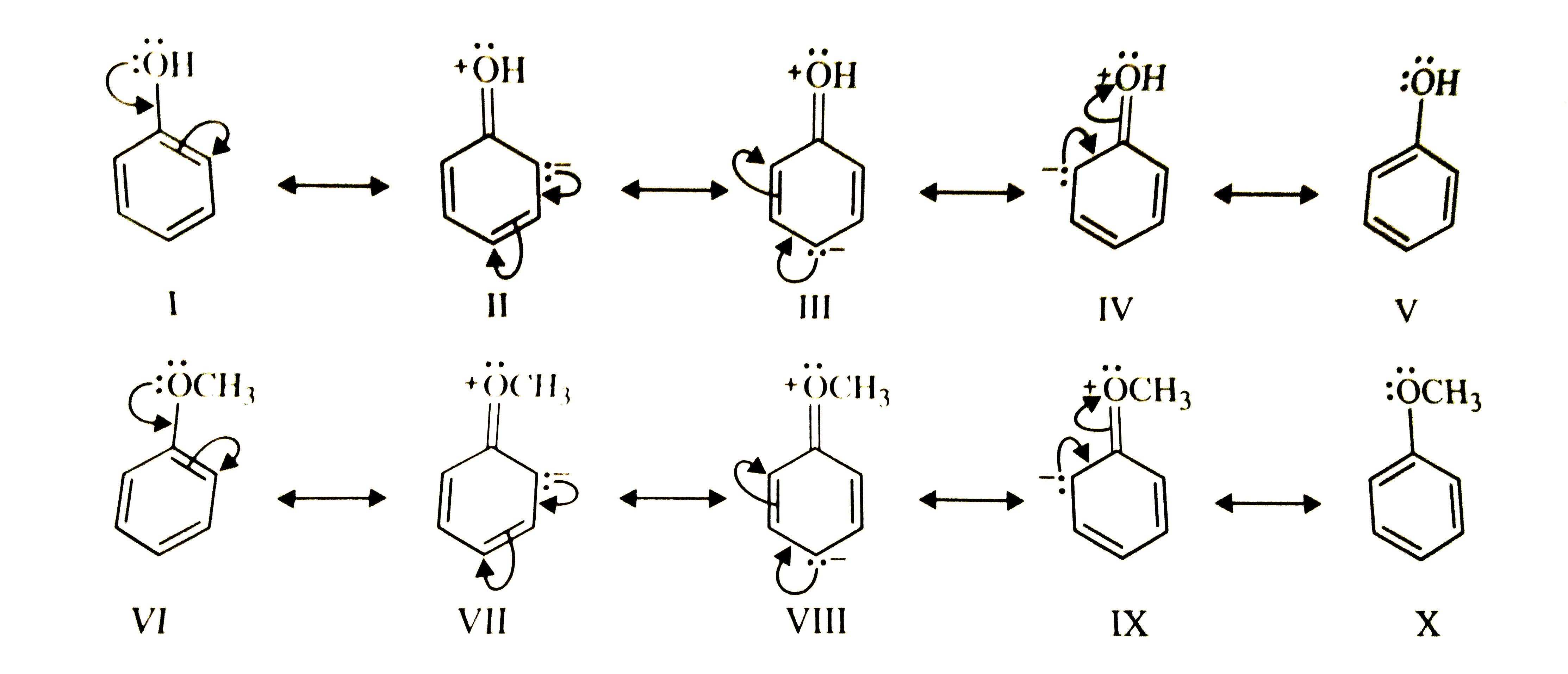
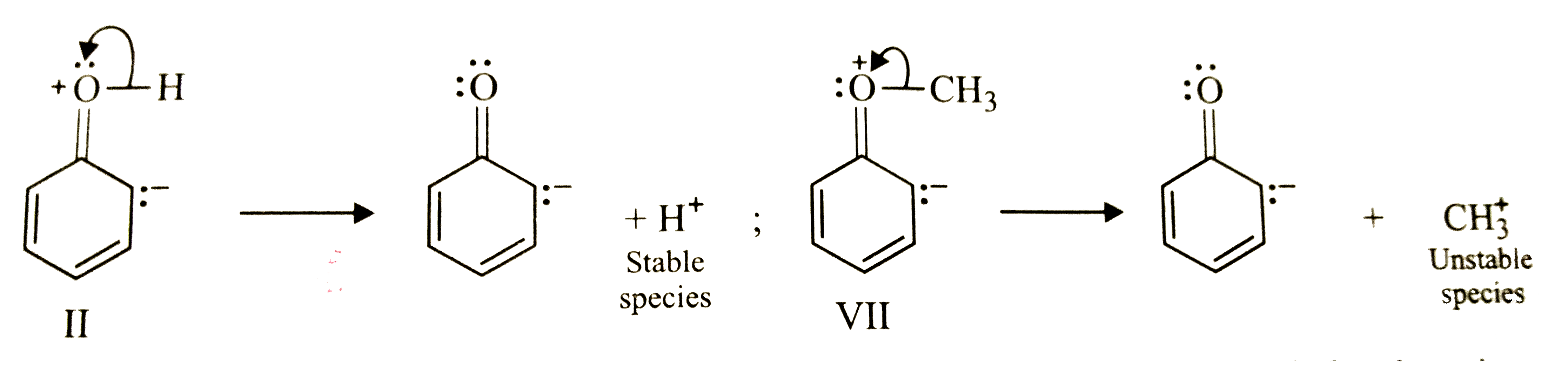
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
ALCOHOLS, PHENOLS AND ETHERS
PRADEEP|Exercise NCERT QUESTIONS AND EXERCISES WITH ANSWERS (NCERT INTEXT SOLVED QUESTIONS)|7 VideosALCOHOLS, PHENOLS AND ETHERS
PRADEEP|Exercise NCERT QUESTIONS AND EXERCISES WITH ANSWERS (NCERT INTEXT UNSOLVED QUESTIONS)|12 VideosALCOHOLS, PHENOLS AND ETHERS
PRADEEP|Exercise TEST YOUR GRIP (II. FILL IN THE BLANKS)|37 VideosALDEHYDES, KETONES AND CARBOXYLIC ACIDS
PRADEEP|Exercise IMPORTANT QUESTIONS FOR BOARD EXAMINATION|29 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
PRADEEP-ALCOHOLS, PHENOLS AND ETHERS-CONCEPTUAL QUESTIONS
- An organic (A) reacts with PCl(5) to produce another compound (B). (B...
Text Solution
|
- Arrange the following compounds in the increasing order of the propert...
Text Solution
|
- Arrange the following in order of their Increasing basicity: H(2)O, ...
Text Solution
|
- Why (CH(3))(3)COH is less acidic than (CH(3))(3)SiOH although carbon i...
Text Solution
|
- Draw the structrue and name the product formed if the following alcoho...
Text Solution
|
- Dehydration of alcohol to form an alkene is always carried out with co...
Text Solution
|
- Acid catalysed dehydration of t-butanol is faster than that of n-butan...
Text Solution
|
- Give the structure of the compound, C(C(4)H(8)) which when treated wit...
Text Solution
|
- 3,3-dimethylbutan-2-ol losses a molecule of water in the presence of c...
Text Solution
|
- Predict the major product of the following reaction: C(6)H(6)+(CH(3))(...
Text Solution
|
- Which is a stronger acid, phenol or cresol? Explain.
Text Solution
|
- How do you account for the fact that unlike phenol, 2,4-dinitrophenol ...
Text Solution
|
- Unlike phenols, alcohols are easily protonated. Or Alcohols are easily...
Text Solution
|
- Haloalkanes can easily be prepared from alcohols while aryl halides ca...
Text Solution
|
- Which of the following is the correct method for synthesising methyl-t...
Text Solution
|
- Identify the product of the following reaction: CH(3)-underset(CH(3)...
Text Solution
|
- Ethers are cleaved by acids and not by bases. Explain.
Text Solution
|
- Anisole is less reactive than phenol towards electrophilic substitutio...
Text Solution
|