Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
CP SINGH-REFLECTION OF LIGHT-EXERCISES
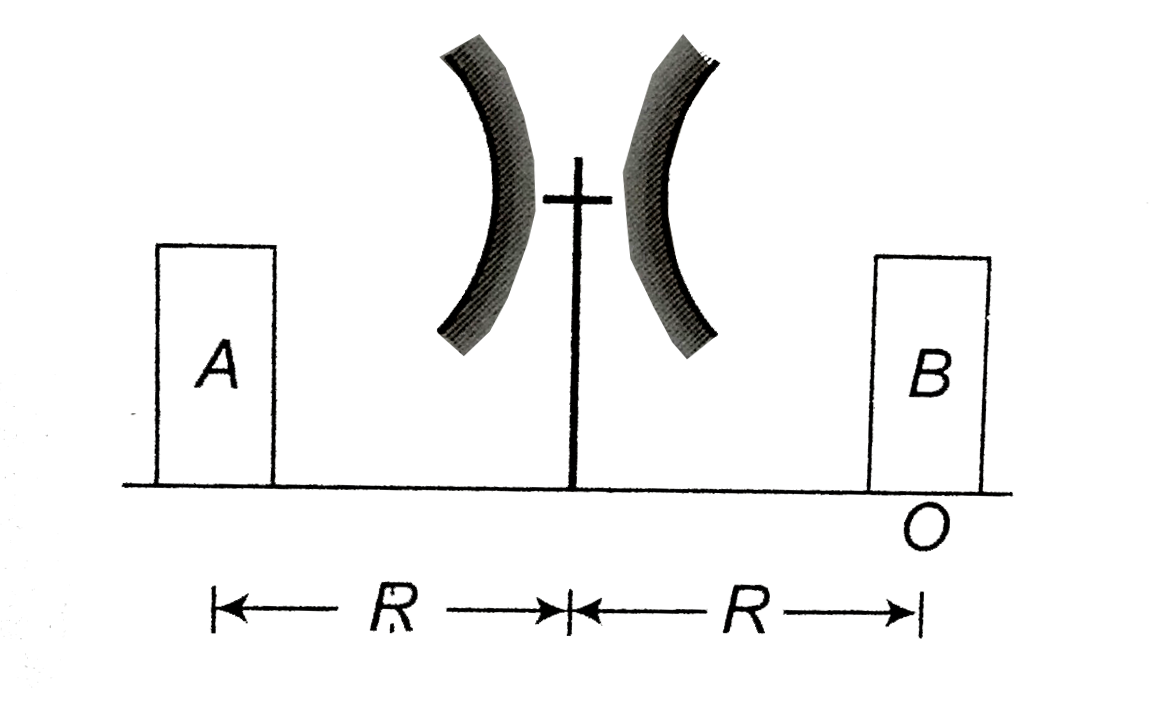
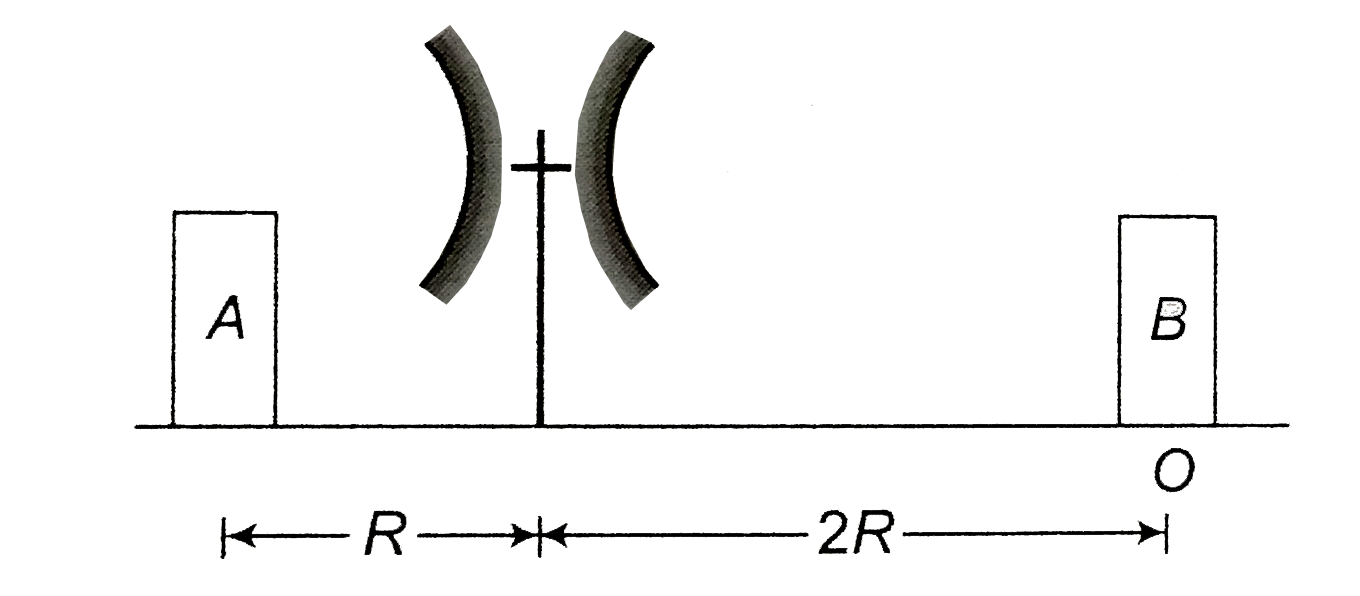
- Two concave mirrorsof equal radi of curvature R are fixed on a stand f...
Text Solution
|
- Choose the correct option:
Text Solution
|
- Ray optics is valid when characteristic dimensions are
Text Solution
|
- The light reflected by a plane mirrorr may form a real image
Text Solution
|
- A point source of light is placed in front of a plane mirror.
Text Solution
|
- Figure shows two rays A and B being reflected by a mirror and going as...
Text Solution
|
- A thick plane mirror shows a number of images of the filament of an el...
Text Solution
|
- A man is 180 cm tall and his eyes are 10 cm below the top of his head....
Text Solution
|
- A boy of height 1.5m with his eye level at 1.4m stands before a plane ...
Text Solution
|
- A man is standing at distance x from a plane mirror in front of him. H...
Text Solution
|
- When a plane mirror is placed horizontally on level ground at a distan...
Text Solution
|
- A man 180 cm tall stands 4.5 m in front of a larger vertical plane mir...
Text Solution
|
- A plane mirror reflects a beam of light to form a real image, The inci...
Text Solution
|
- How many images will be formed if two mirrors are fitted on adjacent w...
Text Solution
|
- The number of images formed by two plane mirrors inclined at 60^@ of a...
Text Solution
|
- Two plane mirrors are inclined to each other at an angle theta. A ray ...
Text Solution
|
- A ray of light is incident on a plane mirror at an angle of incidence ...
Text Solution
|
- A ray reflected successively from two plane mirrors incline at a certa...
Text Solution
|
- Two plane mirrors are placed perpendicular to each other. A ray strike...
Text Solution
|
- Two plane mirrors are inclined at 70^@. A ray incident on one mirror a...
Text Solution
|
- A ray of light makes an angle of 10^@ with the horizontal and strikes ...
Text Solution
|