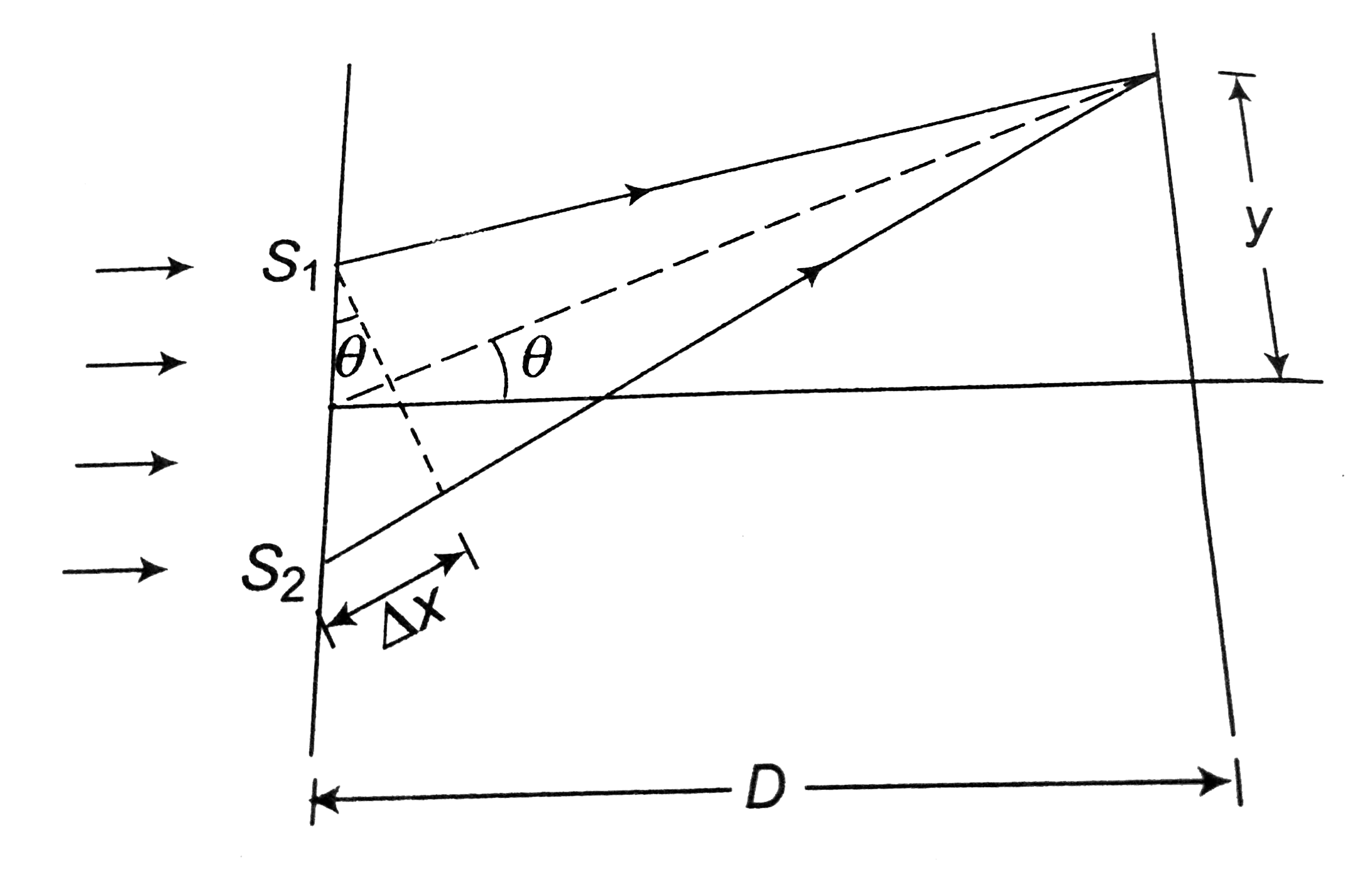
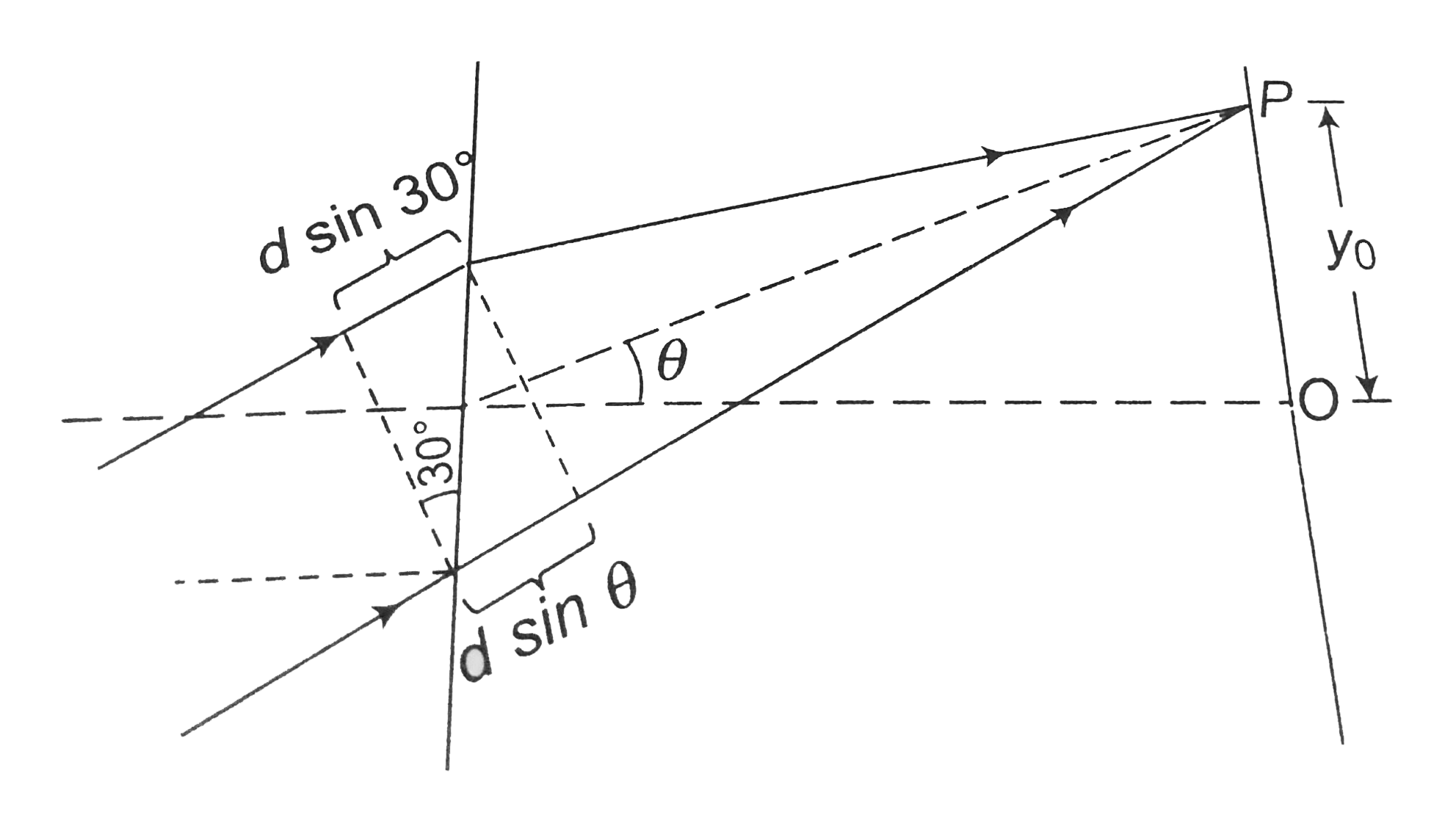
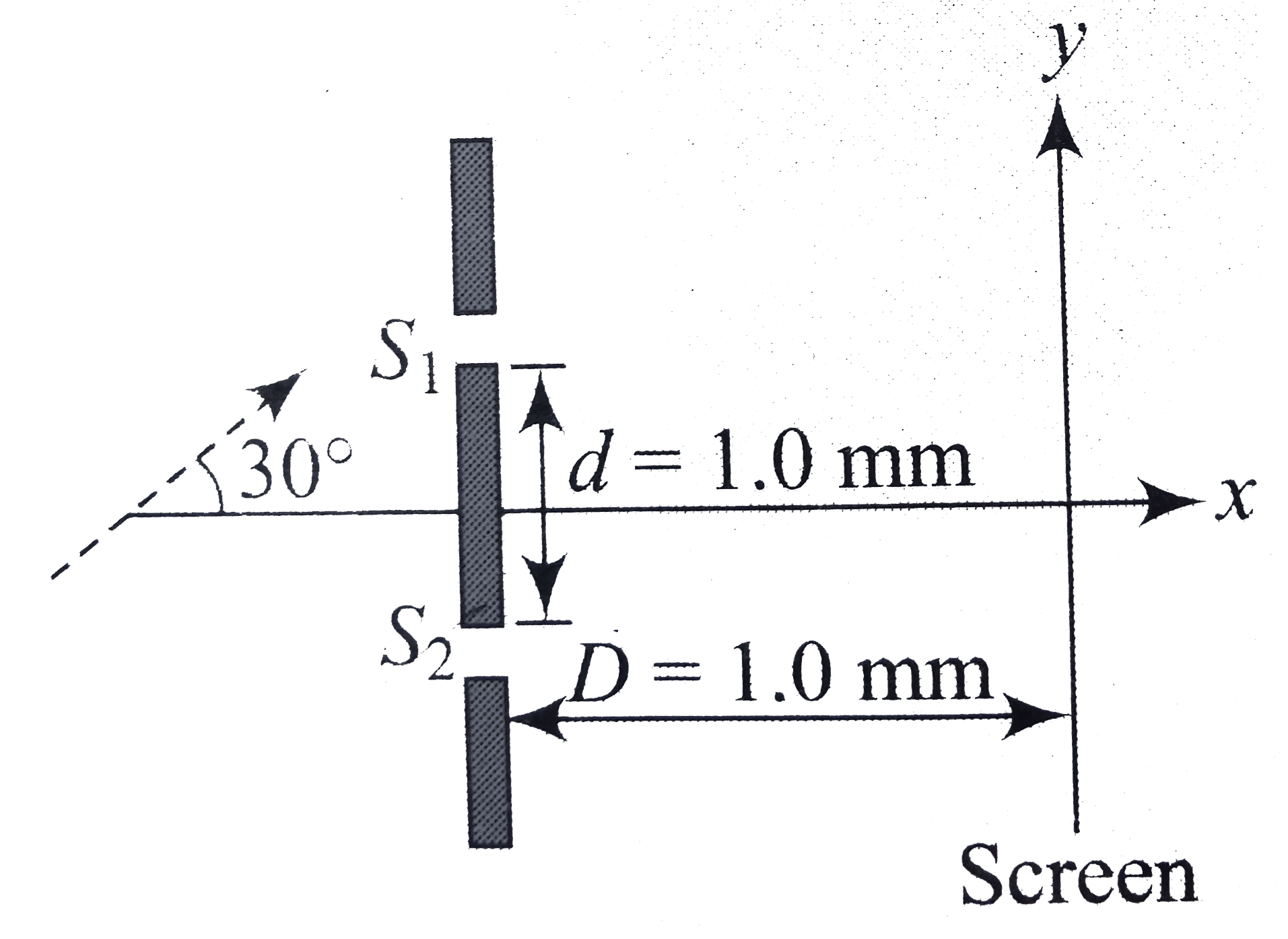Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
CP SINGH-WAVE NATURE OF LIGHT-EXERCISES
- A coherent parallel beam of microwaves of wavelength lambda = 0.5 mm f...
Text Solution
|
- Lifgt is
Text Solution
|
- The speed of light depends
Text Solution
|
- The equation of a light wave i written as y=Asin(kx-omegat). Here y r...
Text Solution
|
- When light is refracted into a medium
Text Solution
|
- Wave nature of light follows because
Text Solution
|
- Ray optics is valid when characteristic dimensions are
Text Solution
|
- Light appears to travel in straight lines since
Text Solution
|
- The velocity of light in diamond, glass and water decreases in the fol...
Text Solution
|
- Choose the correct option:
Text Solution
|
- Choose the correct option: (i) A surface on which the wave disturban...
Text Solution
|
- A wavefront and a ray of light are
Text Solution
|
- Huygen's principle of secondary waves
Text Solution
|
- Huygen's priciple of secondary wavelets may be used to
Text Solution
|
- Which one of the following phenomena is not explained by Huygens const...
Text Solution
|
- By Huygen's wave theroy of light, we cannot explain the phenomenon of
Text Solution
|
- In the adjoining figure, a wavefront AB moving in air is incident on a...
Text Solution
|
- In the adjacent diagram, CP represents a wavefront and AO & BP, the co...
Text Solution
|
- Which of the following sources gives best mionochromatic light?
Text Solution
|
- A laser beam is used for carrying our surgery because it
Text Solution
|
- Two sources of light are said to be coherent if the waves produced by ...
Text Solution
|