Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
RD SHARMA-AREA OF PARALLELOGRAMS AND TRIANGLES-All Questions
- A B C D is a trapezium with A B|\|D C . A line parallel to A C int...
Text Solution
|
- Diagonals A C\ a n d\ B D of a quadrilateral A B C D intersect a...
Text Solution
|
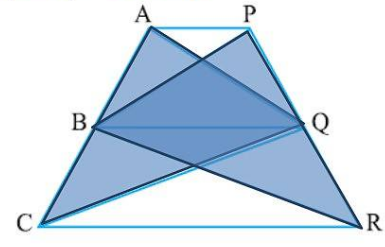
- In Figure, A P B Q\ C Rdot Prove that a r\ ( A Q C)=\ a r\ (P B R)
Text Solution
|
- In Fig.9.29, a r\ (B D P)\ =\ a r\ (A R C)and a r\ (B D P)\ =\ a r\ (A...
Text Solution
|
- Diagonals A C and B D of a quadrilateral A B C D intersect at O in suc...
Text Solution
|
- In Fig. 9.25, diagonals AC and BD of quadrilateral ABCD intersect at O...
Text Solution
|
- A point O inside a rectangle A B C D is joined to the vertices. Prov...
Text Solution
|
- Show that the area of a rhombus is half the product of the lengths ...
Text Solution
|
- A B C D IS A PARALLELOGRAM AND O is any point in its interior. Prov...
Text Solution
|
- A quadrilateral A B C D is such that diagonal B D divides its area in ...
Text Solution
|
- Parallelogram A B C D and rectangle A B E F have the same base A B and...
Text Solution
|
- O is any point on the diagonal B D of the parallelogram A B C Ddot Pro...
Text Solution
|
- Triangles A B C and +DBC are on the same base B C with A, D on opposit...
Text Solution
|
- D and E are points on sides AB and AC respectively of DeltaA B Csuch...
Text Solution
|
- If the medians of a A B C intersect at G , show that a r( A G B)=a r(...
Text Solution
|
- D, E and F are respectively the mid-points of the sides BC, CA and AB...
Text Solution
|
- B D is one of the diagonals of a quadrilateral A B C Ddot\ \ A M\ a...
Text Solution
|
- A B C D is a quadrilateral. A line through D , parallel to A C , me...
Text Solution
|
- If the medians of a A B C intersect at G , show that a r( A G B)=a r(...
Text Solution
|
- X Y isa line parallel to side B C of A B CdotB E A and C F A B meet...
Text Solution
|