Text Solution
Verified by Experts
CP SINGH-ELECTROMAGNETIC INDUCTION-EXERCISES
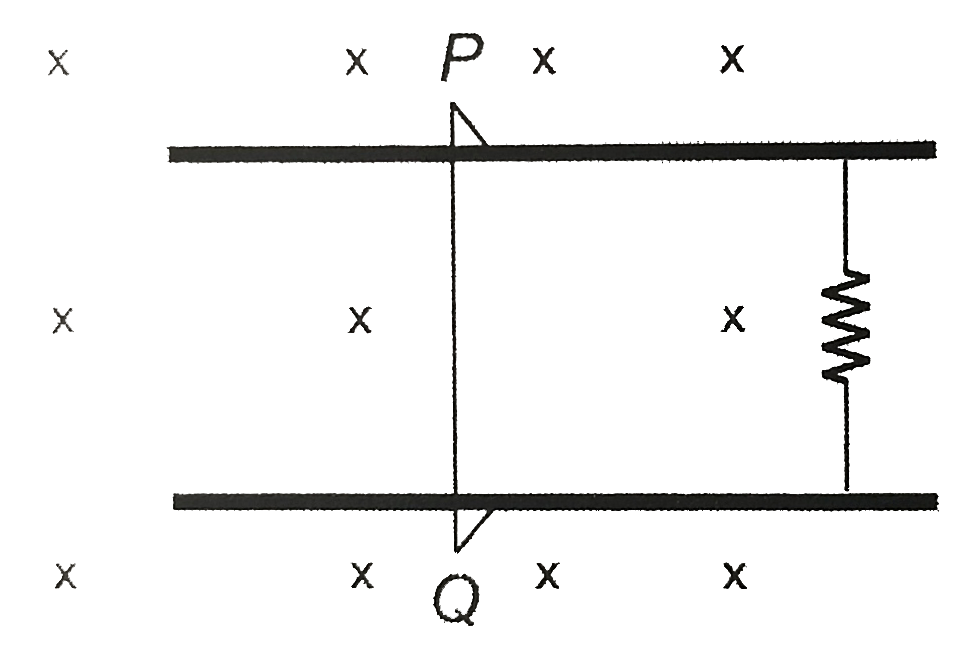
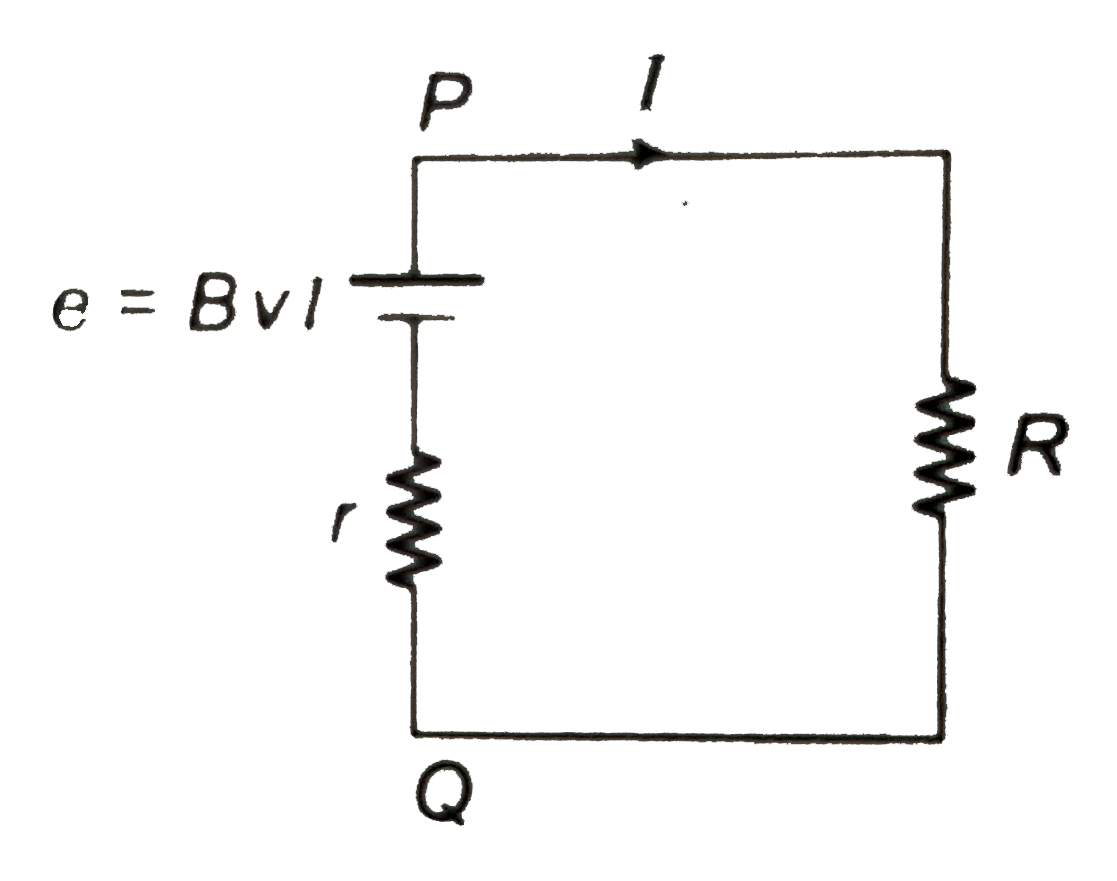
- Consider the situation shown in the figure. The wire PQ has mass m , r...
Text Solution
|
- The direction of induced current in the loop
Text Solution
|
- A current-carrying wire is placed, below a coil in its plane, with cur...
Text Solution
|
- A wire is bent to form the double loop shown in figure. There is a uni...
Text Solution
|
- Two different wire loops are concentric and lie in the same plane. The...
Text Solution
|
- A bar magnet is moved along the axis of a copper ring placed far away ...
Text Solution
|
- Consider the situation shown in . if the switch is closed and after so...
Text Solution
|
- Solve the previous question if the closed loop is completely enclosed ...
Text Solution
|
- As shown in the figure, P and Q are two coaxial conducting loops separ...
Text Solution
|
- shows a horizontal solenoid connected to a battery and a switch. A cop...
Text Solution
|
- An aluminium ring B faces an electromagnet A. The current I through A ...
Text Solution
|
- A conduting ring R is placed on the axis of a bar magnet M . The plane...
Text Solution
|
- Two circular loops of equal radii are placed coaxially at some separat...
Text Solution
|
- Two identical coaxial circular loops carry a current i each circulatin...
Text Solution
|
- Two circular coil P and Q are arranged coaxially as shown. The sign co...
Text Solution
|
- Two circular loops P and Q are placed with their planes paraller to ea...
Text Solution
|
- A small, conducting circular loop is placed inside a long solenoid car...
Text Solution
|
- A small magnet M is allowed to fall through a fixed horizontal conduct...
Text Solution
|
- In the previous question, the directions of the current flowing in the...
Text Solution
|
- A copper ring having a cut such as not to from a complete loop is held...
Text Solution
|
- Lenz's law is consequence of the law of conservation of
Text Solution
|