Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
- A line charge with linear charge density lambda is wound around an ins...
Text Solution
|
- Find the ratio of magnetic dipole moment and magnetic field at the cen...
Text Solution
|
- A line charge with linear charge density lambda is wound around an ins...
Text Solution
|
- A disc of radius R is rolling without sliding on a horizontal surface ...
Text Solution
|
- A nonconducting ring of uniform mass m, radius b and uniform linear ch...
Text Solution
|
- Charge q is uniformly distributed on a disc of radius r. If the disc i...
Text Solution
|
- A non-conducting thin disc of radius R and mass m having charge unifor...
Text Solution
|
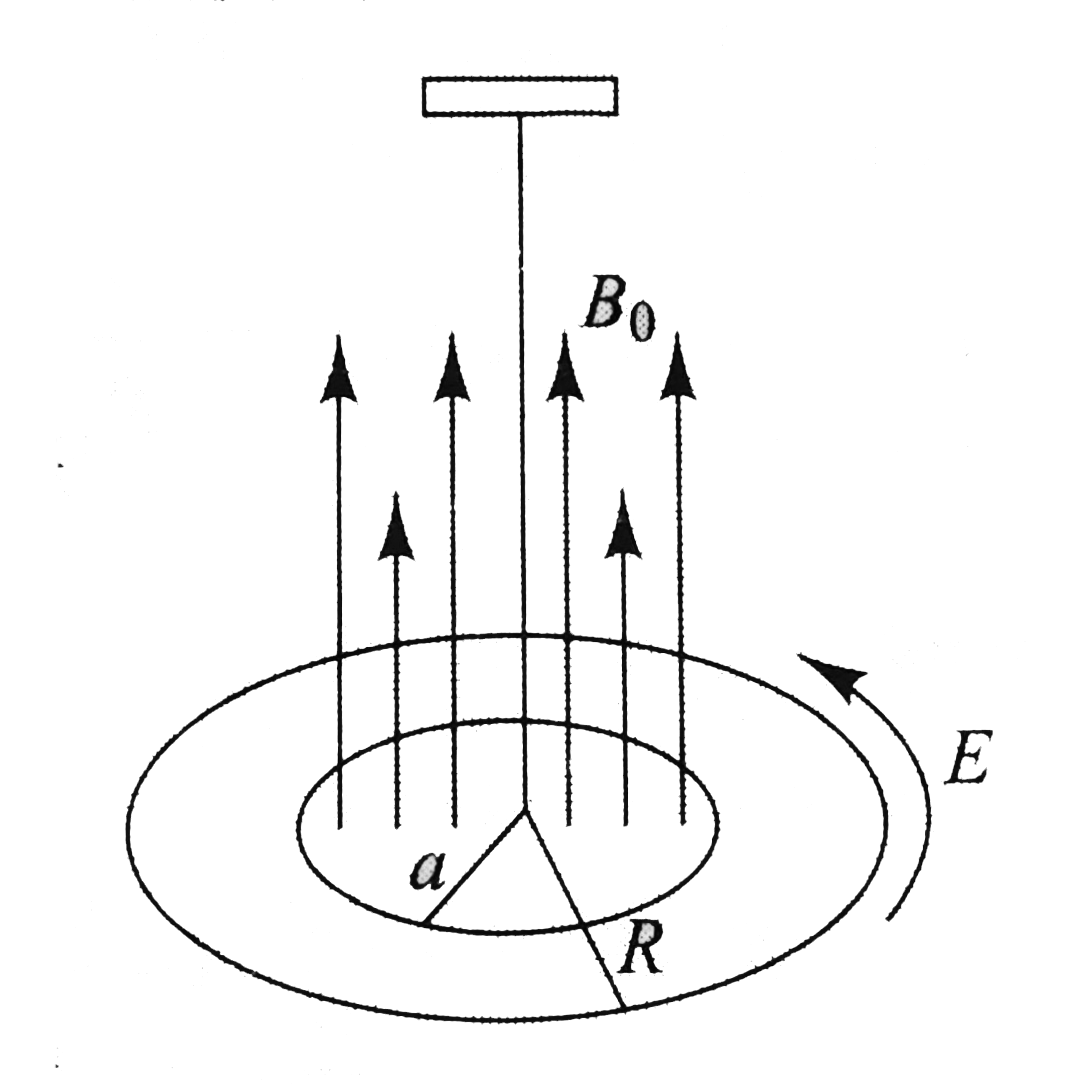
- A flat insulating disc of radius 'a' carries an excess charge on its s...
Text Solution
|
- Charge Q is uniformly distributed on the rim of a thin insulating disc...
Text Solution
|