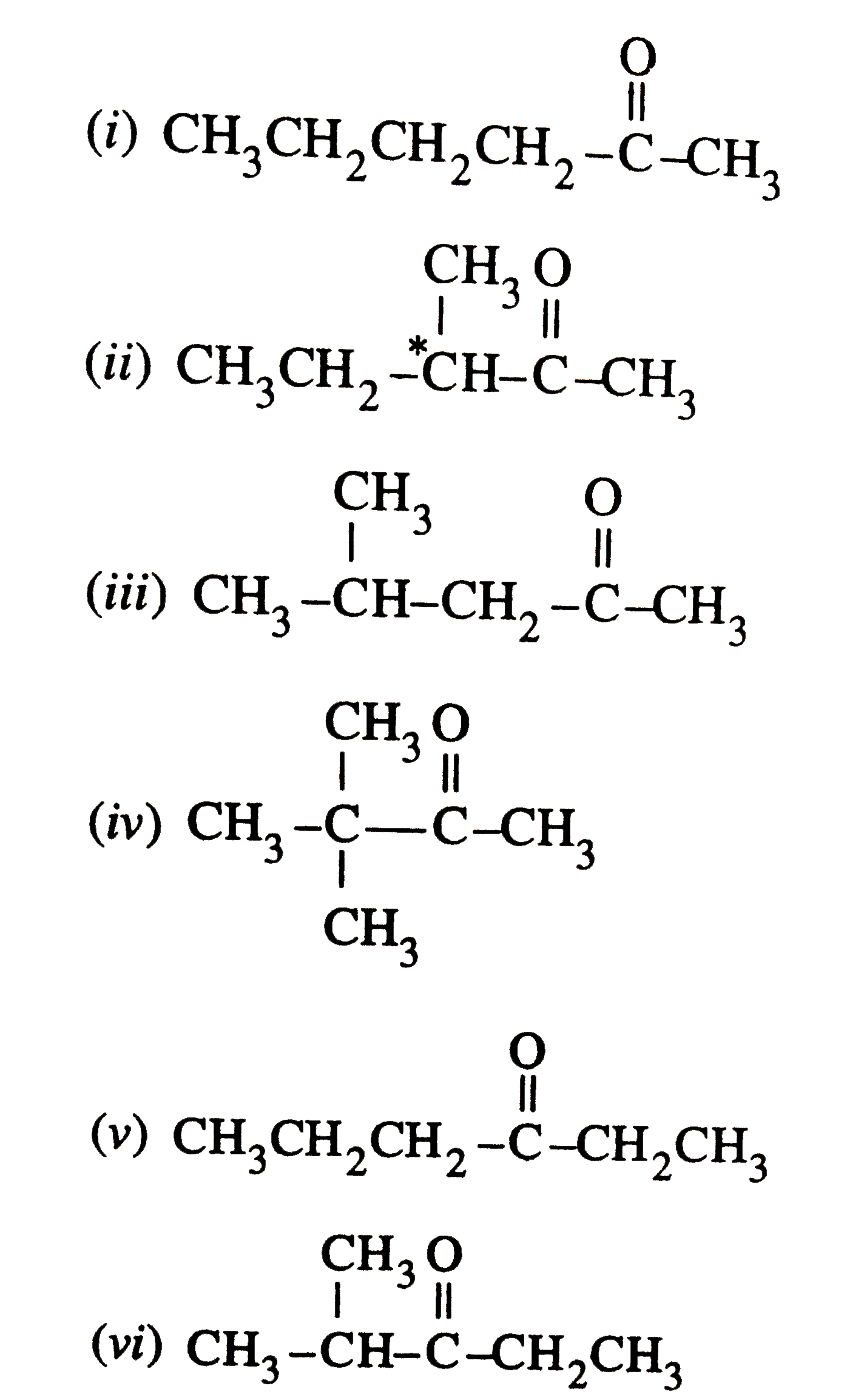Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
ALDEHYDES, KETONES AND CARBOXYLIC ACIDS
PRADEEP|Exercise COMPETITION FOCUS JEE (MAIN AND ADVANCED)/MEDICAL ENTRANCE SPECIEAL (VII. ASSERTION-REASON TYPE QUESTIONS) Type - I|7 VideosALDEHYDES, KETONES AND CARBOXYLIC ACIDS
PRADEEP|Exercise COMPETITION FOCUS JEE (MAIN AND ADVANCED)/MEDICAL ENTRANCE SPECIEAL (ASSERTION-REASON TYPE QUESTIONS) Type - II|14 VideosALDEHYDES, KETONES AND CARBOXYLIC ACIDS
PRADEEP|Exercise COMPETITION FOCUS JEE (MAIN AND ADVANCED)/MEDICAL ENTRANCE SPECIEAL (V. MATRIX-MATCH TYPE QUESTIONS)|1 VideosALCOHOLS, PHENOLS AND ETHERS
PRADEEP|Exercise IMPORTANT QUESTIONS FOR BOARD EXAMINATIONS.|29 VideosAPPENDIX
PRADEEP|Exercise MODEL TEST PAPER <br> (Section C )|15 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
PRADEEP-ALDEHYDES, KETONES AND CARBOXYLIC ACIDS -COMPETITION FOCUS JEE (MAIN AND ADVANCED)/MEDICAL ENTRANCE SPECIEAL (VI. INTEGER TYPE QUESIONS)
- Total number of isomeric aldehydes and ketones having the molecular fo...
Text Solution
|
- In the scheme given below, the total number of intramolecular aldol co...
Text Solution
|
- Among the following, the number of reaction (s) that produce (s) benza...
Text Solution
|
- How many of the following compounds undergo aldol condensation? Methan...
Text Solution
|
- Which compound undergo Cannizzro's reaction ?
Text Solution
|
- How many of the osomeric ketones having the molecular formula C(6)H(12...
Text Solution
|
- Consider all possible isomeric ketones, including stereoisomers, of MW...
Text Solution
|
- How many different carboxylic acids are obtained when all the isomeric...
Text Solution
|
- Amongst the following, total number of compounds soluble in sodium bic...
Text Solution
|
- How many beta-ketoacids on heating undergo decarboxylation to give 2-m...
Text Solution
|
- The total number of carboxylic acid groups in the product P is
Text Solution
|