A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
NARAYNA-KINETIC THEORY OF GASES-NCERT BASED QUESTIONS
- The diameter of a gas molecule is 2.4 xx 10^(-10) m. Calculate the mea...
Text Solution
|
- A closed vessel contains a mixture of two diatomic gases A and B. Mola...
Text Solution
|
- Pick the correct statement (s) :
Text Solution
|
- ABCDEFGH is a hollw cube made of an insulator(figure) face ABCD h...
Text Solution
|
- Diatomic molecules like hydrogen haven energy due to both translationa...
Text Solution
|
- In a diatomic molecule, the rotational energy at given temperature
Text Solution
|
- Which of the following diagrams, Fig. depicts ideal gas behaviour ?
Text Solution
|
- When an ideal gas is compressed adiabaticall, is temperature rises the...
Text Solution
|
- An ideal gas undergoes four different processes from the same initial ...
Text Solution
|
- If an avarage person jogs, he produces 14.5xx10^(4) cal//min. This is ...
Text Solution
|
- Consider P-V diagram for an ideal gas shown in figure. Out of fo...
Text Solution
|
- An ideal gas underoges cyclic process of ABCDA as shown in Given P-V d...
Text Solution
|
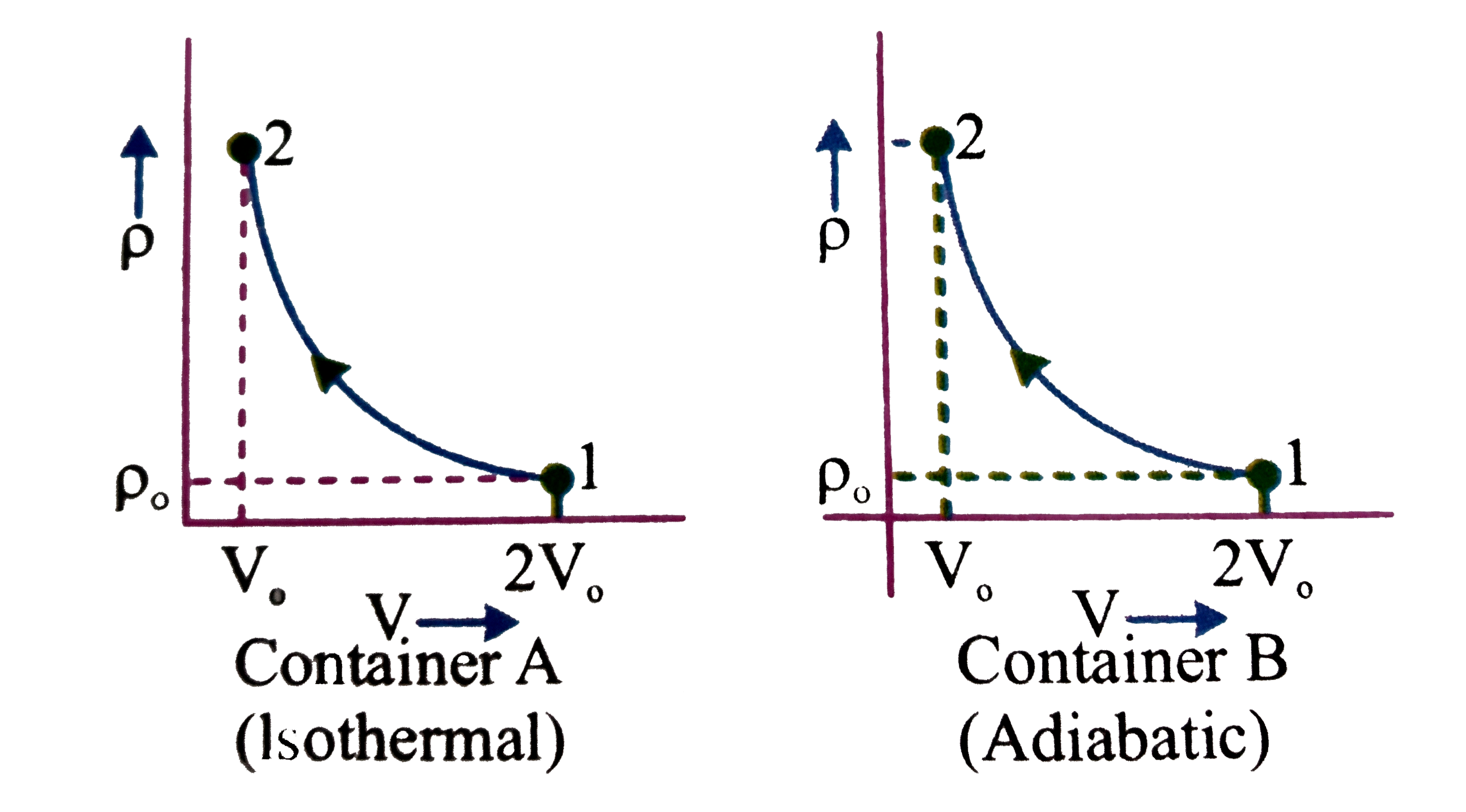
- Consider two containers A and B containing identical gases at the same...
Text Solution
|
- Refer to the plot of temperature versus time (figure) showing the chan...
Text Solution
|
- A glass full of hot milk is poured in the table. It begins to cool gra...
Text Solution
|
- Which of the process described below are irrevesible?
Text Solution
|
- An ideal gas undergoes isothermal process from some initial state i to...
Text Solution
|
- (figure). Shows the P-V diagram of an ideal gas undergoing a change of...
Text Solution
|
- Consider a cycle followed by an engine, (figure) 1 to 2 is isothe...
Text Solution
|
- Consider a heat engine as shown in (figure). Q(1) and Q(2) are heat ad...
Text Solution
|