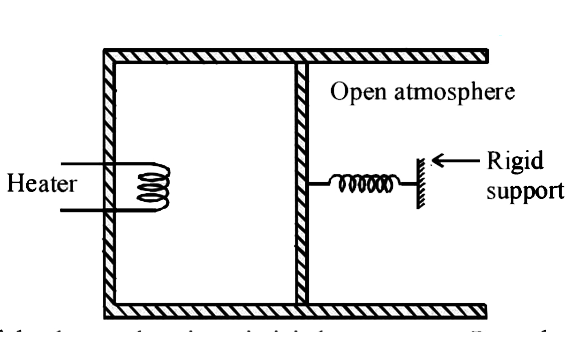
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
NARAYNA-KINETIC THEORY OF GASES-LEVEL-III(C.W)
- Consider the melting of 1g of ice at 0^(@)C to was at 0^(@)C at atmosp...
Text Solution
|
- The equation of state for a gas is given by PV = eta RT + alpha V, whe...
Text Solution
|
- An ideal monoatomic gas is confined in a cylinder by a spring-loaded p...
Text Solution
|
- A cylinder of fixed capacity 67.2 liters contains helium gas at STP . ...
Text Solution
|
- 14 g of N(2) gas is heated in a closed rigid container to increase its...
Text Solution
|
- 70 calories of heat required to raise the temperature of 2 moles of an...
Text Solution
|
- The relation between internal energy U, pressure P and volume V of a g...
Text Solution
|
- If the ratio of specific heat of a gas of constant pressure to that at...
Text Solution
|
- An ideal gas at 27^(@)C is compressed adiabatically to 8//27 of its or...
Text Solution
|
- One mole of a gas expands with temperature T such thaht its volume, V=...
Text Solution
|
- A monoatomic ideal gas, initially at temperature T1, is enclosed in a ...
Text Solution
|
- Three samples of the same gas 'x','y' and 'z', for which the ratio of ...
Text Solution
|
- n moles of an ideal gas undergo a process in which the temperature cha...
Text Solution
|
- m' grams of a gas of a molecular weight M is flowing in a isolated tu...
Text Solution
|
- Heat is supplied to a diatomic gas at constant pressure. The ratio o...
Text Solution
|
- A given quantity of an ideal gas at pressure P and absolute temperatur...
Text Solution
|
- An ideal gas is taken through a cyclic thermodynamic process through f...
Text Solution
|
- During an adibatic compression ,830 J of work is done on 2 moles of a ...
Text Solution
|
- Consider a spherical shell of radius R at temperature T. The black bod...
Text Solution
|
- An ideal gas under goes a quasi static, reversible process in which it...
Text Solution
|