A
B
C
D
Text Solution
AI Generated Solution
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
CHEMICAL BONDING (ADVANCED)
VK JAISWAL|Exercise ONE OR MORE ANSWER IS/ARE CORRECT|84 VideosCHEMICAL BONDING (ADVANCED)
VK JAISWAL|Exercise MATCH THE COLUMN|26 VideosCHEMICAL BONDING (ADVANCED)
VK JAISWAL|Exercise Level 2|156 VideosCHEMICAL BONDING (BASIC)
VK JAISWAL|Exercise Level 3 (Passive 11)|6 Videos
VK JAISWAL-CHEMICAL BONDING (ADVANCED)-Level 3
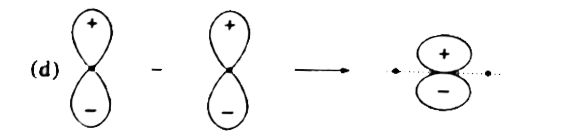
- According to MOT, two atomic orbitals overlap resulting in the formati...
Text Solution
|
- According to MOT, two atomic orbitals overlap resulting in the formati...
Text Solution
|
- According to MOT, two atomic orbitals overlap resulting in the formati...
Text Solution
|
- According to MOT, two atomic orbitals overlap resulting in the formati...
Text Solution
|
- According to MOT, two atomic orbitals overlap resulting in the formati...
Text Solution
|
- Polar covalent molecules exhibit dipole moment. Dipole moment is equal...
Text Solution
|
- Polar covalent molecules exhibit dipole moment. Dipole moment is equal...
Text Solution
|
- Polar covalent molecules exhibit dipole moment. Dipole moment is equal...
Text Solution
|
- Polar covalent molecules exhibit dipole moment. Dipole moment is equal...
Text Solution
|
- Polar covalent molecules exhibit dipole moment. Dipole moment is equal...
Text Solution
|
- In general boiling point of covalent compounds is affect due to incre...
Text Solution
|
- In general boiling point of covalent compounds is affect due to incre...
Text Solution
|
- In general boiling point of covalent compounds is affect due to incre...
Text Solution
|
- The molecule in which an atom is associated with more than 8 electrons...
Text Solution
|
- The molecule in which an atom is associated with more than 8 electrons...
Text Solution
|
- The molecule in which an atom is associated with more than 8 electrons...
Text Solution
|
- Colour of compounds occurs due to phenomenon of polarisation, charge t...
Text Solution
|
- Colour of compounds occurs due to phenomenon of polarisation, charge t...
Text Solution
|
- Colour of compounds occurs due to phenomenon of polarisation, charge t...
Text Solution
|
- Hydrogen bond is the given to the relatively weak secondry interaction...
Text Solution
|