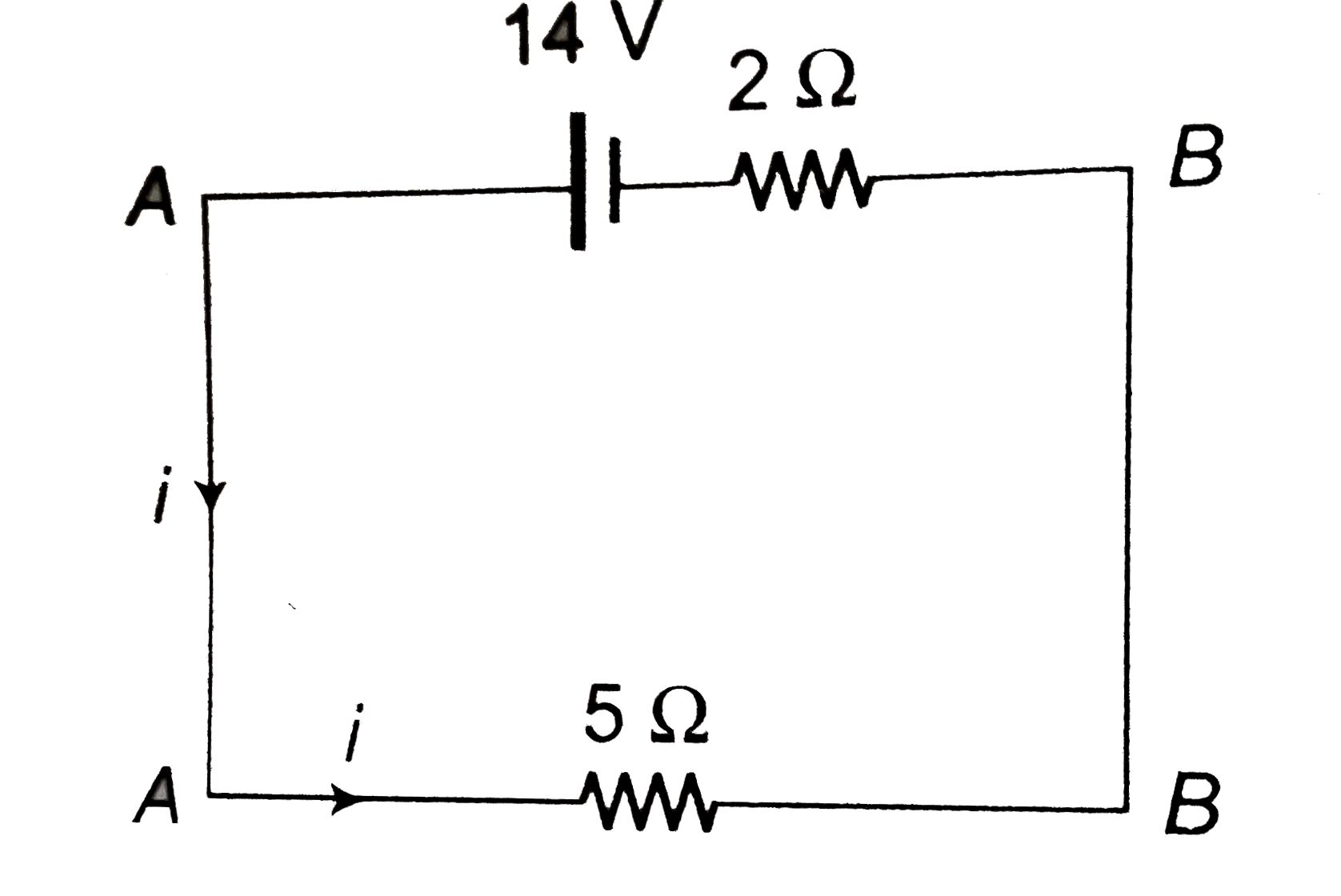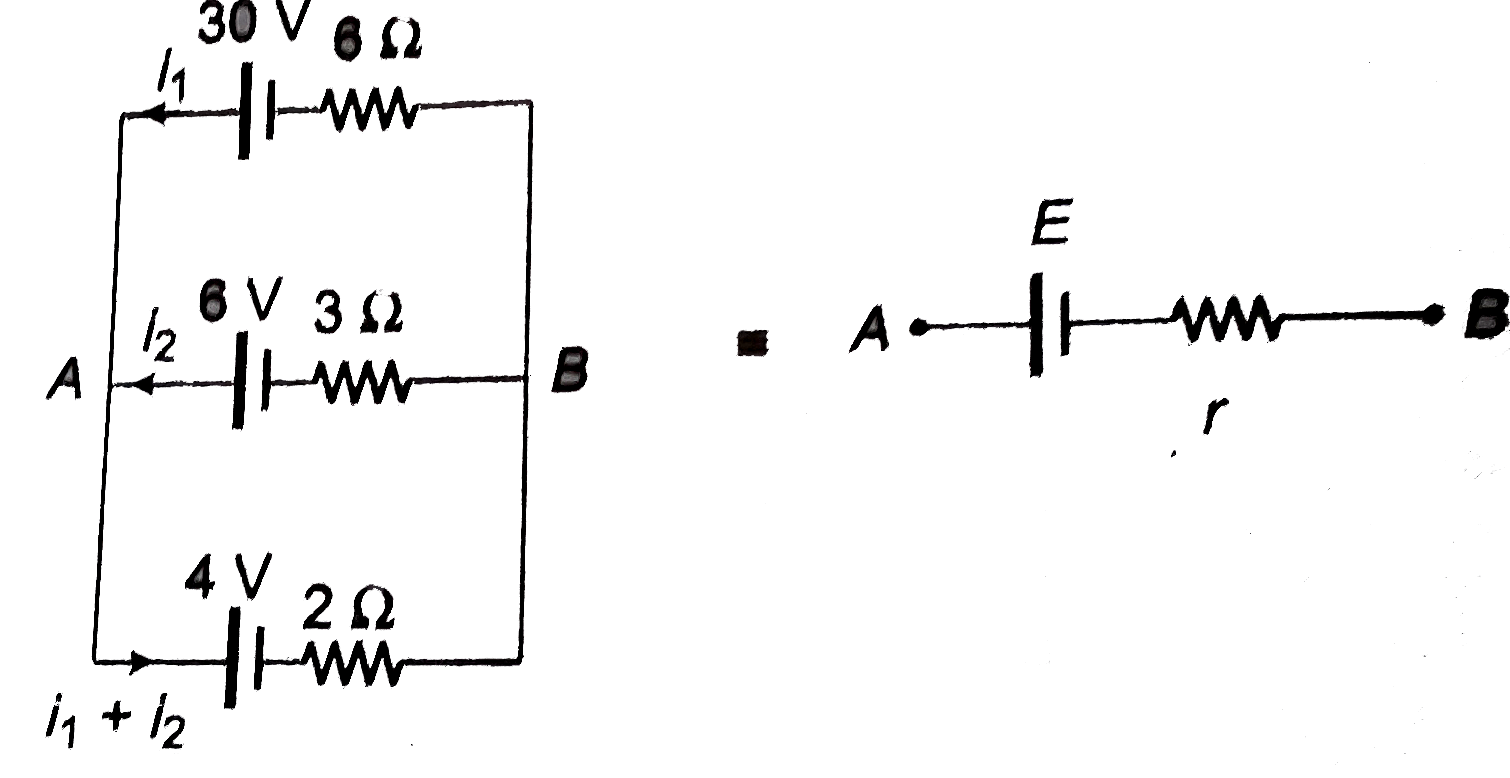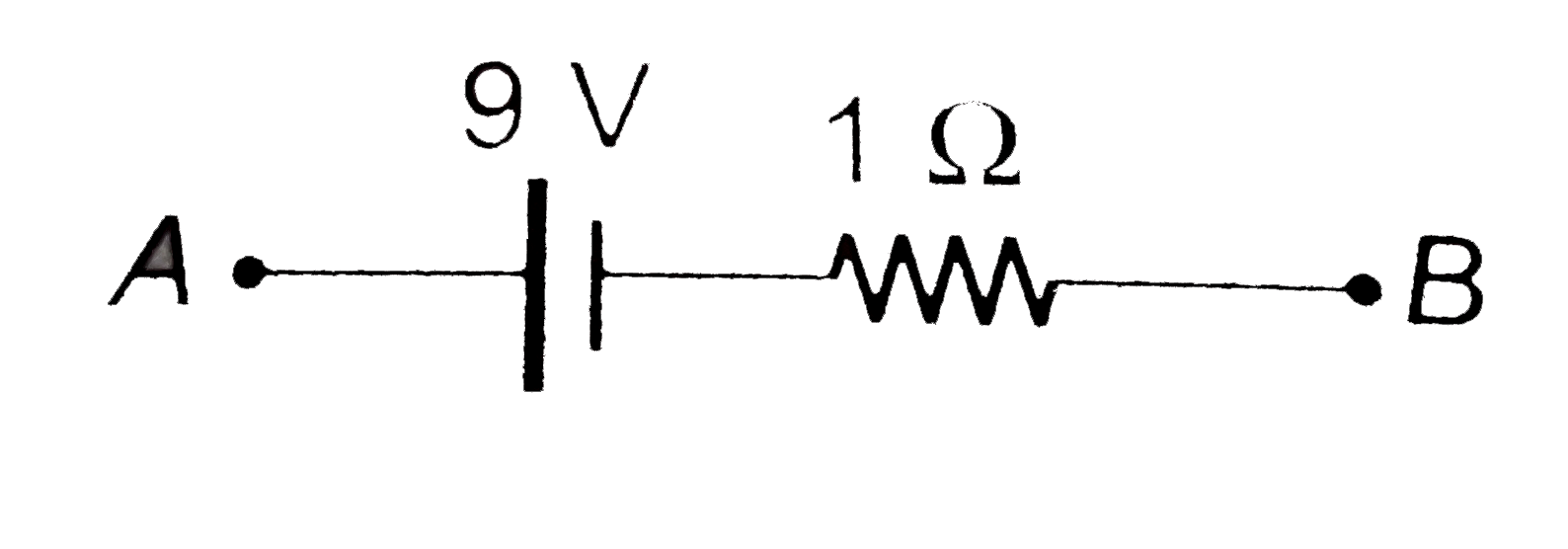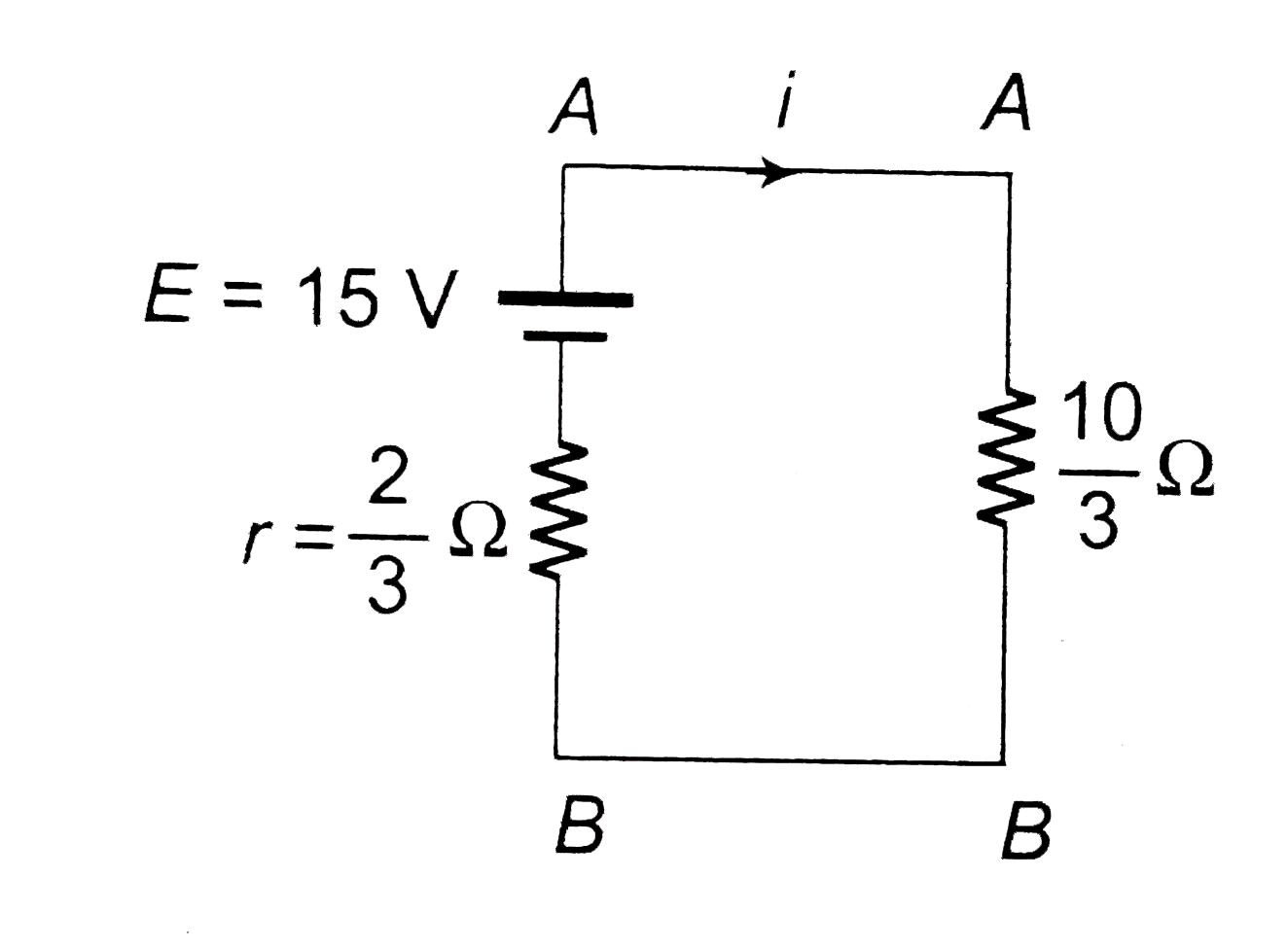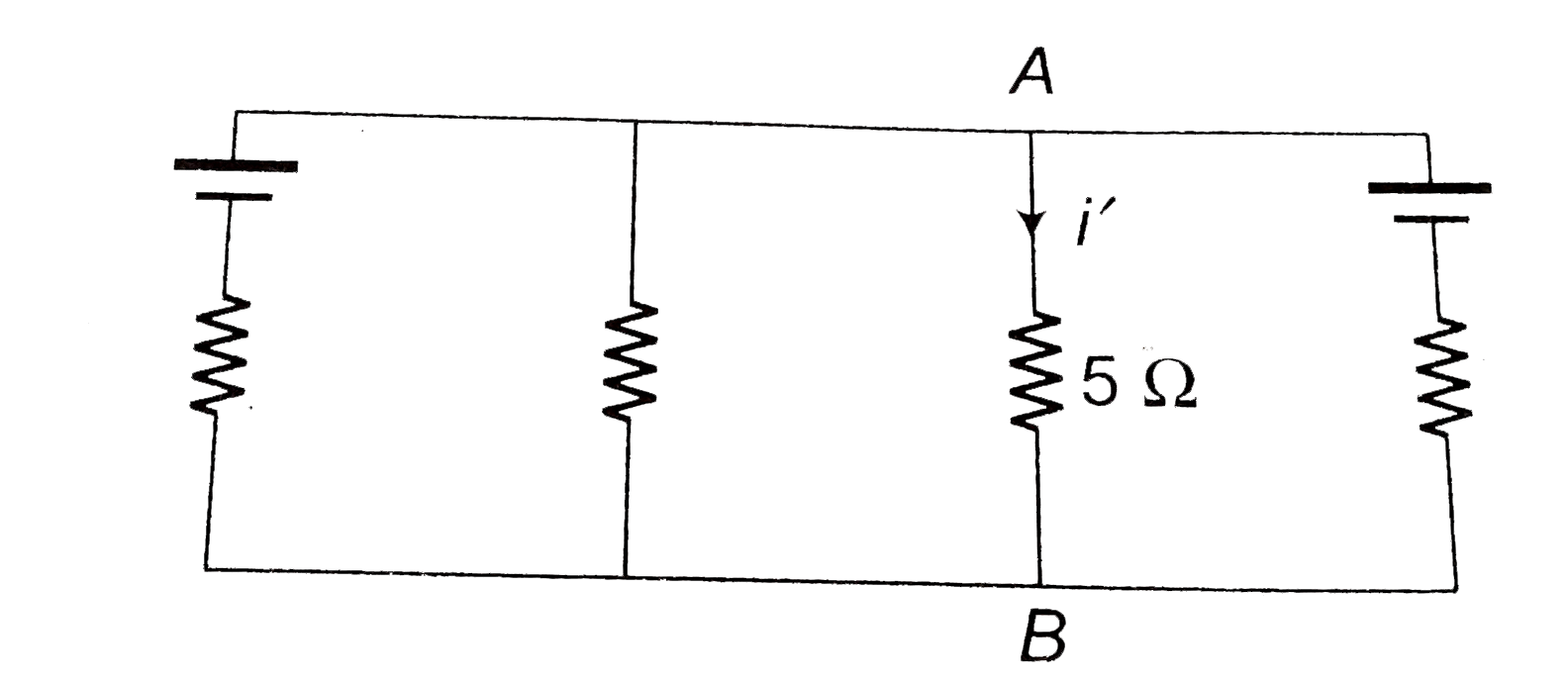Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
CP SINGH-CURRENT ELECTRICITY-Exercise
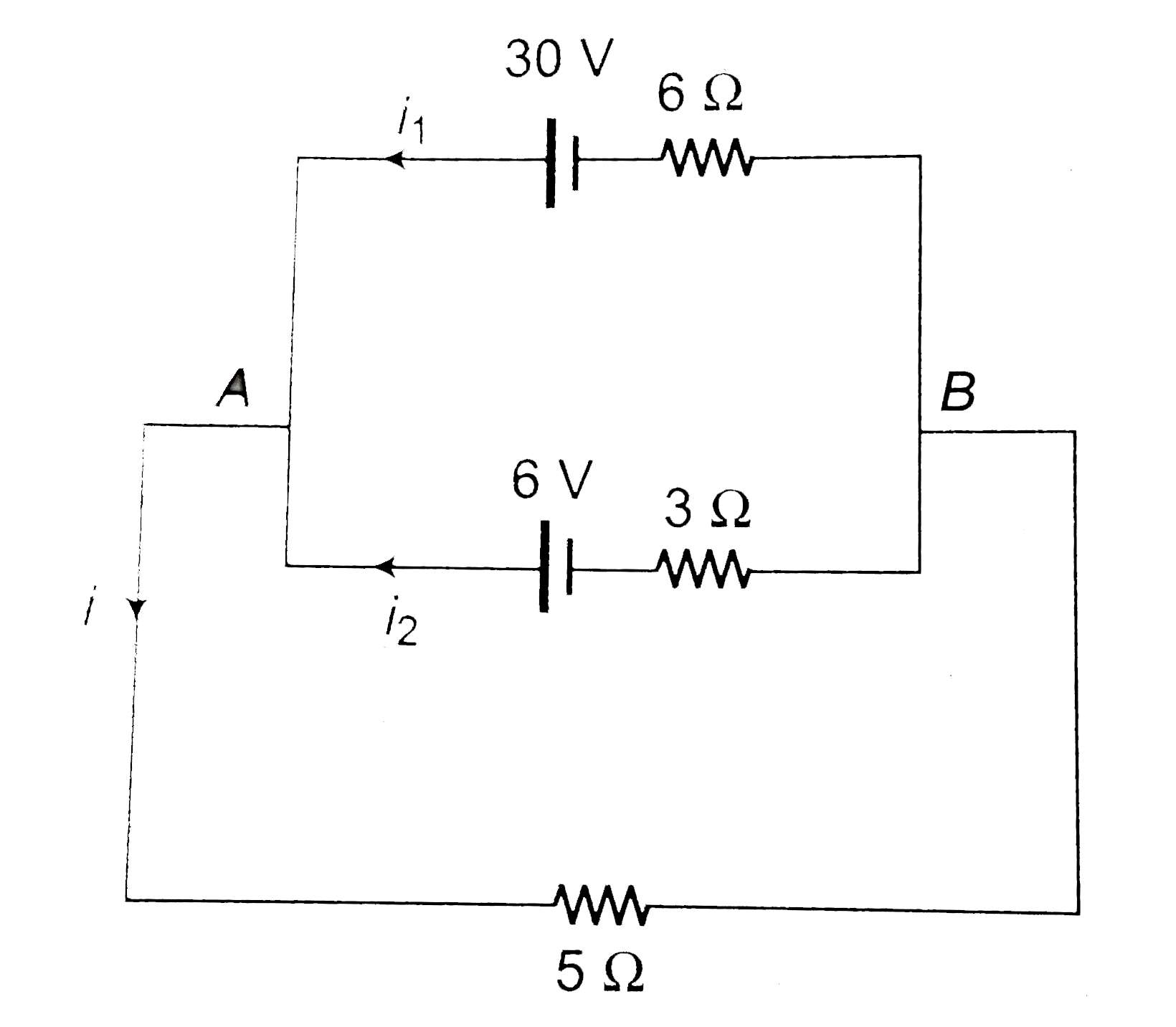
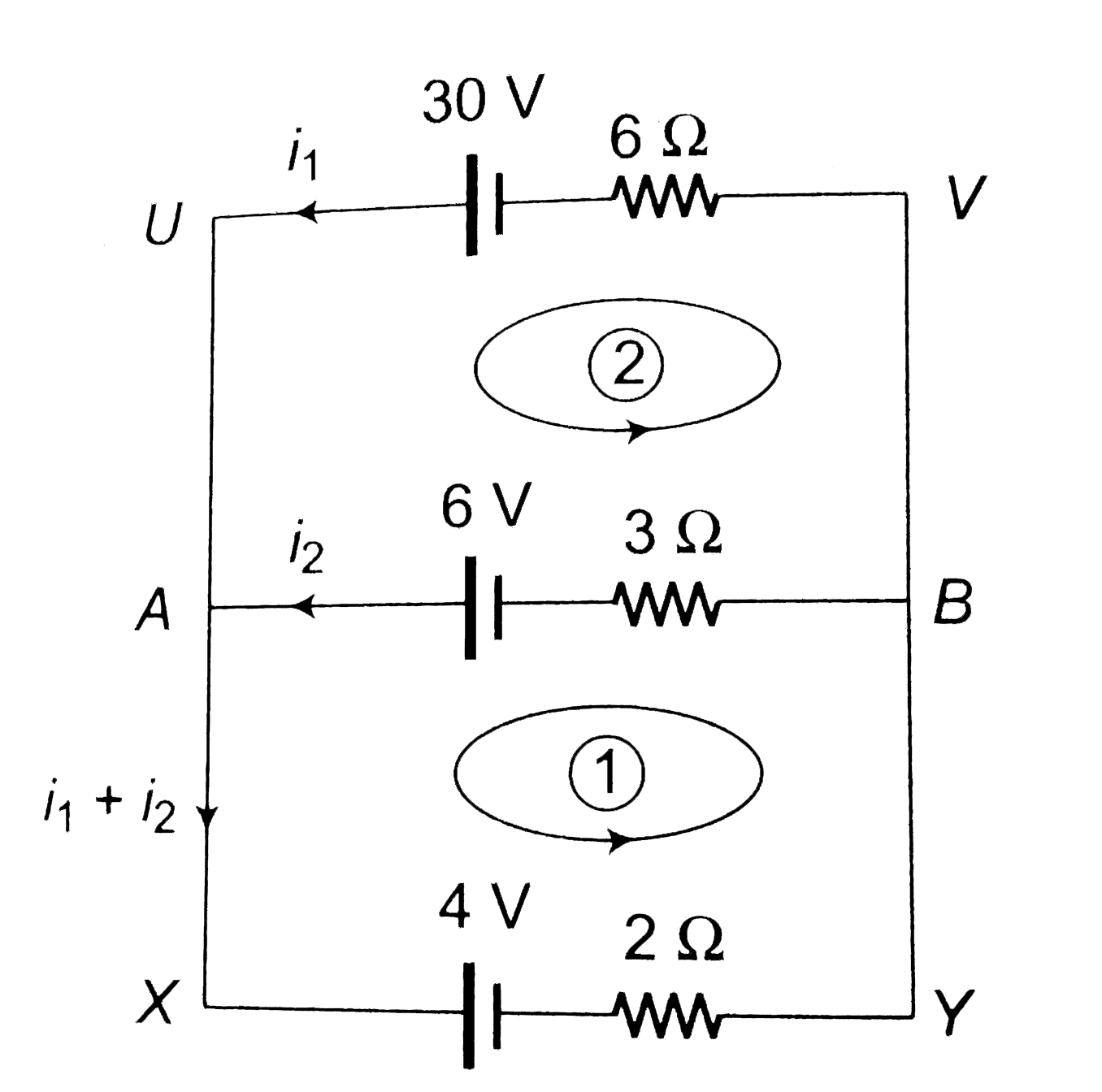
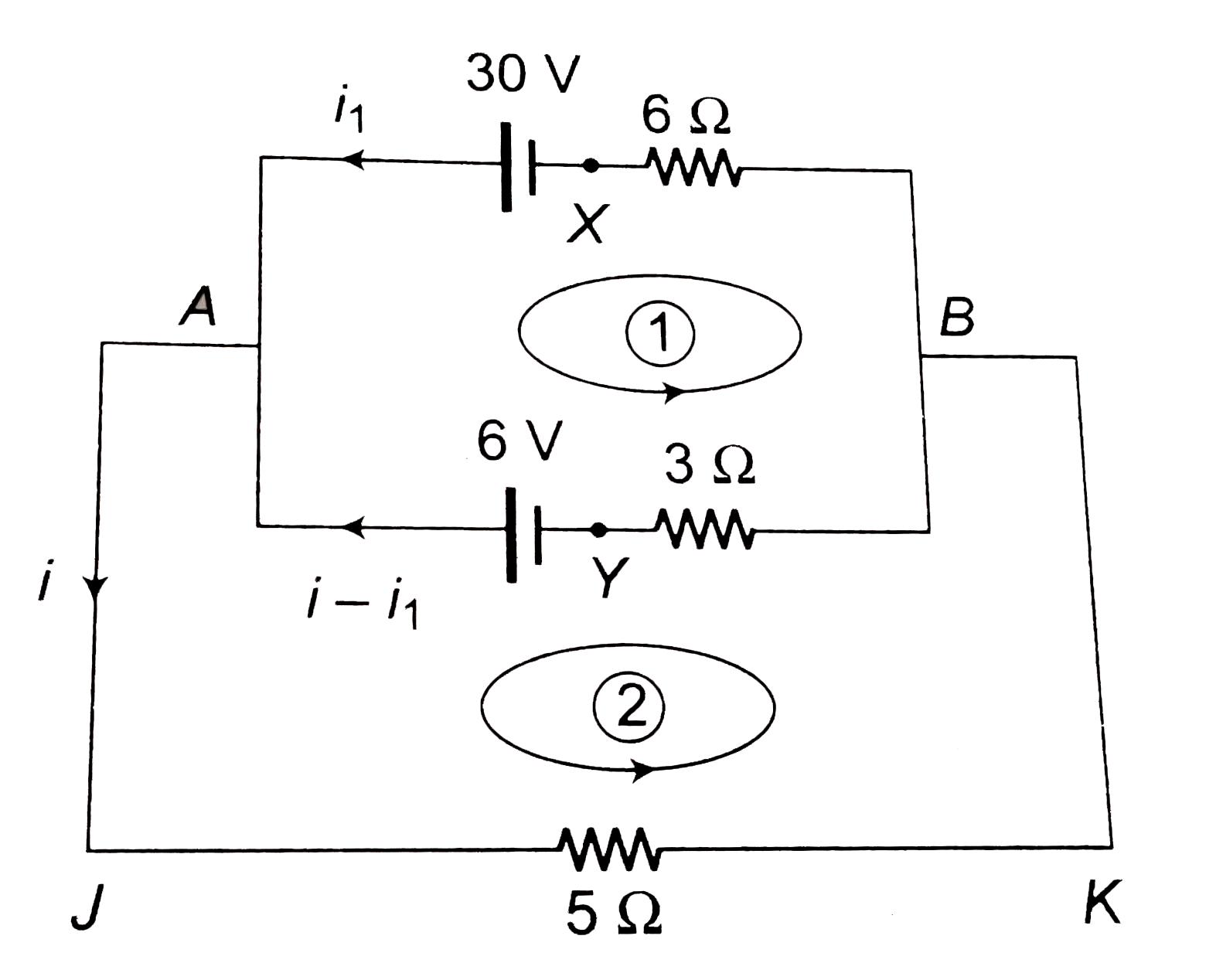
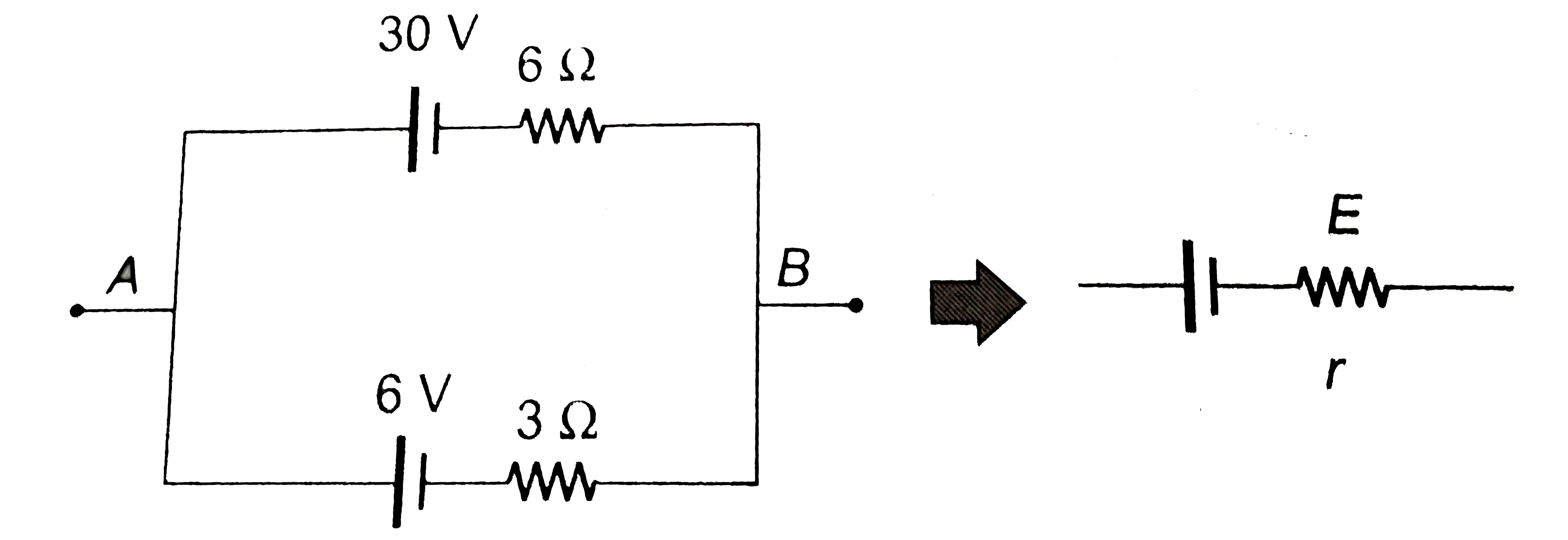
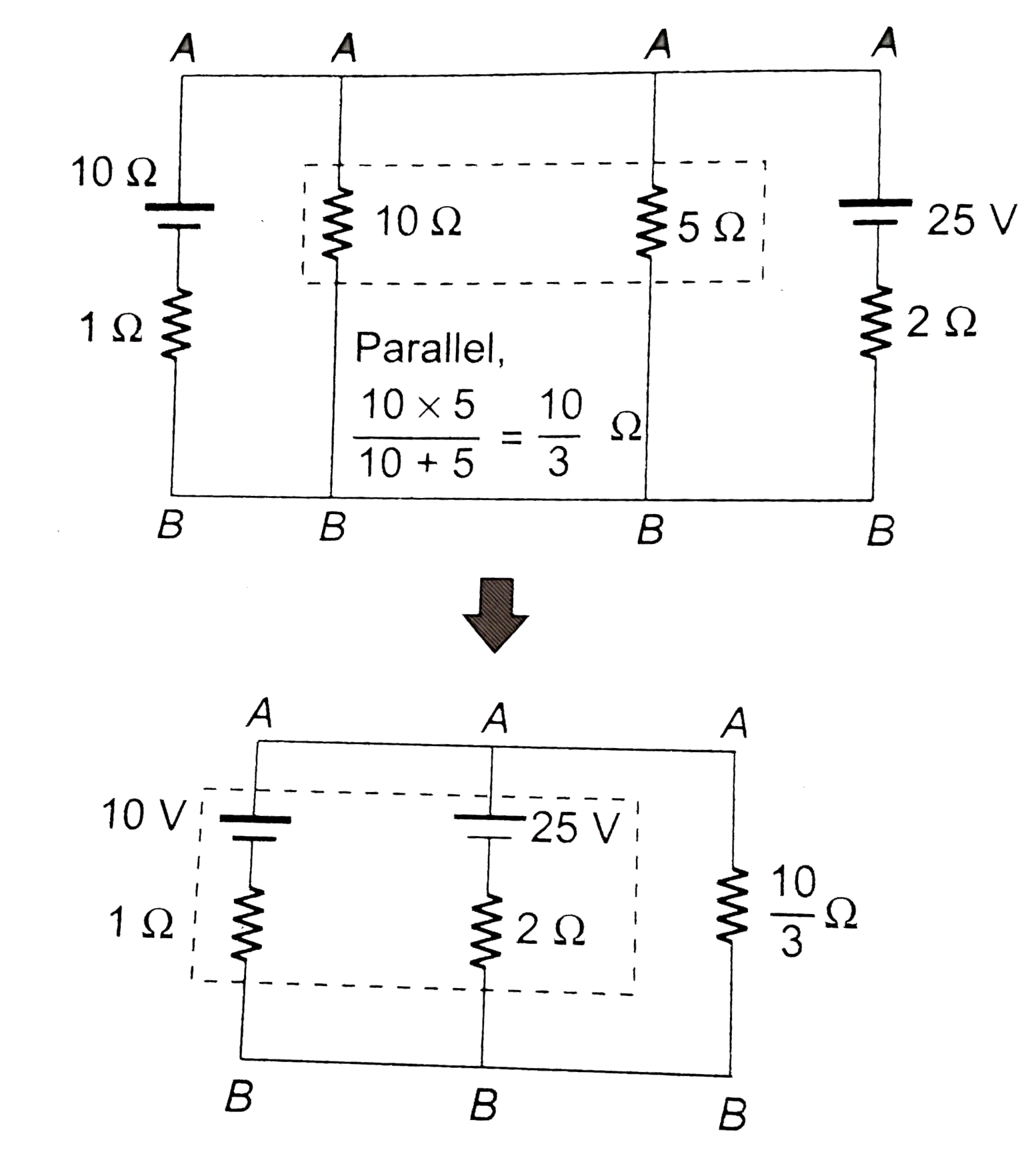
- (a) Find the value of i and potential difference across each cell. ...
Text Solution
|
- In an atom, an electron moves in an orbit of radius r with a speed v, ...
Text Solution
|
- The current flowing through wire depends on time as, 1 = 3t^(2) + 2t +...
Text Solution
|
- We have two wire A and B of the same mass and the same material. The d...
Text Solution
|
- A wire of resistance R is elongated n-fold to make a new uniform wire....
Text Solution
|
- A wire of a certain material is stretched slowly by ten percent. Its n...
Text Solution
|
- If a copper wire is stretched to make it 0.1% longer wha is the percen...
Text Solution
|
- A ring is made of a wire having a resistance R(0) = 12 Omega. Find the...
Text Solution
|
- The massses of the three wires of copper are in the ratio 1 : 3 : 5. A...
Text Solution
|
- Dimensions of a block are 1 cm xx 1 cm xx 100 cm. If specific resistan...
Text Solution
|
- In the above question, the resistance between the square faces is.
Text Solution
|
- The resistance between ends will be .
Text Solution
|
- A material of resistivity rho is formed in the shape of a truncated co...
Text Solution
|
- Which of the following is correct regarding drift velocity.
Text Solution
|
- A steady current flows in a metallic conductor of non-uniform cross-se...
Text Solution
|
- A current of 5 A is passing through a metallic wire of cross-section a...
Text Solution
|
- A Steady current flows in a metalic conductor of non uniform cross sec...
Text Solution
|
- A straight conductor of uniform cross section carries a time varying c...
Text Solution
|
- Two resistors A and B have resistances R(A) and R(B)respectively with ...
Text Solution
|
- The resistance of a metallic conductor increases with temperature due ...
Text Solution
|
- A metallic resistor is connected across a battery.If the number of col...
Text Solution
|
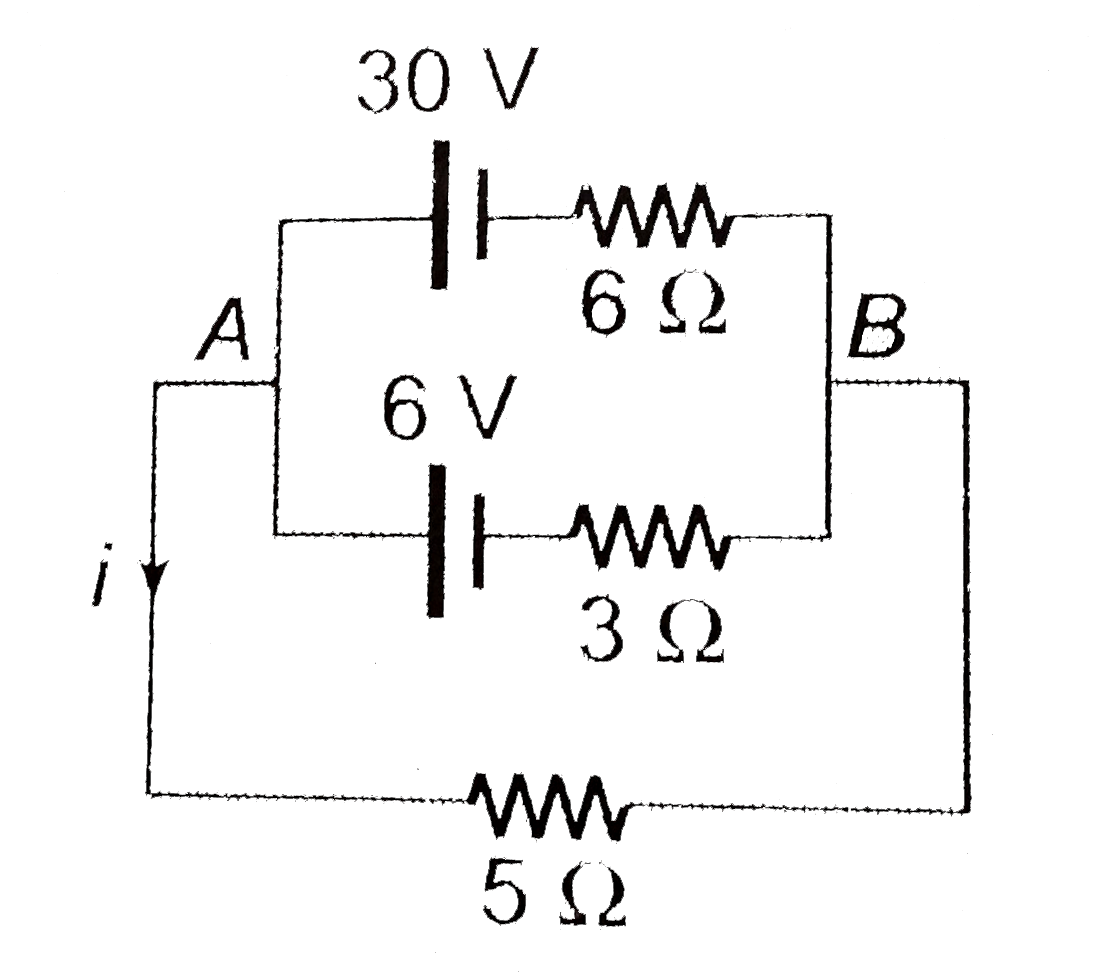
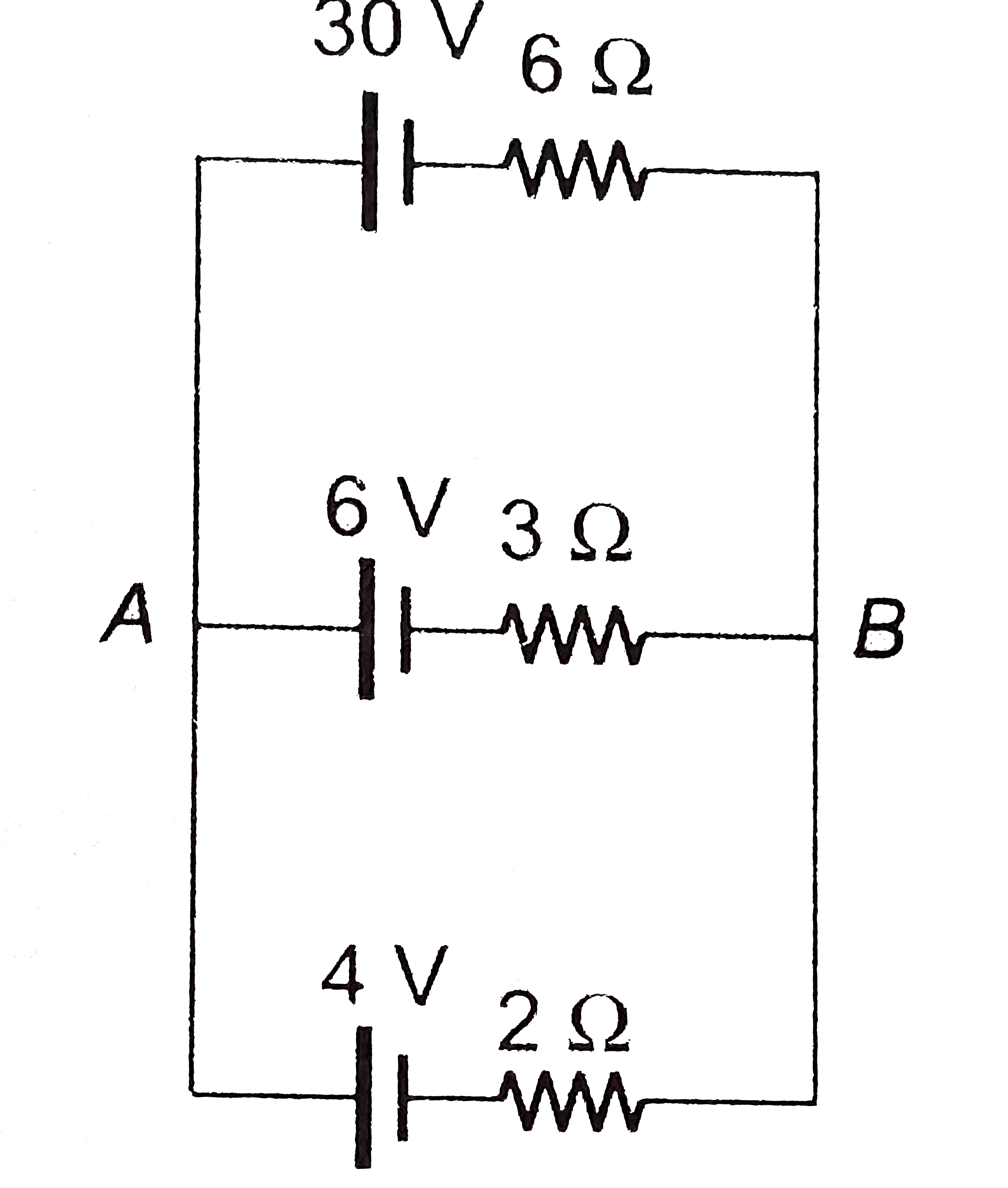
 .
.