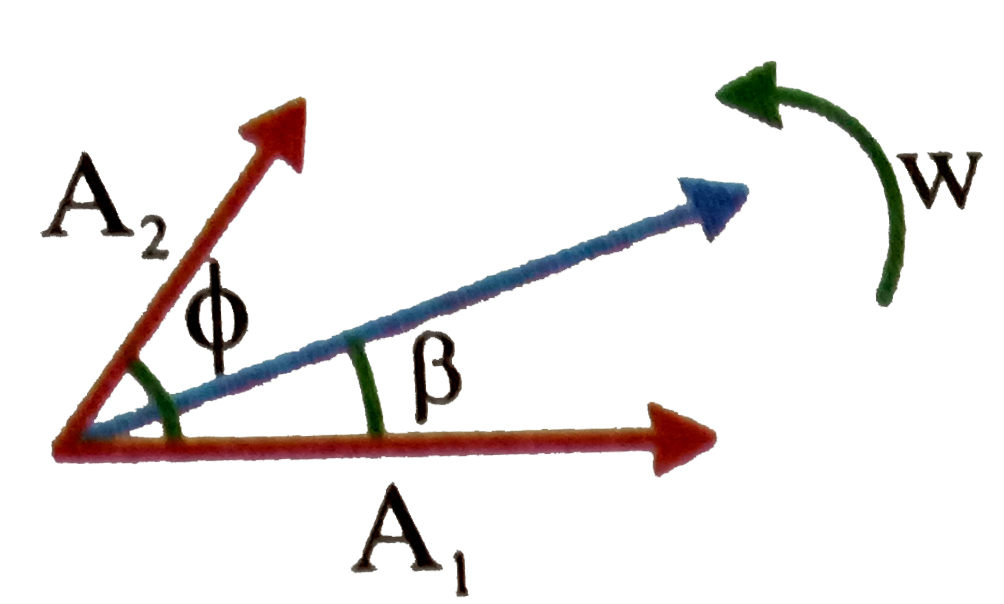
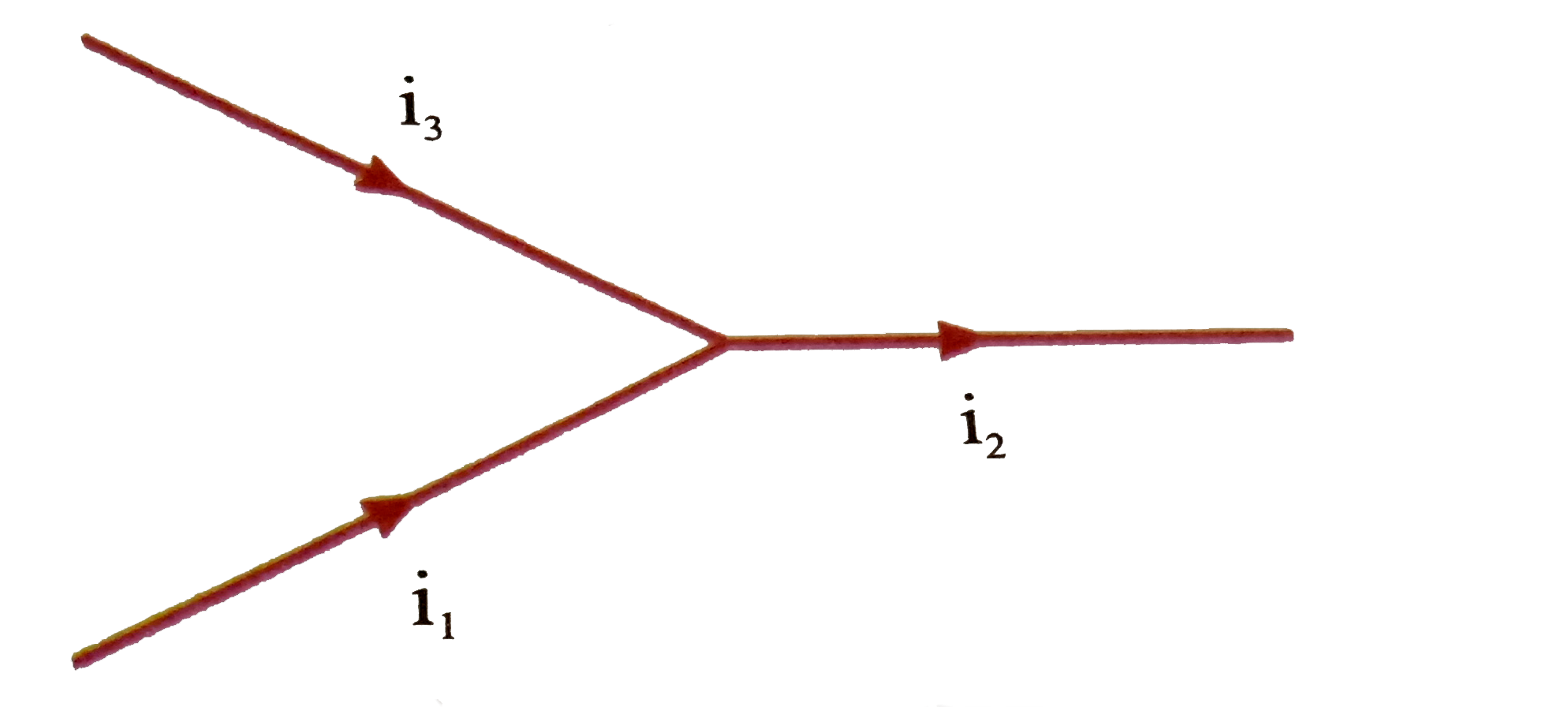
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
NARAYNA-ALTERNATING CURRENT-LEVEL - VI
- A series circuit connected across a 200 V, 60 Hz line consists of a ca...
Text Solution
|
- A series circuit connected across a 200 V, 60 Hz line consists of a ca...
Text Solution
|
- The maximum values of the phasors (currents and voltage) in AC circuit...
Text Solution
|
- The maximum values of the phasors (currents and voltage) in AC circuit...
Text Solution
|
- The maximum values of the phasors (currents and voltage) in AC circuit...
Text Solution
|
- A series R-L-C circuit has R = 100 ohm. L = 0.2 mH and C = (1)/(2) mu ...
Text Solution
|
- A series R-L-C circuit has R = 100 ohm. L = 0.2 mH and C = (1)/(2) mu ...
Text Solution
|
- A series R-L-C circuit has R = 100 Ohm. L = 0.2 mH and C = (1)/(2) mu ...
Text Solution
|
- The potential difference across a 2 H inductor as a function of time i...
Text Solution
|
- The potential difference a 2 H inductor as a function of time is shown...
Text Solution
|
- In the given arrangement the square loop of area 10 cm^(2) rotates wit...
Text Solution
|
- In the given arrangement the square loop of area 10 cm^(2) rotates wit...
Text Solution
|
- In the given arrangement the square loop of area 10 cm^(2) rotates wit...
Text Solution
|
- A 20 V 5 watt lamp is used in ac main 220 V and frequency 50 c.p.s. ...
Text Solution
|
- A 20 V 5 watt lamp is used in ac main 220 V and frequency 50 c.p.s. ...
Text Solution
|
- A 20 V 5 watt lamp is used in ac main 220 V and frequency 50 c.p.s. ...
Text Solution
|
- In the circuit shown in the figure R = 50 Omega, E(1) = 25 sqrt(3) vol...
Text Solution
|
- In the circuit shown in the figure R = 50 Omega, E(1) = 25 sqrt(3) vol...
Text Solution
|
- In the circuit shown in the figure R = 50 Omega, E(1) = 25 sqrt(3) vol...
Text Solution
|
- A physics lab is designed to study the transfer of electrial energy fr...
Text Solution
|