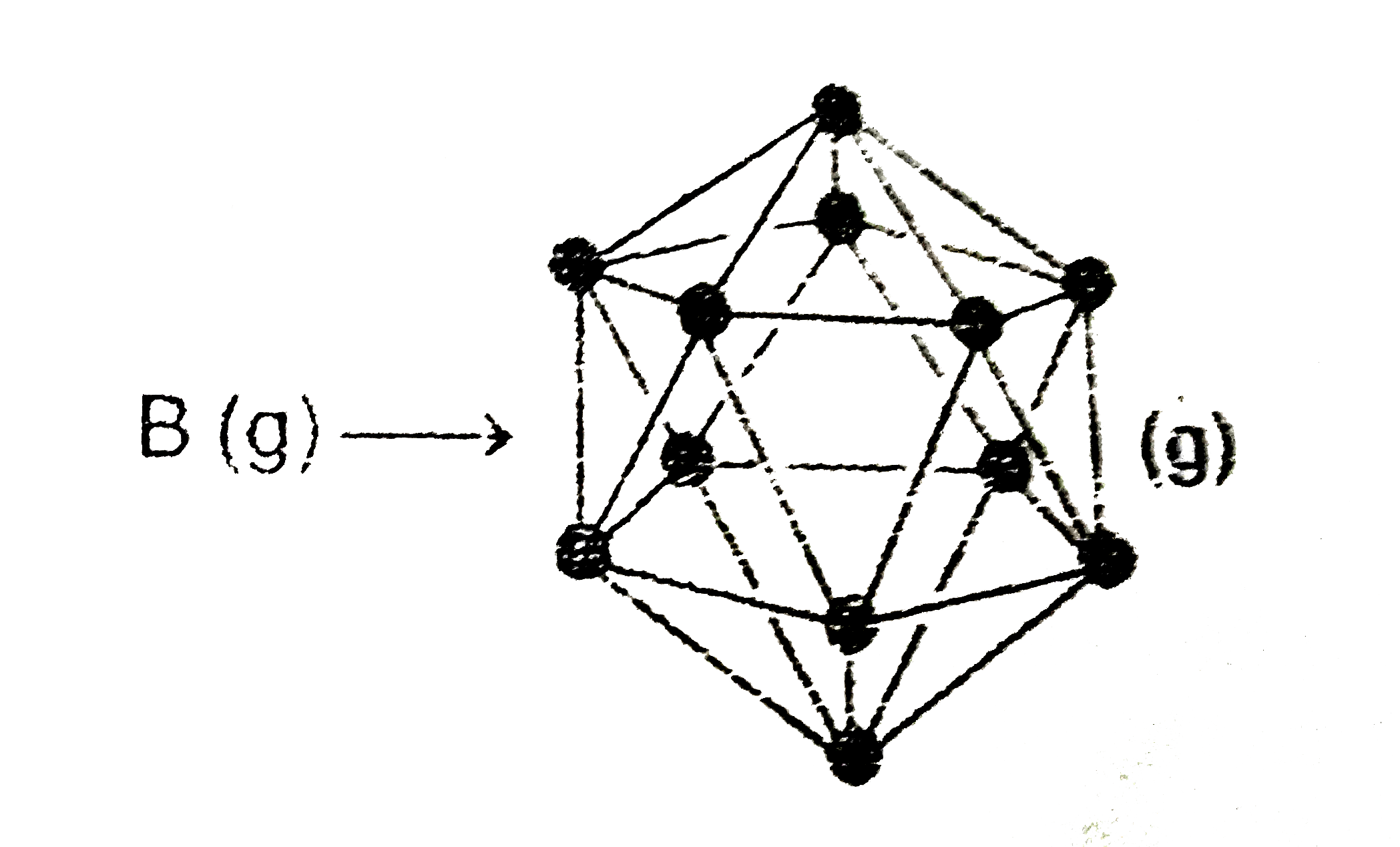Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
- Boron exist in different allotropic forms. All allotropic form contain...
Text Solution
|
- One of the allotropic form of boron is alpha - rhombohedral boron. Num...
Text Solution
|
- Boron exist in different allotropic forms .All allotropic fropm contai...
Text Solution
|
- In crystalline form boron exists as Icosahedron that has x faces and y...
Text Solution
|
- In the icosahedron of B(12) unit each boron atom is bonded to how many...
Text Solution
|
- Boron exist in different allotropic forms. All allotropic form contain...
Text Solution
|
- Give oxidation state of all boron atom in borax.
Text Solution
|
- डाइबोरेन में दो बोरॉन परमाणु परस्पर दो ………. आबन्धो द्वारा संयुक्त रहते...
Text Solution
|
- Give the names of 3 crystalline allotropic forms of boron.
Text Solution
|