Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
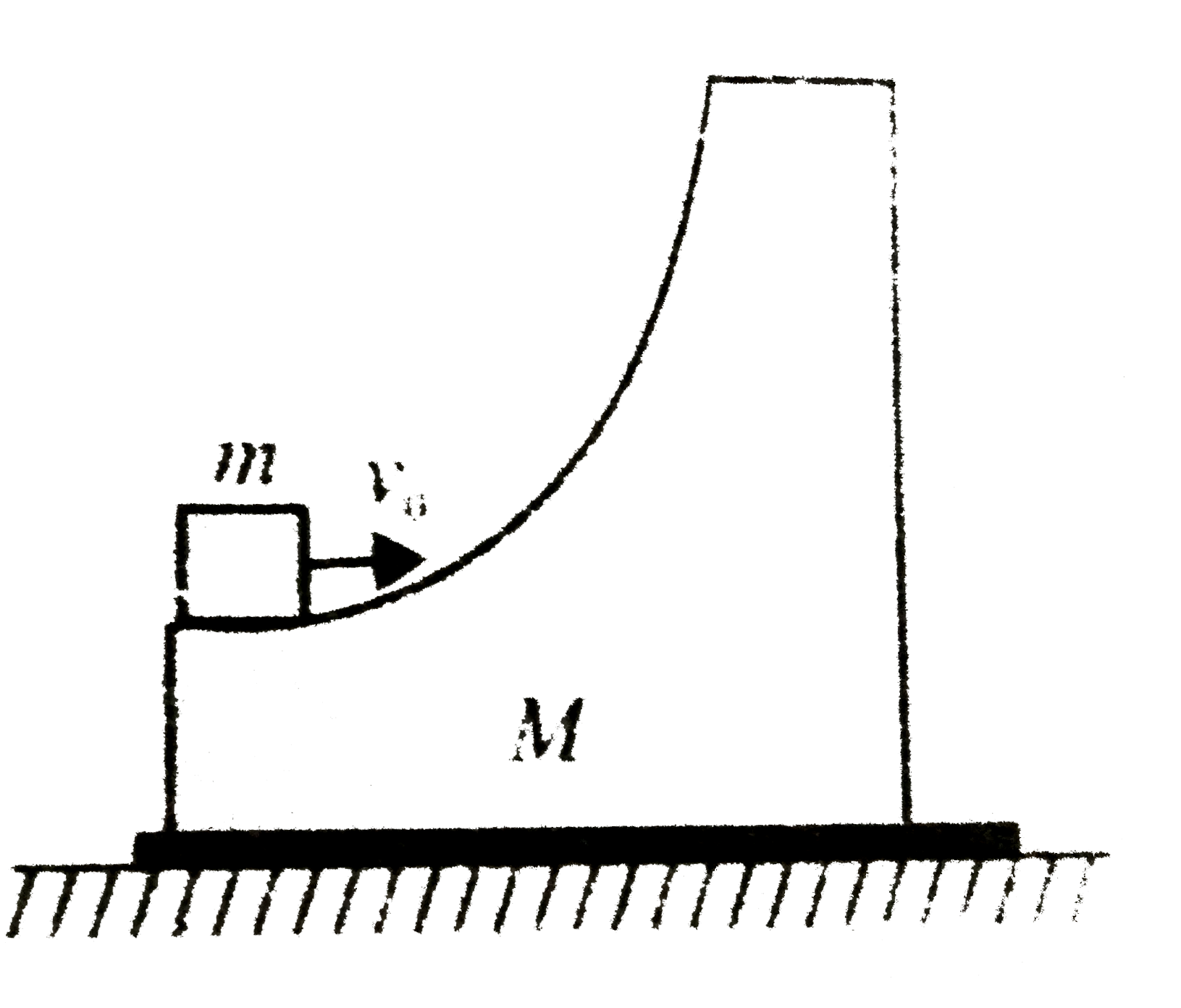
- A smooth wedge of mass M rests on a smooth horizontal surface. A block...
Text Solution
|
- All surfaces shown in figure are smooth. Wedges of mass 'M' is free to...
Text Solution
|
- A block of mass m rests on a stationary wedge of mass M. The wedge can...
Text Solution
|
- A small block of mass m is placed at rest on the top of a smooth wedge...
Text Solution
|
- A block of mass m is placed at rest on a smooth wedge of mass M placed...
Text Solution
|
- A small ball of mass m is projected with a minimum horizontal velocity...
Text Solution
|
- A smooth wedge of mass M rests on a smooth horizontal surface. A block...
Text Solution
|
- A block of mass m is pushed towards the movable wedge of mass M and he...
Text Solution
|
- A triangular wedge of mass M lies on a smooth horizontal table with ha...
Text Solution
|